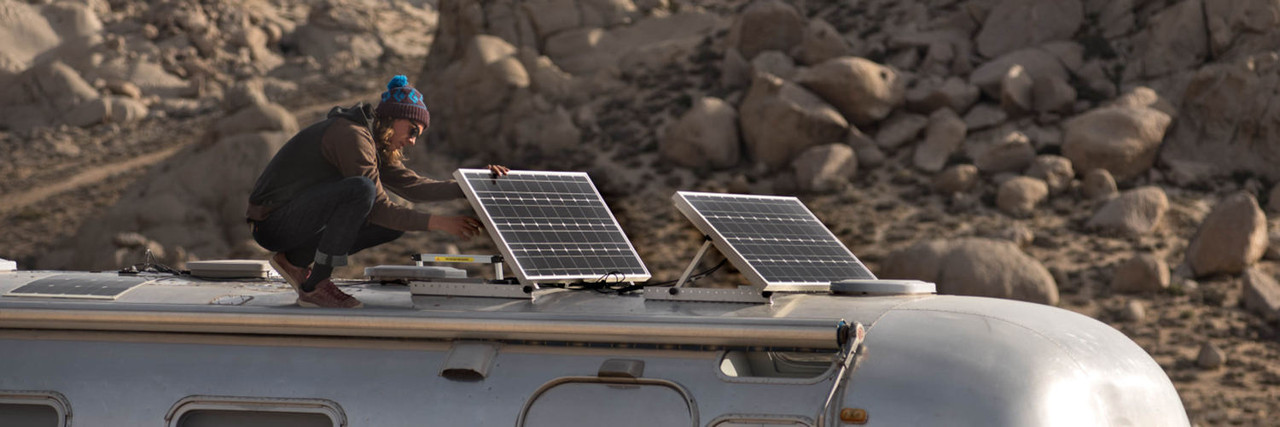
What Is Solar Energy Used For? The 9 Most Solar Panels Usages
Solar panels have emerged as a cornerstone of renewable energy, transforming the way we harness and utilize power. These innovative devices capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. As concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability grow, understanding the diverse applications of solar panels becomes increasingly important. From powering homes and businesses to enabling space exploration, solar technology has proven its versatility and effectiveness across various sectors. This article explores the nine most common uses of solar panels, shedding light on how this technology is shaping our present and future energy landscape.
The Benefits of Solar Energy
Before delving into the specific uses of solar panels, it's essential to understand why solar energy has become such a crucial part of our sustainable future:
- Renewable and Clean: Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun, an inexhaustible resource that will last for billions of years. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power generation doesn't produce harmful emissions or pollutants, making it a clean alternative for our energy needs.
- Cost-Effective: While the initial investment in solar panels may seem high, they can significantly reduce or eliminate electricity bills over time. The long-term savings, coupled with potential government incentives, make solar energy an economically attractive option for many households and businesses.
- Low Maintenance: Solar panels are designed to be durable and require minimal upkeep, often needing only occasional cleaning to maintain efficiency. With lifespans typically exceeding 25 years, they offer a reliable and low-maintenance energy solution for decades.
- Energy Independence: By generating their own electricity, solar panel users can reduce their reliance on the traditional power grid and fossil fuels. This energy independence not only provides security during power outages but also contributes to a more resilient and decentralized energy infrastructure.
- Versatility: The adaptability of solar technology allows for its use in a wide range of applications, from powering small gadgets to energizing large-scale power plants. This versatility makes solar energy accessible for various needs, from individual consumers to industrial-scale operations.
What is Solar Energy Used for
Imagine a world where the sun not only brightens our days but also fuels our lives. This isn't a distant dream – it's the reality that solar energy is creating right now. From the rooftops of suburban homes to the vast expanses of solar farms, from the streets of bustling cities to the farthest reaches of space, solar power is revolutionizing how we generate and use energy.
But what exactly is solar energy used for? The answer might surprise you with its breadth and impact:
- Illuminating homes and powering appliances, slashing electricity bills while shrinking carbon footprints
- Energizing businesses, from small cafes to sprawling industrial complexes, boosting both sustainability and bottom lines
- Pumping life-giving water to crops in sun-drenched fields, making agriculture more efficient and eco-friendly
- Propelling electric vehicles further, paving the way for cleaner transportation
- Bringing light and connectivity to remote villages, bridging the global energy divide
- Beaming crucial data from satellites, advancing our understanding of Earth and beyond
- Purifying water in drought-stricken regions, turning seawater into a life-saving resource
Solar energy is more than just an alternative – it's a revolution. It's not just about using the sun's power; it's about brightening the prospects of our planet and every life on it. So, the next time you feel the sun's warmth on your skin, remember: you're feeling the touch of our energy future.
