What are Lithium-Ion Batteries? Everything You Need to Know
Lithium-ion batteries are dominating the consumer market. Today, companies are boosting sales of their portable electric, energy solutions, and e-transports with these rechargeable batteries. But, what are lithium-ion batteries in simple words?
Turns out, Li-ion battery technology is nothing new! The first-ever Li cell came out in 1991. Two decades later, in 2019, John Goodenough, Akira Yashino, and M. Stanley contributed significantly to the development of modern lithium batteries and received the Nobel Prize in chemistry.
Since then, lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized the rechargeable batteries market across industries. Let's learn more about how these batteries work, their types, and applications.
What are lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries, smaller in size with better power capabilities and high energy density. These batteries have single or multiple cells carrying Li ions with a protective circuit board. Lithium-ion batteries are typically used to charge devices like smartphones, electric vehicles, etc.
For starters, lithium-ion battery technology consists of the following.
- Electrodes are the negative and positive charged ends of the cell. The electrodes in a Li-ion battery are connected to the current collectors.
- The Electrolyte is a substance (liquid or gel) that conducts the electric current.
- The Anode and Cathode are the negative and positive electrodes, respectively.
- Positive and Negative Current Collectors are conductive foils connected to each terminal of the cell.
- The Separator is a film, used to separate the electrodes and enables the lithium ions exchange to the device.
How do lithium-ion batteries work?
In a Li-ion battery, the two electrodes store the ions. These ions move between the anode and cathode, which creates the electric current and powers the electronics.
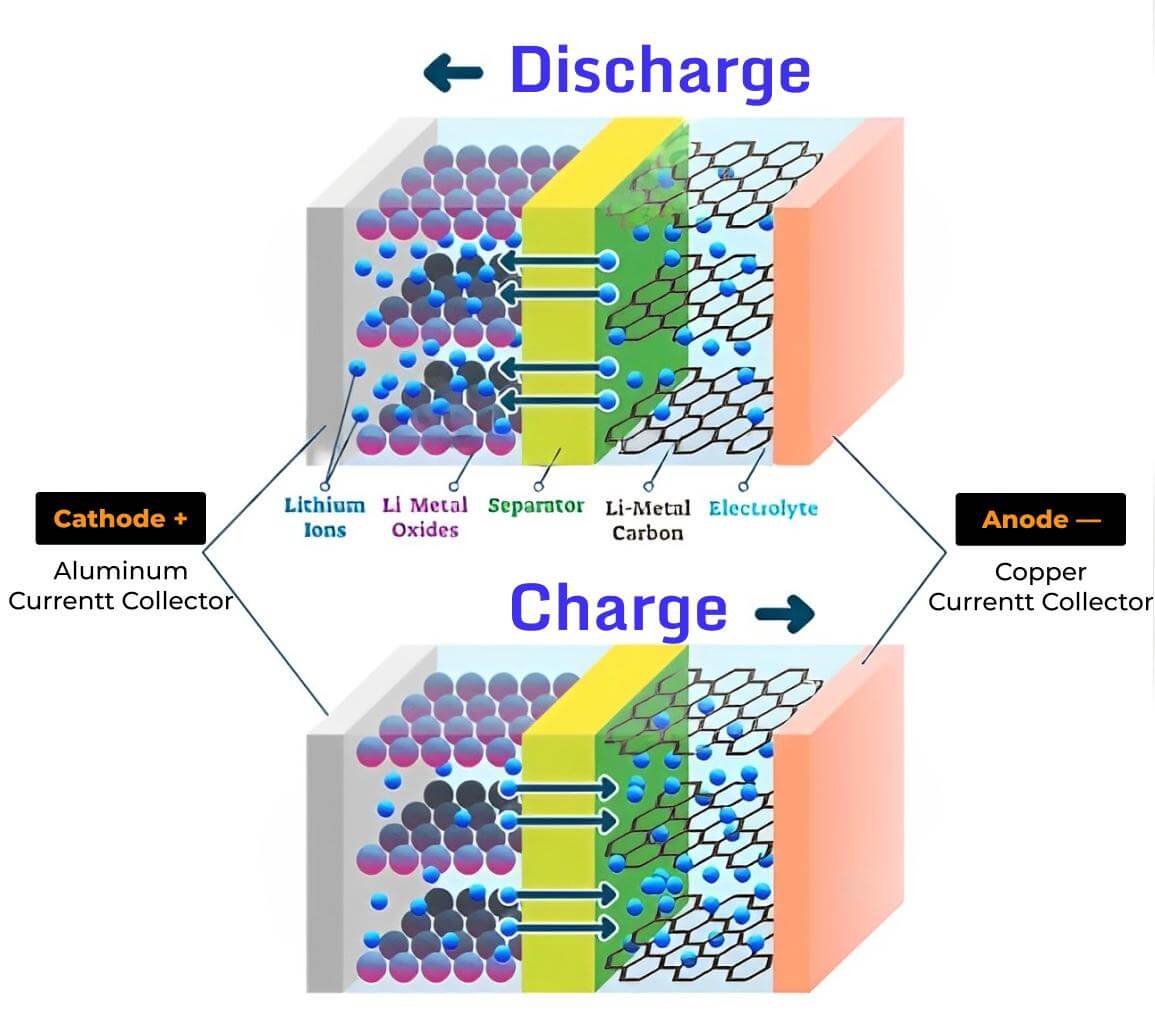
Now, let's discuss it in detail. First, the electrolyte carries the positively charged ions from the negative to the positive electrode, and vice versa. This produces electrons in the negative electrode, creating a charge on the other side of the current collector.
