
Solar Energy Glossary
Introduction
Well begun is half done! The first thing to build a solar system is to get familiar with the terms and jargons. This article contains terminologies that are commonly used in the solar power industry, helping you simplify your solar power journey.
![]() Note: The glossary is regularly updated. To receive the latest updates, you can bookmark or save this article.
Note: The glossary is regularly updated. To receive the latest updates, you can bookmark or save this article.
Jump to letters: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
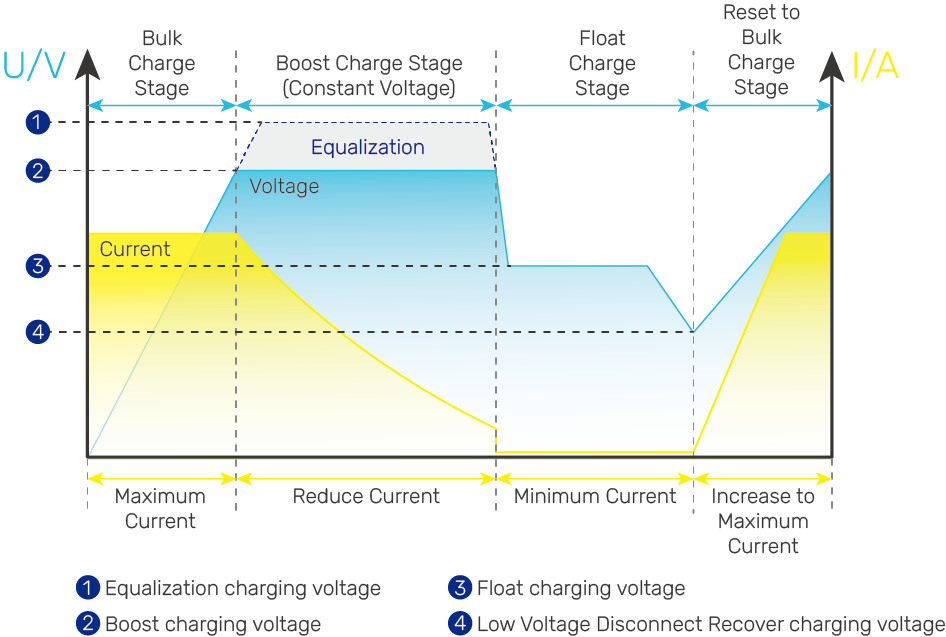
Absorption Charge: The second charge stage that occurs after the Bulk Charge is complete and the battery is about 80% to 90% charged during battery charging. In this stage, the charge controller or battery charger supplies a constant voltage with a reducing current when the batteries approach a full state of charge. See Boost Charge, Equalization Charge, and Float Charge.
Alternating Current (AC): A type of electrical current, in which the direction of the electron flow switches back and forth at regular intervals or cycles.
Alternator: As part of a car's charging system with the battery and voltage regulator, an alternator converts mechanical power from the engine into electricity, which is stored in the battery.
Ampere (amp or A): The unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb moving past a point in 1 second, or 6.241509074×1018 electrons' worth of charge moving past a point in 1 second.
Ampere-Hour (Ah or amp hour): A unit of electric charge, having dimensions of electric current multiplied by time. It represents the amount of energy charge in a battery for 1 ampere of current to flow in an hour. Ampere-hour is used to measure a battery capacity.
Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the surrounding area at your installation site
Anti-islanding: A protection mechanism commonly required in grid-tied inverters to turn off the inverter from the grid in case of a power failure. Islanding refers to a situation where a solar power system continues to provide electricity even when the grid is down. This puts utility workers into the danger of electrical shock.
Array: A collection of connected solar panels.
Auxiliary Battery: Also known as house battery. As the secondary battery that keeps certain electrical systems running in a vehicle, an auxiliary battery serves as a backup to the starter battery when the engine is off.
B
Backbone Topology: Originally refers to the central structure or layout of a computer network, typically in a larger-scale network configuration. At Renogy, we use backbone topology to describe two or more internet working devices connected to each other by a single cable in a parallel fashion. See the example below. Related read: Daisy Chain Topology.