Important Usages of Solar Panels
Solar panels, the cornerstone of renewable energy technology, have revolutionized how we harness the sun's power for a multitude of applications. From powering homes and businesses to enabling space exploration, these photovoltaic marvels are driving sustainable solutions across various sectors. The following nine applications showcase the versatility and far-reaching impact of solar panels in our modern world, demonstrating their crucial role in shaping a cleaner, more energy-efficient future.
1. Residential Power Generation
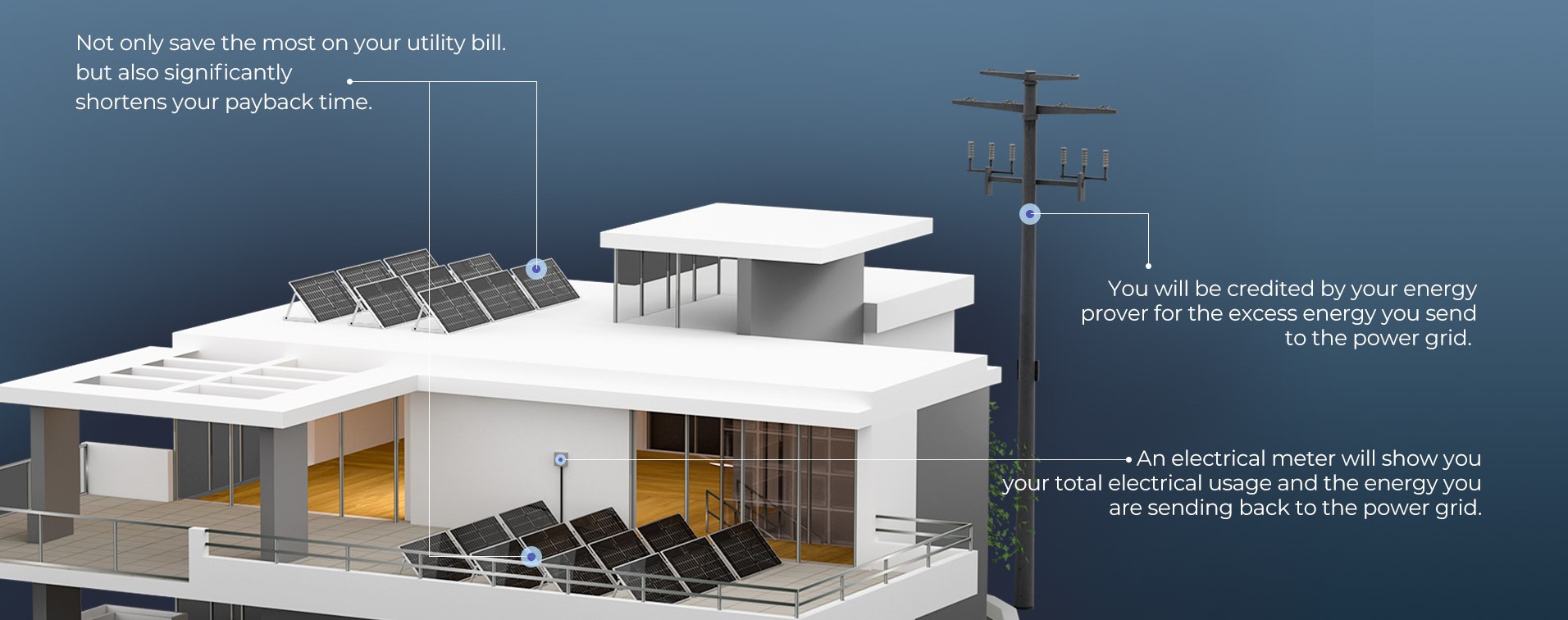
Solar panels adorning rooftops have become a common sight in neighborhoods worldwide. These silent energy producers convert abundant sunlight into electricity, empowering homeowners to take control of their energy consumption. By reducing or eliminating electricity bills, solar panels offer significant long-term savings. Moreover, many regions allow homeowners to sell excess power back to the grid, turning their roofs into micro power plants and fostering energy independence.
