A Complete Guide to Solar PV
Many homeowners are shifting to using solar photovoltaics system, known as solar PV, to cut bills and mitigate their impacts to the society as electricity price continues to soar and effects of climate change. This complete guide will familiarize you with everything you should know about the solar photovoltaics including the details on the aspects of the installation, costs, savings, and maintenance. Whether you are a first-time ‘solar’ seeker or preparing for ‘solar switch’ this guide points you in the right direction about what you need to know about Solar PV for your home. We will explain all the terms, guide through the procedure, and reveal how to use the energy of the sun.
What is Solar Photovoltaics(Solar PV)
Solar photovoltaics (Solar PV) is a technology that converts sunlight into electricity using solar cells. These cells contain layers of semiconducting material, usually silicon. When the sun shines on the cell, photons energize electrons in the semiconductor which leads to their movement through it and creation of DC electric power.
The entire PV system involves many parts such as PV modules or panels having solar cells inside them; one or more inverters that convert DC output into AC (alternating current); racking and mounting equipment; wires and electrical connections; and sometimes batteries for energy storage. The system may be connected to an existing electricity grid or work off-grid for remote areas.
Since they are modular systems with many parts that can be put together in different ways depending on needs, it is possible to have any number of solar panels for a house or business. By adding more panels and enlarging the overall system size you can generate more electricity. Single modules usually have power ratings between 250 – 400 watts while commercial or utility-scale installations reach into the megawatts.
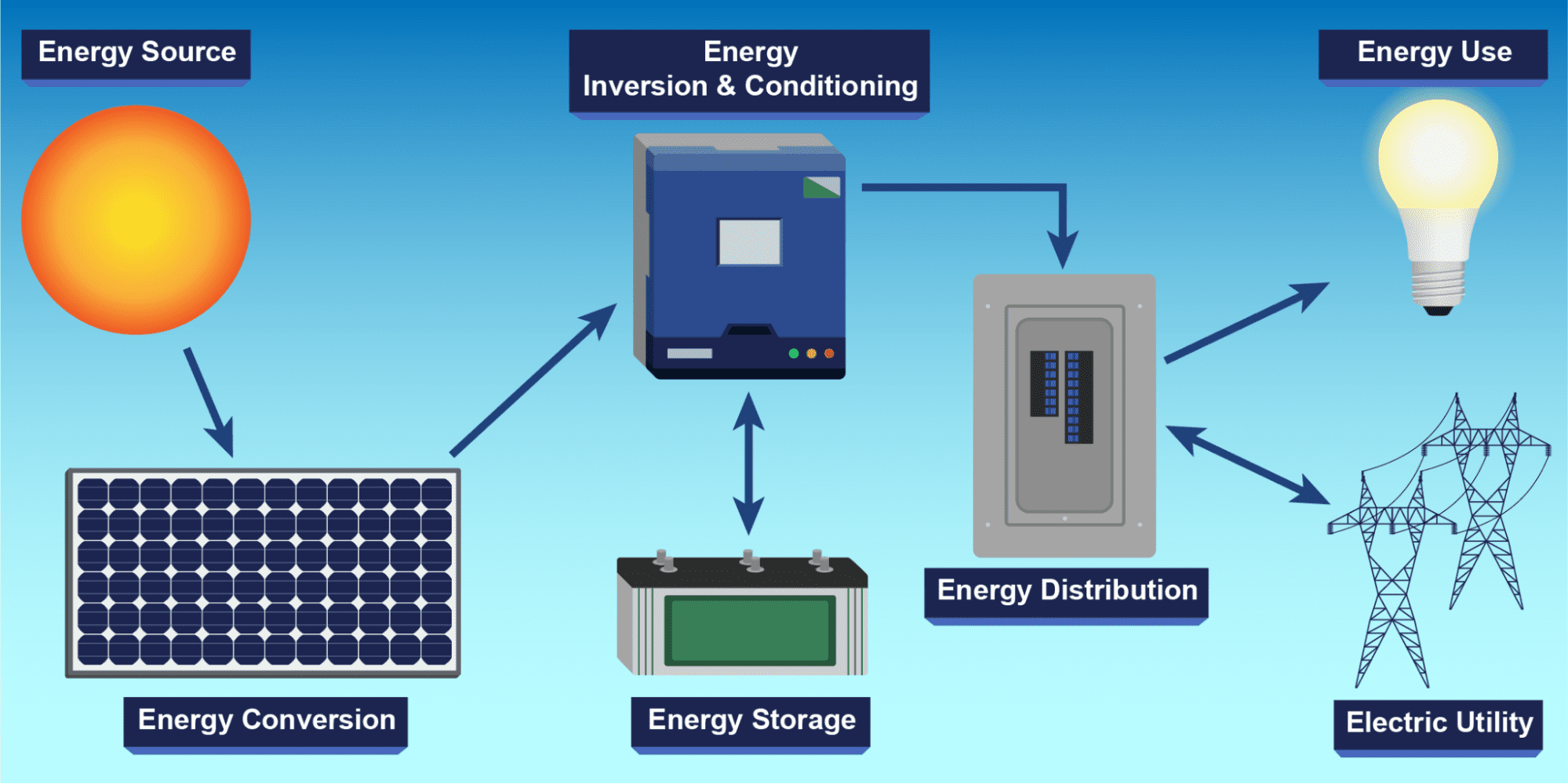
Key Components of a Solar PV System
There are several key components that constitute a whole solar PV system. These are:
Photovoltaic Cells
These are the devices that convert sunlight into electricity. Individual cells are wired together and encapsulated into modules or solar panels. Below are two types of commonly used technologies:
- Monocrystalline silicon: Produced from a single silicon crystal in cylindrical shape. They have the highest rates of efficiency but also they are more costly.