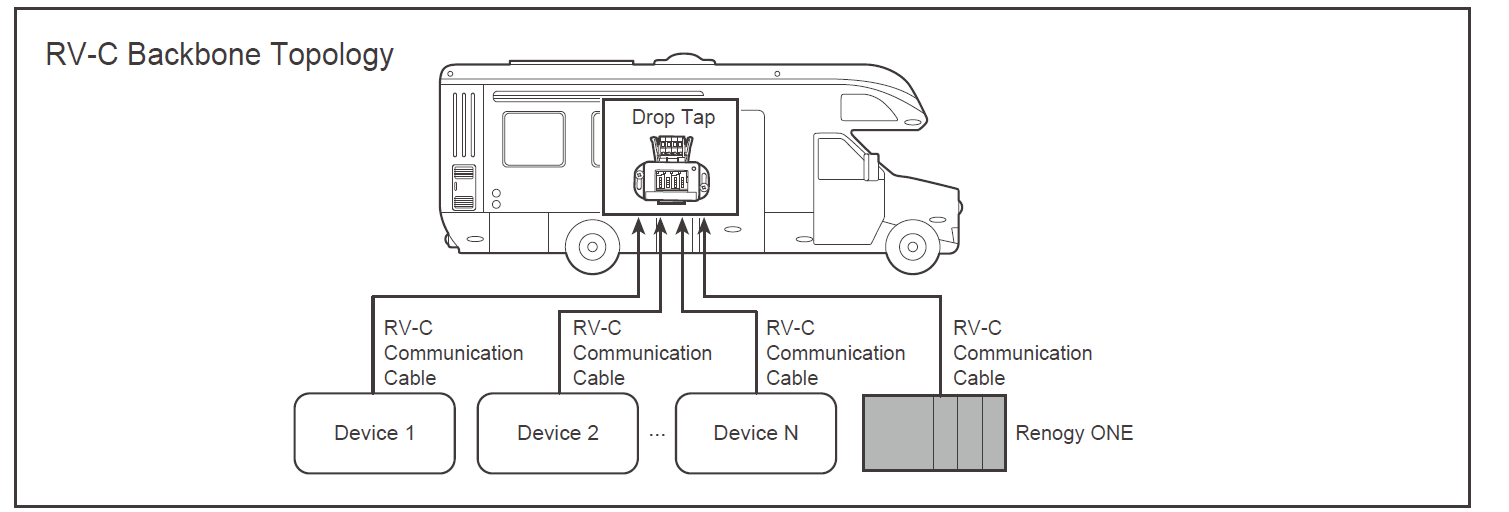
Battery Balancer: A battery balancer or battery regulator is an electrical device in a battery pack that performs battery balancing. Battery balancing and battery redistribution refer to techniques that improve the available capacity of a battery pack with multiple cells (usually in series) and increase each cell's longevity.
Battery Temperature Sensor: A battery temperature sensor measures ambient or internal temperature of a battery, ensuring optimal operational conditions and performance. Typically integrated with charge controllers or battery chargers, these sensors aid in temperature compensation during the charging process by providing accurate temperature data to the controller or charger.
Battery Voltage Sensor: A compact electronic device designed to precisely measure the voltage across the terminals of a battery. Typically integrated into battery management systems or charge controllers, it continuously monitors the battery's voltage level, providing crucial information for optimizing performance and ensuring efficient charging. By detecting overcharge, undercharge, or other voltage-related issues, the sensor plays a vital role in maintaining the health and longevity of battery systems in various applications.
Boost Charge: Boost charge is a typical charge stage followed by Bulk Charge when the charge controller or battery charger charges the battery at a high current and constant voltage for a short period of time. Boost charge generally applies if the battery has been discharged heavily. See Equalization Charge, and Float Charge.
Bulk Charge: The first charge stage during battery charging. The charge controller or battery charger supplies constant current until the battery voltage increases to the boost voltage. It uses 100% of available solar power to recharge the battery. See Boost Charge, Equalization Charge, and Float Charge.
C
CAN (Controller Area Network) Communication: A robust and widely used communication protocol primarily employed in automotive and industrial applications. It is a multi-master, serial communication protocol that enables microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other without a host computer.
In a solar power system installed in an RV (Recreational Vehicle), CAN facilitates communication between different devices such as solar charge controllers, battery monitors, inverters, and other system components to exchange information such as voltage, current, temperature, and status data, allowing for centralized monitoring and control of the entire solar power system.
Charge Cycle: The process of charging a rechargeable battery and discharging it as required into a load. The term is typically used to specify a battery's expected life, as the number of charge cycles affects life more than the mere passage of time. Discharging the battery fully before recharging may be called "deep discharge"; partially discharging then recharging may be called "shallow discharge".