The Renogy 2PCS Bifacial 550 Watt Monocrystalline Solar Panel is an excellent choice for residential solar power due to its high efficiency, durability, and ability to capture sunlight from both sides for maximum energy output.
2. Commercial and Industrial Applications
Businesses are increasingly turning to solar energy to power their operations sustainably. Large-scale solar arrays installed on vast rooftops or open spaces significantly offset energy consumption, leading to substantial reductions in operational costs. Beyond the financial benefits, this shift towards solar power demonstrates a commitment to corporate social responsibility, enhancing brand image and appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
3. Agricultural Uses
The agricultural sector has embraced solar technology to boost efficiency and reduce costs. Solar-powered irrigation systems ensure crops receive water even in remote locations, while electric fences powered by the sun keep livestock secure without the need for grid connectivity. Innovative applications like solar-dried crops and solar-heated greenhouses are revolutionizing farming practices, extending growing seasons and improving crop yields while minimizing energy expenses.
4. Transportation
As the world shifts towards electric mobility, solar panels are playing a crucial role. Integrated into electric vehicles, they extend driving ranges by continuously charging batteries. Furthermore, the proliferation of solar-powered charging stations is addressing range anxiety and supporting the growing electric vehicle market, making sustainable transportation more accessible and practical.
5. Portable and Mobile Devices
The miniaturization of solar technology has led to its integration into everyday items. From solar-powered calculators and watches to portable chargers, these devices offer convenience and reduce reliance on traditional power sources. Innovative products like backpacks and clothing with built-in solar panels are pushing the boundaries of mobile energy, allowing users to charge devices on the go and stay connected in remote locations.
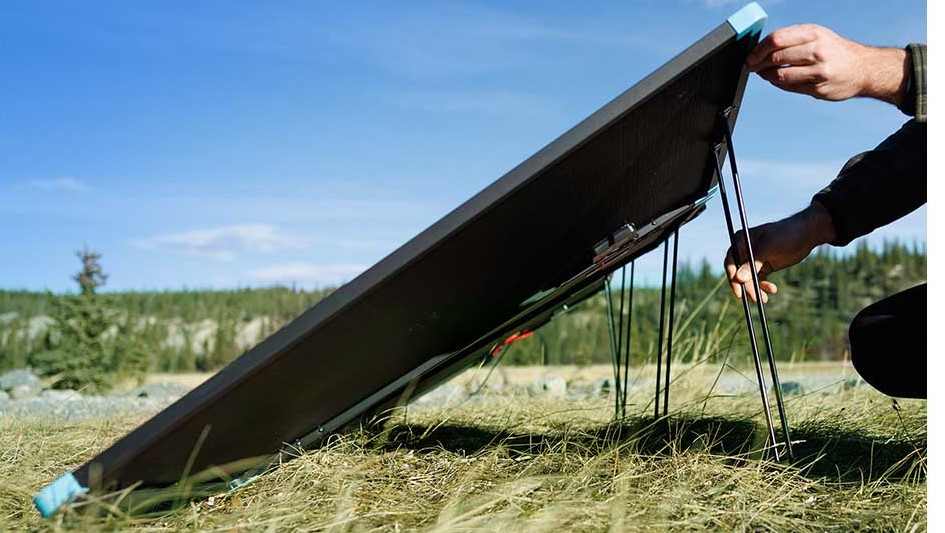

Learn more details about the Renogy 400W Lightweight Portable Solar Suitcase, which is perfect for traveling, offering high efficiency and easy setup to keep your devices powered on the go.
6. Space Exploration
In the vast expanse of space, solar panels serve as lifelines for our exploratory missions. Satellites orbiting Earth, space stations housing astronauts, and interplanetary probes venturing into the solar system all rely on solar panels as their primary power source. These specialized panels are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, including extreme temperature fluctuations and radiation exposure. By converting sunlight into electricity even millions of miles from Earth, solar paneltechnology enables long-duration missions and continuous data collection, advancing our understanding of the cosmos.
7. Water Heating and Desalination
Solar energy is making significant strides in addressing global water challenges. Solar thermal collectors efficiently heat water for domestic use, reducing reliance on gas or electric water heaters. On a larger scale, solar-powered desalination plants are emerging as a sustainable solution to freshwater scarcity in coastal regions. These plants use the sun's energy to remove salt and impurities from seawater, producing potable water without the high energy costs and carbon footprint associated with traditional desalination methods.