The generated current then flows through the device being powered, so it reaches the negative current collector. At the end, a separator is placed to block the electrons inside the battery, while maintaining the exchange of lithium ions.
Charging and discharging
When you are charging the battery, the lithium ions from the cathode get separated from the electrons. These ions move from the cathode to the anode, passing through the electrolyte. Finally, they recombine with the electrons and neutralize electrically.
During the discharging cycle, the opposite occurs. The ions move from the cathode, pass through the electrolyte, and reach the anode.
Eventually, this lithium ions movement creates an electric potential difference, called voltage. Connecting your device to the battery setup forces the electrons to power it.
Types of lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are not the same and have different chemical compositions, depending on the electrode material. Let's discuss them in detail along with their best-suited applications.
Lithium Iron Phosphate LFP
LFP batteries use phosphate and graphite carbon as the positive and negative electrode, respectively. These substitutes are the safest, have longer life cycles, and have good electrochemical stability. LFPs are cheaper than other nickel-based options but offer less specific energy. Hence, you will find these batteries in short-range electric vehicles (EVs).
Lithium Cobalt Oxide LCO
Unlike LFPs, LCO batteries have high specific energy but shorter life spans. These batteries are thermally unstable and not fit for high-load applications. LCOs are generally preferred for low-power applications like smartphones, laptops, etc.
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide NMC
NMCs use nickel, cobalt, and manganese to give an all-round performance. These batteries have higher proportions of nickel for energy density and long life. Moreover, the use of manganese and cobalt promotes thermal stability. NMCs work great in powering electric powertrains like scooters, e-bikes, etc.
Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide NCA
NCA also uses higher nickel proportions, promoting energy density and power. However, these batteries use aluminum to promote stability, making them pricier and less safe. NCAs are used to power high-performance, high-load EV models like Tesla.
Lithium Manganese Oxide LMO
LMO batteries use lithium manganese electrodes as cathodes. It promotes safety, fast charging, and thermal stability. However, they have a shorter lifespan. Hence, in EVs, LMOs are often paired with NMCs to help with a longer drive range.
Lithium Titanate LTO
In all the above-mentioned batteries, the cathode composition differs. However, LTOs have a unique chemistry where they replace the anode surface from graphite to lithium titanate. This, with the cathode arrangement of LMO and NMC, offers better safety and longer life. Such batteries are used for uninterrupted power backups like emergency solar energy storage.
Key applications of lithium-ion batteries
Let's look at a few key areas where lithium-ion batteries are commonly used.
1. Uninterrupted power supply backups
These batteries are a great emergency backup for power outages and inconsistencies. Vulnerable equipment like medical instruments, telecommunication setups, and technical setups gets an uninterrupted power supply with Li-ion batteries.
2. Electric vehicle industry evs
Lithium batteries have revolutionized the electric vehicle industry. Today, high and low-load electric vehicles use such arrangements to ensure a longer running life. Currently, these batteries are used in Tesla Model X, Model S, and Model 3 for power generation.
3. Mobile vehicles
Today, mobile vehicles like e-bikes and wheelchairs use lithium batteries. It helps compact vehicles with longer lifespans, lightweight, and energy performance.
4. Digital personal assistance
The high energy density and fast charging of rechargeable Li-ion batteries also make them excellent for charging gadgets like smartphones, smartwatches, etc. You will also find them being used in day-to-day handheld appliances like streamers, irons, and more.
5. Energy storage
Lithium batteries are used for solar and wind energy storage. It helps in stockpiling surplus energy for emergencies like sunless days, unexpected maintenance issues, etc.
Benefits of lithium-ion batteries
Most consumer products today use lithium batteries as a selling feature. Here is what makes them attractive for buyers and sellers.
1. High energy density
Lithium-ion batteries are top performers in energy density. Simply put, this density is the ability of a battery to store energy. Generally, lead-acid batteries have an energy density around 50-100 wh/kg, compared to lithium batteries with a range of 260-300 wh/kg.
2. Lightweight
An average lithium-ion battery has 50-60% of the weight of the traditional batteries. Hence, these substitutes work best for compact solutions like smartphones, e-bikes, e-readers, etc.
3. Long lifespan and fast charging
Lithium-ion batteries have no mattery effect. Batteries with a memory effect tend to remember repeated partial discharges, which causes them to lose their energy-storing capacity. Hence, with no backing memory, these batteries offer longer lifespans.
For instance, a lithium iron phosphate LiFePO4 used to power a boat lasts around 1000 to 10,000 cycles. In comparison, an SLA lead battery only lasts between 50 and 500 cycles. Moreover, the chemistry of Li-ion batteries also helps them accept current faster, promoting quicker charging than their counterparts.
