What is Battery Voltage? Why Does It Matter and How to Measure
Batteries have become an integral part of our lives. Whether you want to run cars or household appliances or charge laptops, mobile devices, or digital cameras, batteries play a crucial role. Different batteries offer different voltage outputs that are suitable for different applications.
Understanding the battery voltage is important for both professionals and everyday users. It tells you whether you need a 24V deep cycle battery, a 12V car battery, or a 1.5V battery cell. You might have encountered various misconceptions about battery voltage, right?
This article explains what the battery voltage is, how it is produced, how it is different from current, how it is measured, and more.
What is battery voltage?
Are you wondering what does the battery voltage mean? Well, it is the electrical potential difference between the two (positive and negative) terminals of the battery. The standard unit to measure battery voltage is volt (V). It is a fundamental property of a battery that determines how much power it can deliver.
In other words, the electrical force between two points (the battery itself and the connected device) in a circuit is called the battery voltage. Understanding this voltage is important, as it determines how much voltage you need for certain applications, the battery's state of charge, and the amount of power a battery can supply.
Different factors, like cell count and battery chemistry, influence battery voltage. Remember, the voltage of a battery isn't static, as it changes during the charging and discharging processes.

What produces voltage in batteries?
A battery consists of four key components: cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator. The cathode is the positive terminal of the battery and it is made up of oxidizing metal, e.g., graphite oxide, copper oxide, and lithium oxide. In contrast, the anode is the negative terminal of the battery, which is made up of platinum, graphite, or zinc.
Both anode and cathode are dipped into an electrolyte and are separated from each other. Therefore, electrons can't flow freely from one side to another. But when you use a conducting material to connect the battery terminals, electrons start to move from the negative terminal (anode) to the positive terminal (cathode).
The movement of electrons between the terminals is called a chemical reaction. This is how the voltage in batteries is produced.
Voltage and current: What's the difference?
It seems that current and voltage are interchangeable, but both are distinct measures of electricity. The measure of difference in electrical potential is called voltage. It is measured in volts (V). In comparison, current measures the rate of electron flow, and is measured in amperes (A).
A higher voltage can lead to a higher current flow, but it is true if the resistance of the circuit remains the same. Similarly, the higher electrical potential leads to the higher voltage, and the higher current value results in the faster flow of electrons.
If we talk about more differences between the battery voltage and current, voltage is a scalar quantity, which means it has magnitude but no specified direction. On the other hand, current is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and a specific direction. When it comes to measurement, a voltmeter is used to measure the voltage, whereas an ammeter is used to calculate the current.
How is battery voltage measured?
If you want to ensure optimal battery performance and determine its state of charge, measuring the battery voltage is necessary. There are different methods to measure the voltage of a battery, e.g., a multimeter and a battery monitor. Let's look at both one by one.
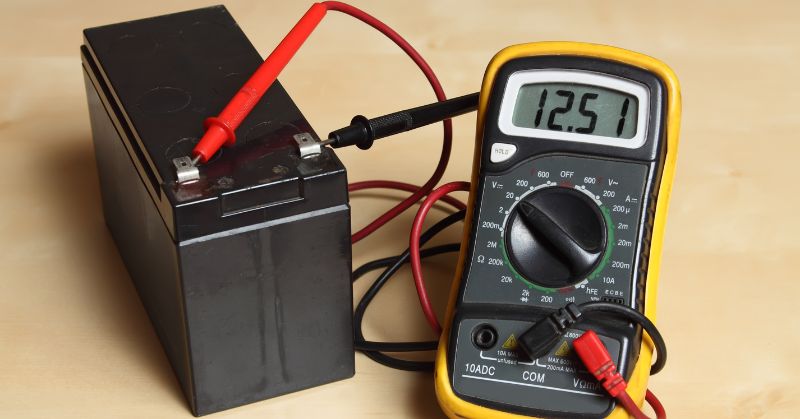
1. Measuring the battery voltage with a multimeter
This versatile tool helps you determine the battery's state of charge accurately. Here's how to check the battery voltage with a multimeter.
- Set the multimeter to DC voltage.
- Connect the red wire of the multimeter to the battery's positive terminal.
- Connect the black wire to the negative terminal.
- Read the voltage displayed on the multimeter.
2. Measuring the battery voltage with the battery monitor
A battery monitor and sensor measures and displays real-time voltage and current data to monitor and assess the battery's performance and health. This device is used in the battery management system to make sure the connected devices are functional.