- Polycrystalline silicon: Made from many fragments of silicon melted together. They have lower efficiency but cost less as well.
Thin-film cells can be used too, where a thin layer of photosensitive material is applied on to a substrate like glass or stainless steel. Flexible thin-film panels are light-weight.
Inverters
Inverters change the direct current (DC) power produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity for use at home or office. Grid-tied systems match phase with grid power and feed excess solar energy back. The following are examples:
- Microinverters: Small units installed on each panel to maximize its output.
- String inverters: Single inverters for a string of panels.
- Central inverters: Large inverters for utility-scale arrays.
Racking, Wiring, and Other Parts
Racking or mounting systems fix solar panels securely at an optimum angle. Roof mounts bolt into roof rafters while ground mounts anchor them into the earth. Electrical wiring, disconnect switches and combiner boxes take power from the array to the inverters while monitoring systems track performance of the system.

How does solar PV work
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity through a fascinating process. When sunlight hits the solar panels, which are made up of many individual photovoltaic cells, it excites the electrons within the cells' semiconductor material, typically silicon. This excitement causes the electrons to flow, creating an electric current. The cells are connected in series and parallel configurations to form a solar panel, and multiple panels are often linked together to create a solar array. This direct current (DC) electricity is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) suitable for use in homes and businesses.
What Solar PV system will suit your house?
If you want to size a solar PV system for your house, it is necessary to estimate your electric load requirements based on the results of which you will be able to determine the number of solar panels together with the additional equipment. The most important initial step is estimating power consumption.
Determining Power Consumption Needs
It will be necessary for you to determine the average daily electricity demand at home or in business. To do this:
- Make a record of all electric appliances and devices with their wattage rating
- Estimate how many hours each appliance will be used per day
- Multiply watts by hours to get watt-hours/day for each device
- Sum up watt-hours/day for all devices
For instance, if you use 100-watt light bulb 5 hours daily, it means that only light alone consumes 500 watt-hours per day. Perform this calculation for every electrical device including computers, fridge, air conditioner, etcetera.
The total will give you your average daily energy consumption, which must be matched by your solar PV system. Add at least 10-20% more as a safety buffer. You can do these calculations using a solar PV calculator.
Sizing the PV Panels
Once you have the total watt hours per day that must be produced by the solar panel system, sizing photovoltaic panels involves:
- Dividing the total daily watt-hours by peak sun hours of your place. This gives us total watts-peak (Wp) rating required for our PV panels.
- Checking out specifications on different solar module models until we find one with at least this amount of Wp output – most standard modules are 250-400 Wp each.
- Then figuring out how many units are needed by dividing total Wp capacity needed with single module’s output in Wp and rounding up to nearest whole number.
For example, if I need 3000Wpsystem and choose 300wpmodule, I will require 10modules.
Sizing the Battery Bank
For off-grid systems, batteries store excess solar energy during the day to provide power at night. To size your battery bank:
- Determine the total daily watt-hours consumed by appliances (from previous calculations)
- Account for 10-20% losses in charging and discharging the batteries
- Divide by the typical depth of discharge, usually 50%, to get the amp-hour capacity needed
- Select compatible deep cycle batteries that meet the required amp-hour rating
Sizing the Charge Controller and Inverter
Two other key components are also sized according to the PV array:
- The charge controller regulates power from the PV panels to the batteries. Size it 25-30% above the total Wp of your PV array.
- The inverter converts DC electricity from the array to usable AC power. Match its continuous wattage to your total PV array Wp.
Solar PV system Installation
Setting up solar PV system by oneself can be a fulfilling DIY project if you are ready to dedicate your time and effort. Here are the main steps:

Site Evaluation
Begin by examining your roof. Ensure it is in good condition, determine its usable size as well as its angles, assess how much sunlight it receives throughout the day. It should have a reasonable access to direct sunlight for efficient operation. Also look at your family’s electricity requirements.
System Design
Proceed to design your system. Know how many panels you need and arrange them on top of the roof. Plan the wiring runs accounting for any obstacles that maybe present. Find out about permit requirements, if any.
Buying Equipment
Afterwards, buy reliable components such as panels, inverters, racking, combiner boxes plus more equipment if necessary. All components must be compatible with each other. Looking around may assist in finding good deals.
Installation
The crucial part entails installing them properly; mount racking systems used to fix them and place accordingly on the roof according to plan run any wire connections neatly making sure all connections are tight enough. Safety is key when working on top of a roof.
Testing and Activation
Test comprehensively after installation. Then apply for utility approvals and net metering if needed. With all paperwork complete officially activate the system and begin generating solar power!
Although DIY solar requires careful planning and research however it results into getting a customized system which is quite satisfying because you did it yourself.Be certain you adhere to all codes while obtaining proper permits.
Conclusion
We believe this ultimate guide will give you an understanding of solar photovoltaic technology as well as solar PV system installation process. The truth is, since the cost keeps going down while subsidies increase and electricity becomes expensive, it is becoming more cost-effective for homeowners to adopt solar energy systems.
Ensure that you recognize your requirements, explore different alternatives available and engage experts who can help in solarizing your home.
FAQ
How much does a typical residential solar system cost?
For a home, you should expect to pay around $2.50-$3.50 per watt for installed photovoltaic modules. This means that a 5 kilowatt installation will be priced at approximately $12,500 – $17,500 before any applicable federal or state incentives. Your geographical location and the size of the installation will greatly affect the actual price paid.
Is it possible to sell surplus electricity back to utility companies when using solar panels?
Certainly! If you generate more electricity than you use on any given day through net metering arrangements with local utilities, they must credit your account accordingly – this is often called “selling” power back into the grid.











