How to Troubleshoot A Lithium-ion Battery If It Can Not Be Fully Charged?
Why can't my Lithium-ion battery be fully charged? If you're into tech, dealing with a Lithium-ion battery that won't be fully charged can be a real pain, how to do the battery troubleshooting? Even with a fancy battery bank, you might run into this issue. If you're stuck with a Lithium-ion battery that just won't be fully charged, there are some easy tricks to try. Let's figure out why your power's acting up and what you can do about it.
This troubleshooting guide applies to the following products:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery 12 Volt 50 AH(SKU: RNG-BATT-LFP-12-50)
- 24V 25Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery(SKU: RBT2425LFP)
- 24V 50Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery(SKU: RBT2450LFP)
- RNG-BATT-LFP-12-100
- RNG-BATT-LFP-12-170
Why Can’t My Lithium-ion Battery Be Fully Charged?
Unfortunately, when your Lithium-ion battery can not be fully charged, there could be a variety of reasons behind the problem. The issues might stem from a damaged battery or external factors unrelated to the lithium battery itself. It may require some trial and error as well as battery troubleshooting to uncover the underlying cause.
What Are The Factors Affecting Lithium Iron Battery Being Fully Charged?
1. The battery has triggered certain protection states (low-temperature/high-temperature protection, over-current protection, etc.), preventing the battery from being fully charged.
2. Mismatch between the parameters of the charging device and the charging parameters of the battery, leading to the inability to fully charge the battery.
3. Malfunction of the charging equipment, resulting in the inability to fully charge the battery.
4. The battery has exceeded its cycle life or has been used for an extended period, leading to capacity degradation and the inability to be fully charged.
5. Improper usage:
a. The battery is left in an over-discharged state for an extended period without activating charging, resulting in battery damage and the inability to be fully charged.
b. The load current exceeds the battery's maximum continuous discharge current.

Troubleshooting RV Battery Problems: A Step By Step Guide
1.Exclude other BMS protection possibilities. Confirm whether the battery has triggered any corresponding protections (low-temperature protection, over-current protection, etc.), preventing it from being fully charged.
------Possible Results------
Positive: The battery is in a certain BMS protection state. Take appropriate measures.
Negative: Confirm that the battery is not in any BMS protection state. Please proceed to the remaining steps.
2. Exclude the possibility of charger and charging parameter mismatch. Check the parameter settings of the charger, referring to the provided image.
------Possible Results------
Positive: Charging parameters are incorrect, or the charger is mismatched. Take appropriate measures.
Negative: Charger parameters match. Please proceed to the remaining steps.
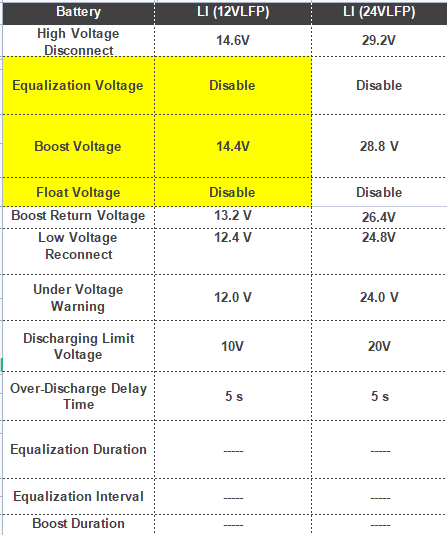
3. Exclude charger malfunction. Please try to replace the battery or charger for cross-validation.
------Possible Results------
Positive: Charger malfunction. Take appropriate measures.
Negative: Charger is normal. Please proceed to the remaining steps.
4. Confirm the battery's lifespan. Please try to accurately calculate the number of cycles and duration that the battery has been used.
------Possible Results------
Positive: The battery has exceeded the cycle life or warranty period. It can be determined as a normal battery degradation.
Negative: The battery has not exceeded the cycle life or warranty period. Please proceed to the remaining steps.
If the influencing factors mentioned in steps 1, 2, 3, 4 are all ruled out, it can be determined as a product fault. Next, based on the results of step 5, determine whether the battery failure is due to improper usage or a quality issue with the battery itself.
5. Clarifying the impact of human factors.
During the use and storage of batteries, it is crucial to avoid the following two situations:
- Prolonged deep discharge of the battery.
- Discharge current exceeding its maximum continuous discharge current.
Both of these situations can cause damage to the battery, defined as damage resulting from improper use.
Note: When storing the battery, it should be charged to 30%-50%, and the battery should be charged every 3-6 months to prevent over-discharge. For specific details, please refer to the following link:
Battery Storage and Maintenance Tips
How to Store Lithium Batteries & Care of lithium batteries - Renogy United States