What is the normal voltage?
The definition of the normal voltage may vary depending on the battery type. The voltage of a household AAA battery will be different from a car battery. The reason behind this fact is the type of chemical reactions occurring within the battery. The reactions where oxidation-reduction is more favorable generate higher voltages.
Apart from the chemical reactions, high-voltage batteries have multiple cells connected in series. It results in the increased voltage. For example, a single AAA battery is a single-cell battery, but an RV battery consists of 4, 5, or 6 cells. Therefore, the average voltage of a fully charged car battery is around 12.6V. It is also called the resting voltage.
The voltage of a AAA battery is 1.5 volts. Both batteries have different power applications due to their varying voltages. Before you choose a specific battery for any electronic device, don't forget to match the voltage correctly. It will help you increase the battery lifespan and keep the device away from damage.
The increased temperature or bulged case is a sign of an overcharged battery. In contrast, slow engine crank, clicking sound, and dim headlights often indicate that the battery is dying.
Types of batteries and their voltages
The cell count and the chemistry determine how much voltage a battery can supply, as stated earlier. Different battery types may show different voltage levels when they are fully charged. This difference in the output voltages is due to the type of chemical reactions.
Understanding the battery voltage is essential to ensure you have selected the right battery for a specific application. This section discusses the voltage differences between lead-acid and lithium batteries.
1. Lithium batteries
This is the advanced technology that has taken the battery world by storm. Lithium batteries, specifically lithium-ion batteries, are considered ideal for all kinds of electric vehicles, marines, boats, and RV electronics. This is because of their higher energy density and higher voltages compared to conventional lead-acid batteries.
When a 12V lithium battery is fully charged, it may reach a voltage of around 13.6V. Even after losing 10% of their total capacity, they maintain a voltage of 13.4V at rest. Moreover, lithium batteries deliver constant voltage and come with higher battery capacity. However, proper charging and discharging practices must be followed to ensure the longevity and safety of lithium batteries.
Specific chargers are required to charge lithium batteries that perfectly match their chemistry. In addition, you should continuously monitor the voltage to avoid over or undercharging.

2. Lead-acid batteries
They offer applications like e-mobility, marine power, industrial settings, renewable energy storage, backup power, starting engines, and more. The nominal voltage of a lead-acid battery (when fully charged) is around 12.7 volts. Though these batteries have been used as a reliable backup power source for years, they don't offer an energy density equal to lithium-ion batteries.
The reason why most boat and RV enthusiasts prefer lead-acid batteries over other alternatives is their affordable prices. But, Li-ion batteries offer a longer lifespan (2,000 to 3,000 charge cycles) and become cost-effective in the long run. On the other hand, lead-acid batteries can last for only 300 to 500 charge cycles. Similarly, the efficiency of lead-acid batteries is lower (80-85%) than their Li-ion counterparts (at least 95%).

Is high battery voltage dangerous?
The battery voltage may or may not be dangerous. It becomes dangerous once it reaches a certain level. According to OSHA standards, if the voltage of a battery is below 50V, it is not dangerous, as the human body can safely deal with shocks of up to 50V. Anything above this threshold can be lethal.
If we look into the power distribution of a human body, it tells us that legs and arms offer a resistance of at least 500 ohms. It means that the dangerous current will not pass through the human heart at 50 volts. On the other hand, the human body acts as a conductor for the voltage above 50V. Therefore, it can be very dangerous for life.
Various effects a higher voltage can produce include cardiac arrest, broken bones, eye injuries, burns, and more. The reason behind these dangers is that a current of 10mA may disrupt the electrical conductivity when it passes through the heart.
Importance of voltage in battery selection
Knowing the battery voltage plays a crucial role in selecting the right battery for various applications. For example, the voltage enables you to estimate the amount of power you can get from a specific battery. Moreover, it helps you determine the state of charge of the battery. Furthermore, it lets you know the amount of voltage you need to run various electronic devices.
If we don't have a clear understanding of the battery voltage, we won't be able to use batteries safely and efficiently. Simply put, knowing the battery voltage helps you ensure the compatibility of the battery with different devices and keep them away from potential damages.
Conclusion
The battery voltage is the measure of electric potential difference between the two terminals. Understanding the battery voltage is very important, as it lets you know the maximum power you can obtain from your battery to run or charge various appliances or devices.
Moreover, having a clear understanding of the voltage of a battery ensures its optimal performance and enhanced safety, as it helps you avoid over and undercharging.
Frequently asked questions
What voltage is a 12 volt battery at 50%?
When the voltage of a 12-volt battery drops to 12.05 volts, it reaches its 50% capacity. The voltage reduces further with each decrease in the battery's capacity.
How do I know if my battery voltage is too low?
Using a multimeter to measure the battery voltage directly is the best and quickest way to determine if the voltage is too low. If the voltage of your battery is below 12.2 volts, it is the sign of a low battery.
What happens if I use the wrong voltage battery?
The use of a wrong voltage battery may result in different issues. It depends on whether the battery voltage is lower or higher than the required one. If the battery voltage is high, it may cause the devices to overheat. In the case of low voltage, the devices may not get enough power to function properly.