8. Lighting for Public Spaces
Solar-powered lighting solutions are transforming urban and rural landscapes alike. Streetlights, park illumination systems, and traffic signals equipped with solar panels operate independently from the grid, enhancing public safety while significantly reducing municipal energy costs. These self-sufficient lighting systems are particularly valuable in remote areas or during power outages, ensuring continuous illumination. Additionally, their ease of installation makes them ideal for rapidly developing areas or temporary facilities.
9. Remote Power Systems
In locations where traditional grid connections are impractical or prohibitively expensive, solar panels offer a reliable alternative power source. Off-grid homes in rural or isolated areas can achieve energy independence through solar systems coupled with battery storage. Telecommunication towers in remote locations rely on solar power to maintain critical communication links. Scientific research stations in extreme environments, from deserts to polar regions, harness solar energy to power equipment and support living quarters, enabling continuous data collection in some of the world's most challenging locations.
These diverse applications of solar panels illustrate their transformative impact across multiple sectors of society. As technology continues to advance, improving efficiency and reducing cost of solar panels, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of solar energy emerge. From powering our homes to enabling scientific breakthroughs, solar panels are not just a source of clean energy – they are a catalyst for sustainable development and technological progress in the 21st century.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Panels
Solar panels have emerged as a pivotal technology in the transition towards renewable energy, offering a range of benefits while also presenting certain challenges. The advantages of solar panels, such as their ability to provide clean energy, reduce electricity costs, and promote energy independence, have driven their increasing adoption worldwide. However, potential drawbacks, including high initial costs and weather dependence, must also be considered.
Advantages:
- Clean Energy: Solar power produces no emissions during operation, contributing to reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced Electricity Costs: After initial installation, solar panels can significantly lower or eliminate electricity bills over their lifetime.
- Low Maintenance: Solar systems require minimal upkeep, typically just occasional cleaning and inspections.
- Energy Independence: Solar power reduces reliance on the grid and fossil fuels, providing energy security.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing research continually improves efficiency and reduces costs.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for solar panel installation can be substantial, though prices are decreasing.
- Weather Dependence: Solar panel efficiency can be affected by cloudy or rainy weather, reducing energy production.
- Energy Storage Challenges: Storing solar energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days can be expensive and technologically complex.
- Space Requirements: Large solar installations require significant space, which may not be available in all locations.
- Environmental Concerns: While operation is clean, the production of solar panels involves some environmental impact, including resource extraction and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
Solar panels have revolutionized our approach to energy generation and consumption. From powering homes and businesses to enabling space exploration, their applications are diverse and expanding. As technology advances and costs decrease, solar energy is becoming increasingly accessible and efficient. While challenges such as initial costs and energy storage remain, the benefits of solar power in reducing carbon emissions and providing energy independence are undeniable. As we face global energy challenges and climate change, solar panels will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a more sustainable future. Their continued adoption and development promise a cleaner, more resilient energy landscape for generations to come.
FAQs about Solar Panels
1. How do solar panels work, and how efficient are they?
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the panels, it excites electrons in silicon cells, generating an electric current. The efficiency of solar panels typically ranges from 15% to 22% for commercially available panels, meaning they convert that percentage of received sunlight into usable electricity. However, research prototypes have achieved efficiencies of over 40%. Factors affecting efficiency include panel quality, orientation, shading, and local climate conditions.
2. What is the average lifespan of solar panels, and how much maintenance do they require?
The average lifespan of solar panels is about 25-30 years, though many continue to produce energy beyond this period at reduced efficiency. Solar panels require minimal maintenance, primarily consisting of occasional cleaning to remove dirt, dust, or debris that might block sunlight. In snowy regions, clearing snow from panels may be necessary. It's recommended to have a professional inspection every few years to check for any damage or degradation. The inverter, which converts DC power from the panels to AC power for home use, typically needs replacement after 10-15 years.
3. Can solar panels work during cloudy days or at night?
Solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, although at a reduced efficiency compared to sunny conditions. The amount of electricity produced depends on the cloud density, with production typically ranging from 10% to 25% of the panel's rated capacity on overcast days. However, solar panels do not produce electricity at night due to the absence of sunlight. To address this, many solar power systems either connect to the electrical grid for nighttime power or use battery storage systems to store excess energy produced during the day for use at night.