Charge Stages: A battery goes through multiple charge stages with varied charging voltage and current specific to the stage.
The following is a typical example of a charging graph.
Current: The amount of charge per unit time. This is analogous to the flow rate of water in a pipe when comparing it to fluid flow. Measured in amperes (A).
D
Daisy Chain Topology: A group of connectivity devices linked together in a serial fashion. The example below lists a scenario where devices are connected in RV-C daisy chain topology:
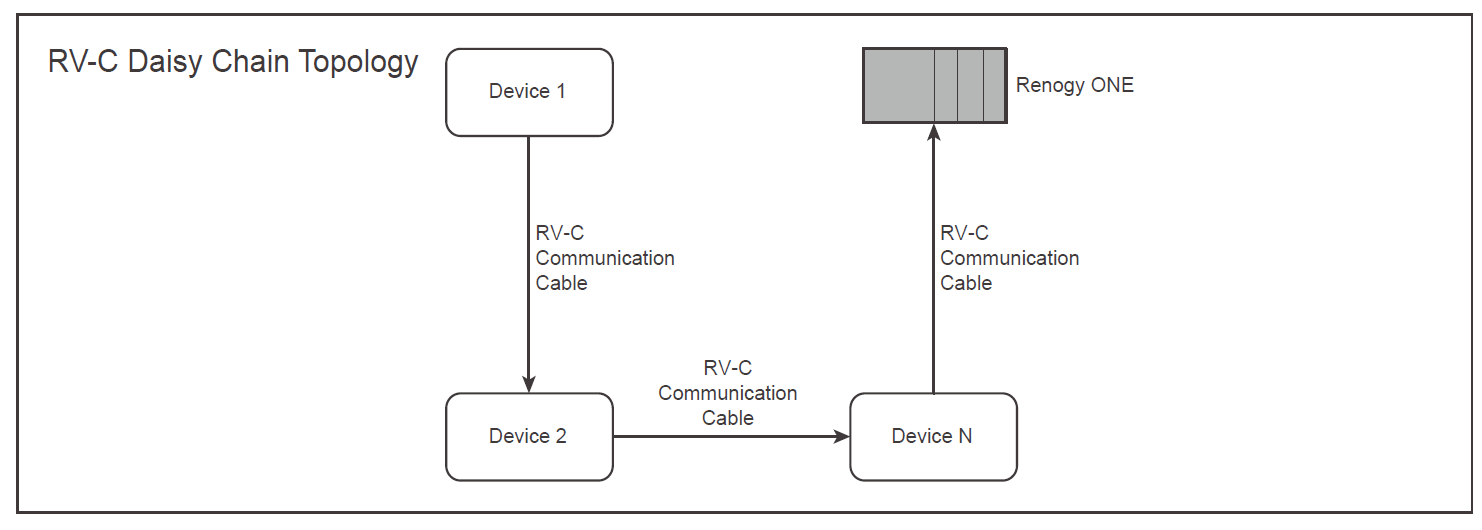
Deep Cycle Battery: A battery designed to be discharged and recharged multiple times. These batteries are commonly used in applications such as boats, RVs, and solar power systems. They are capable of providing a steady amount of power over an extended period of time.
Direct Current (DC): Electrical current which flows consistently in one direction.
Duty Cycle: The ratio of time a load or circuit is ON compared to the time the load or circuit is OFF. For batteries, a duty cycle represents the percentage of time the battery is actively supplying power (discharging) relative to its total operational time, including both discharging and charging periods. A high duty cycle indicates that the battery is frequently being discharged, while a low duty cycle suggests less frequent discharging. For instance, a 20% duty cycle battery indicates that the battery spends 20% of the time in the discharged state, while the remaining 80% of the time may involve periods of charging.
E
Electricity: Electricity is the flow of electrons through a conducting material. The flow of electricity can be used to generate, consume, and transfer power. Due to the nature of electricity, we cannot see it actually flowing. It sometimes helps to imagine electricity as analogous to the flow of water in order to make sense of it. The flow of electricity can be a highly complicated phenomenon so it is very often easier to understand via such analogies. There are three main characteristics of electric flow: voltage, current, and resistance.
Equalization Charge: Equalization charge only applies to batteries such as non-sealed, vented, flooded, and wet cell lead acid batteries. Refer to the user manual of the battery or contact the battery manufacturer to see if this stage is needed.
