
How to Tell If a Smart Lithium Battery Is Bad and How to Test Smart Lithium Batteries?
This troubleshooting guide applies to the following products:
- 48V 50Ah Smart Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery (SKU: RBT50LFP48S-US)
- 12V 100Ah Smart Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery (SKU: RBT100LFP12S-US)
- 12V 100Ah Smart Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery w/ Self-Heating Function (SKU: RBT100LFP12SH-US)
Smart Lithium Battery Issues
Common problems of Smart lithium batteries are:
- Battery not holding charge
- Battery cannot be fully charged
- The battery cannot maintain its charge
- Self-heating function is not working properly
- Communication issue
How to Tell If a Smart Lithium Battery Is Bad?
For common issues with smart lithium batteries, we can typically diagnose the health of the battery by measuring the battery voltage, checking the wiring, and using Bluetooth to check the cell voltages, among other data. Please refer to the corresponding troubleshooting steps for specific problems.
How to Troubleshoot Smart Lithium Batteries?
The following are common issues and corresponding troubleshooting methods for Smart lithium batteries.
Smart lithium battery not holding charge
Troubleshooting steps:
- First, it is necessary to confirm whether the battery has been over-discharged during use and has not been activated for charging for a long period of time;
- Use a multimeter to measure the open-circuit voltage of the battery and check whether the battery is in undervoltage protection mode (if the open-circuit voltage of the battery is below 10V, it means that the battery is in undervoltage protection mode). If the battery is in undervoltage protection mode, remove all connection wires from the battery and use a charger that matches the battery parameters and has lithium battery activation function. Activate and continuously charge the battery when the ambient temperature is above 41℉. After the voltage at the battery terminal rises to 12.4V or above, the battery can enter the normal charging state;
- Check the battery information on the DC Home APP to see if there is any prompt for protection (such as low temperature, overcurrent, etc.). The battery cannot be charged under these protection states;
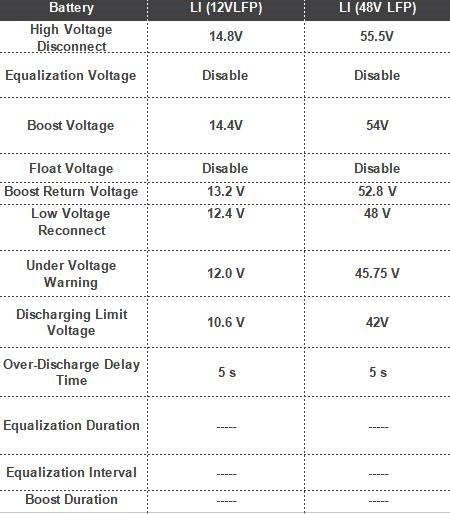
- Check whether the charging parameters of the charger are consistent with the battery parameters (as shown in the figure below). If they are inconsistent, there may be a problem with charging the battery. You can also cross-validate the battery or charger to confirm whether there is a problem with the charger or battery;
- If the above steps still cannot confirm whether the battery is faulty, please contact Renogy for assistance and provide the above troubleshooting results and relevant videos for further confirmation. You can refer to the example video when submitting a case.
Smart lithium battery cannot be fully charged
Troubleshooting steps:
- First, check the battery cell voltages through the DC Home app. If there is a significant difference in voltage between the battery cells, it may be due to one cell reaching the overvoltage threshold first, causing the battery to stop charging and not fully charge. In this case, refer to the troubleshooting steps for "Unbalanced cell voltages".
- Confirm if the battery has been excessively discharged and not activated for a long time during use. It is also recommended to not exceed 80% depth of discharge (DOD).
- During the battery charging process, check the battery information page in the DC Home app for any related protection prompts (such as low temperature or overcurrent). The battery will not fully charge while in these protection states.
- Verify that the charging parameters of the charger match the battery parameters (as shown in the figure below). If they do not match, it may cause issues with charging the battery. Cross-checking the battery or charger can also help confirm if there are any issues.
- If the above steps still cannot confirm whether the battery is faulty, please contact Renogy and provide the system wiring diagram (including load model and power), as well as the above troubleshooting steps and results for further confirmation.