4. Low self-discharge
Traditional batteries lose charging or self-discharge gradually. However, lithium batteries only have a 1.5-2% discharge rate while lead-acid batteries discharge at a 5% rate. Hence, using a lithium alternative in your electronics helps you retain the charge for the longest time.
Lithium-ion Vs. other battery technologies
The advent of rechargeable batteries has entirely transformed the consumer market. Today, be it personal digital assistance, the electric vehicle industry, or emergency backups, Li-ion batteries are desired, despite being expensive. But, why? Let's understand how these batteries compare to popular alternatives across the market.
Lithium-ion vs lead-acid batteries
- Lead-acid batteries usually have a lower energy density, around 50-90 wh/ kg compared to their lithium counterparts with a range between 260 and 300 wh/ kg.
- The size of the lithium battery is much lower than lead-acid batteries.
- Lead batteries are easy to install and cheaper. Comparatively, lithium-ion batteries are double the price with the same capacity, yet lighter and more efficient.
- Li-ion batteries offer 85-100% storing capacity with little discharge. In contrast, lead counterparts have less usable energy with 50% discharge.
LiFePO4 Vs lithium ion batteries
- LiFePO4 uses lithium, iron, and phosphate ions, which are generally safer and more stable. However, lithium batteries have metallic lithium composites as cathodes - power-dense and suitable for high-load applications.
- LiFePO4 batteries tend to have longer lifespans and can last up to 10 years if properly used, as compared to lithium-ion batteries that last up to 3 years.
- LiFePO4 batteries can operate between -4 to 140 degrees Fahrenheit. In comparison, lithium-ion batteries have a narrower range of 32 to 113 degrees Fahrenheit.
Dive deeper into the comparison of LiFePO4 vs. lithium-ion batteries to understand why LiFePO4 is gaining popularity in various applications.
Best lithium iron phosphate batteries
Today, people prefer rechargeable LiFePO4 batteries for added safety and mobility. However, most feel hesitant while buying one, especially considering the hefty prices. In this case, tried and trusted options like Renogy Pro are your safest bet. Here is all you need to know about it.
Renogy Pro Smart Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery

The Renogy 12v 200ah LiFePO4 battery is a well-put alternative for off-road camping. It is built to withstand harsh weather, rough terrain, vibrations, and heat. Among other Renogy batteries, the Pro 12V 200Ah battery stands out for its advanced features to promote easy monitoring, temperature handling, and protection. Plus, it comes with mounting holes for brackets, making it easy to secure it to any surface, RV, van, or SUV.
Here are some highlight features of the Renogy Pro Smart battery.
- Built-in Bluetooth 5.0 for easy monitoring with the Renogy DCHome app.
- Automatic self-heating feature to survive harsh winters and ensure safe charging in sub-zero temperatures.
- Flame-resistant casing, which is waterproof (IP67) and corrosion-resistant, making it protected against abuse.
- Vibration-proof built to counter overlanding in off-grid locations.
- 60+ EV-grade BMS protection, offering precise monitoring in all kinds of weather.
- Easily replaceable BMS design with easy-to-follow replacement guides.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries are more popular today than they ever were. Be it your cell phones, laptops, scooters, and compact power tools, these rechargeable solutions are easily accessible. However, not all lithium batteries work the same. Depending on their chemical composition, these batteries have different applications and uses.
For instance, most transportation and charging solutions use lithium-iron phosphate batteries. This is because they are safe, thermally stable, and apt for low-load applications. So, do your research and find one that fits your criteria best.
FAQs
How long do lithium-ion batteries last?
An average lithium-ion battery has a lifespan of 2 to 3 years. This is anywhere around 300-500 charge/ discharge cycles under normal conditions. A single charge cycle is defined as the period of use, from a fully-charged battery till it is charged again.
However, please keep in mind that rechargeable Li-ion batteries do deteriorate. Hence, they gradually lose their charging capacity, which is irreversible. Once the battery loses capacity, its run time also decreases.
Note: Curious about the lifespan of your lithium batteries? Discover the factors that influence their longevity and get tips on maximizing their performance.
Can lithium-ion batteries be recycled?
Yes, lithium-ion batteries have approximately a 99% recycling rate. Recycling these batteries can recover pricey materials like nickel, manganese, lithium, and cobalt. But, currently, only 5% of these batteries are recycled globally, as the process costs you more than mining the raw materials.
Moreover, the recycling process can be sensitive and complex, as lithium is highly reactive. Hence, it should be carefully handled.
Note: Discover the importance of lithium battery recycling and how it contributes to a circular economy and sustainable energy solutions.
How can I extend the lifespan of my lithium-ion battery?
Extend the lifespan of your Li-ion battery by avoiding high and low temperature extremes. This is because overheating results in deteriorating the health of a lithium battery.
Moreover, the batteries should be stored at a partial charge when stored. As Li+ batteries slowly recharge, turning them off and checking every few months won't lose the charge significantly.