The equalization stage involves two distinct steps. Initially, a constant amount of current is supplied to the battery, aiming to achieve a significantly higher voltage than the float and absorption voltage levels. Once this elevated voltage, known as the equalization voltage, is reached, the controller or charger adjusts its behavior similar to transitioning from bulk to absorption charge. The controller or charger maintains the equalization voltage for a predetermined duration, akin to the transition from the bulk charge to the float charge on the charging curve.
F
Float Charge: Also known as trickle charge that occurs after absorption charge. During this stage, the charge controller supplies a constant voltage which is determined by the battery selected and keeps current at a minimum level. After reaching a constant voltage in the charging process, the charge controller or battery charger reduces the voltage to a float level. At this point, the battery is fully charged, and any excess current is converted to heat or gas. The controller or charger then maintains a lower voltage to offset power consumption, ensuring a full battery capacity. If a load exceeds the charge current, the charger exits float mode and returns to bulk charging. See Boost Charge, Equalization Charge, and Absorption Charge.
Flush Mount: An installation method where an object, such as a device or fixture, is installed so that it sits level with or nearly level with the surrounding surface, usually a wall. See Surface Mount.
G
Grounding: The practice of connecting electrical circuits and devices to the Earth or to a conducting body that serves as a substitute for the Earth in electrical systems. The primary purpose of grounding is to provide a safe path for electrical currents to flow in the event of a fault or surge, directing excess current away from sensitive equipment and preventing electrical shock or fire hazards.
N
Neutral-to-Ground Bonding: Neutral-to-ground bonding in inverters refers to the electrical connection between the neutral conductor and the ground in the AC circuit within the inverter system.
O
On-grid: Also grid-tied, typically referring to a solar power system that is connected to the electrical grid. In an "on-grid" or "grid-tied" solar power system, the solar panels generate electricity that is fed directly into the grid, and the user typically receives credits or compensation for the electricity generated.
Off-grid: Referring to a type of solar power system that operates independently of the electrical grid. In an off-grid solar power system, solar panels generate electricity that is stored in batteries for later use. The system typically includes charge controllers, inverters, and batteries to manage and store the generated energy. Off-grid solar systems are commonly used in remote locations where connecting to the electrical grid is not feasible or cost-effective.
P
Photovoltaic (PV): Pertaining to the conversion of sunlight into electricity.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Technology: A method used in electronics to control the average power delivered to a device by rapidly switching it on and off at varying intervals. In PWM technology, the width of the pulses (the duration the signal is on) is modulated to achieve the desired level of power delivery. By adjusting the duty cycle (the ratio of on-time to total cycle time), PWM allows for precise control over the amount of power delivered to a load.
R
Resistance: The resistance against the current. This causes a voltage drop and consumes energy. This is analogous to the friction in pipes when comparing to fluid flow. Measured in ohms (Ω).
The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is described by Ohm's law:
Voltage = Current * Resistance
Resistive Loads: simple loads where the current and voltage sine waves are in phase with each other.
S
Starter Battery: Also known as starting battery or car battery, providing a high burst of current for a short period of time to start a vehicle. These batteries have a relatively short life and are not designed to be deeply discharged. Lead acid batteries are good starter battery examples.
Surface Mount: An installation method where an object, such as a device or fixture, is mounted directly onto the surface of another object or structure such as a wall, rather than being recessed or embedded within it. This method typically involves attaching the object to the surface using screws, adhesive, or other fasteners.
T
Termination Resistor: a single resistor placed at the end of an electrical transmission line. In electronics, you’ll encounter termination resistors when you’re working with differential pair signals, such as the RS-485. It is a simple component that ensures signal integrity on the bus, especially when high-speed transmission is involved. Furthermore, termination resistors are used to avoid signal reflections.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD): a measurement of the harmonic distortion present in a signal and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency. It tells you how much of the distortion of a voltage or current is due to harmonics in the signal.
Torque: a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. Common torque units: Newton-metre (N⋅m), kgm2sec-2 (kg⋅m2⋅s−2), pound-force-feet (lbf⋅ft), ounce-force inch (ozf⋅in), and pound-force inch (lbf⋅inch)
V
Voltage: The amount of work available per unit charge. This is analogous to the pressure in a pipe when comparing to fluid flow. Measured in volts (V).