Smart lithium battery cannot maintain its charge
Troubleshooting steps:
- To fully charge the battery, use a charger that matches the charging parameters of the battery (as shown in the figure below). For the RBT100LFP12S/RBT100LFP12SH battery, the voltage should be at 14.4V when fully charged, while for the RBT50LFP48S battery, the voltage should be at 54V. Disconnect all the battery connections and let it rest for two hours, then measure the open-circuit voltage of the battery. If the battery terminal voltage of RBT100LFP12S/RBT100LFP12SH is above 13.4V, or RBT50LFP48S is above 51V, it means the battery is fully charged. Leave the battery idle overnight (without any connections to the battery and without significant changes in ambient temperature), and then measure the open-circuit voltage of the battery again. If there is a significant drop in the open-circuit voltage, it indicates that the battery is faulty.
- If there is no significant change in the battery voltage after being left idle, connect a resistive load (such as an electric water heater) to discharge the battery until it reaches low-voltage protection. Record the discharge time, calculate the battery capacity based on the load power and discharge time, and compare it with the rated capacity.

Smart lithium battery self-heating function not working properly
Troubleshooting steps:
- The required conditions for the self-heating function to activate are as follows: the charging voltage of the external charging equipment is more than 0.5V higher than the battery voltage, the charging current is continuously stable and greater than 4A, and the internal temperature of the battery is below 41°F (5°C). After meeting the above conditions, the heating function will start. When the internal temperature of the battery rises above 50°F/10°C, the battery's self-heating function will automatically turn off. It should be noted that the power consumed by the battery's self-heating function comes from the power provided by the external charging equipment and does not consume the battery's own power. The lowest working temperature of the heating element built into the RBT100LFP12SH battery is -4°F/-20°C, and the lowest working temperature of the heating element built into the RBT50LFP48S battery is 14°F/-10°C. If the battery temperature is lower than the lowest working temperature of its heating element, the self-heating function will not activate.
- If all the above conditions are met, but the battery's self-heating function does not start, then the battery heating element is faulty.
- When multiple batteries are connected in parallel, one battery may be heating and charging, while the others stop charging. This is because at the beginning of the heating elements operation, all batteries are in a low-temperature state, and at this time, the heating feature of all batteries is turned on. As the heating continues, one battery (A) will reach the temperature for charging first, and then the current will surge into battery A. At this time, for other batteries, the external voltage is the same as the voltage of battery A. Only when the voltage of battery A is higher than that of other batteries by more than 0.5V, will the heating film of other batteries restart heating.

Smart lithium battery is unable to connect Bluetooth with DC Home APP
Troubleshooting steps:
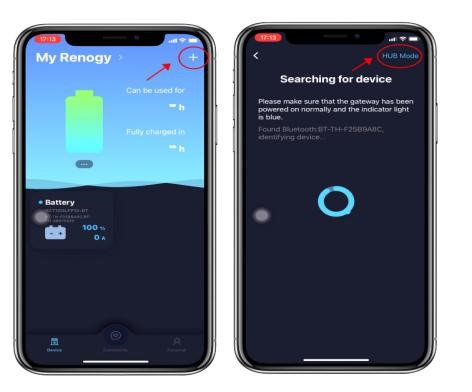
- First, it is necessary to rule out the situation where the Bluetooth is already connected to the DC Home APP on another mobile phone. In this case, Bluetooth cannot be connected. You need to disconnect the Bluetooth from the other phone, then update the DC Home APP to the latest version, and add the device in the DC Home APP by selecting "HUB Mode" to search for Bluetooth, as shown below.
- If the Bluetooth is not connected to any other phone, disconnect all connections to the battery, and measure the battery's open-circuit voltage with a multimeter. If it is below 10V, the battery is in under-voltage protection mode, and its built-in Bluetooth is also in a closed state. In this case, you need to use a charger with lithium activation function to charge the battery fully, and then reconnect the Bluetooth in the DC Home APP. If the battery is not in under-voltage protection mode, give it a charging or discharging current greater than 1A to activate the battery, and then reconnect the Bluetooth in the DC Home APP.
- If you still cannot connect the Bluetooth and DC Home APP after following the above steps, further confirm whether the communication port of the battery is damaged. Check if the BT-2 indicator light is normal. Cross-validation can be done by replacing different BT-2s and batteries.
- If multiple batteries are connected in parallel, check that the communication line specifications and connection methods between the batteries are consistent with the requirements in the product manual.
- Make sure there is no electromagnetic interference device around the battery. Electromagnetic interference will cause Bluetooth communication failure.
- If you still cannot connect the Bluetooth and DC Home APP after following the above steps, please provide the steps and results of the above troubleshooting and a video to Renogy for further analysis. You can refer to the example video when submitting a case.












