Solar Panel Series vs Parallel: What’s The Difference
When it comes to solar panel series vs parallel connections, installers face a choice similar to Volta's: maximize voltage or current? This decision can significantly impact your solar array's performance and efficiency. In this article, we'll explore the pros and cons of each configuration, helping you understand which setup might be best for your solar project.
What’s the Difference Between Wiring Solar Panels in Series or Parallel
The main difference between series and parallel wiring of solar panels is their effect on voltage and current. Series connections increase overall voltage while maintaining constant current, beneficial for long wire runs and certain inverters. Parallel wiring maintains voltage but increases current, useful for higher current needs and partial shading scenarios. This fundamental difference impacts system efficiency and power output. Choosing between series and parallel depends on factors like inverter requirements, roof layout, and local shading conditions. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing solar panel performance and designing an effective solar installation tailored to specific needs.
Wiring Solar Panels in Series
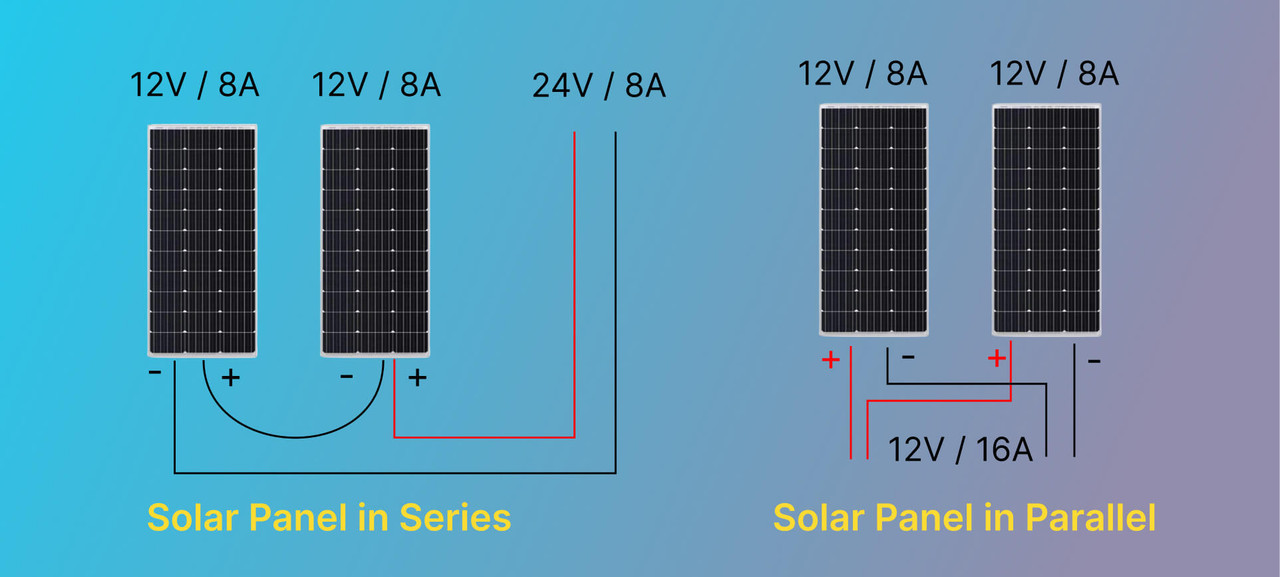
Solar panels connected in series form a specific configuration in photovoltaic systems where multiple panels are linked together in a single line or string. In this arrangement, the positive terminal of one panel is connected to the negative terminal of the next panel, creating a continuous electrical path. The primary purpose of wiring solar panels in series is to increase the overall voltage of the system while maintaining a constant current flow. This configuration is commonly used in both residential and commercial solar installations, particularly when higher voltage outputs are required or when dealing with longer wire runs to minimize power losses.
How do Solar Panels in Series Work?
When solar panels are connected in series, their electrical characteristics combine in a specific way:
- Voltage: The voltages of individual panels add up in a series connection. For example, if you have three panels each producing 30 volts, the total voltage output of the series would be 90 volts (30V + 30V + 30V). This additive voltage property allows systems to achieve higher voltages needed for certain inverters or to offset voltage drops in long wires.
- Current (Amps): Unlike voltage, the current remains constant throughout a series connection. The amperage output of the entire string is equal to the current of a single panel. However, it's important to note that in a series configuration, the current is limited by the lowest-performing panel in the string. If one panel's current output drops due to shading or damage, it will affect the current output of the entire series.
Wiring Solar Panels in Parallel
When discussing solar panel series vs parallel configurations, parallel wiring is a distinct approach to connecting multiple solar panels. In a parallel connection, all positive terminals of the solar panels are connected together, and all negative terminals are likewise joined. This setup differs significantly from solar panels in series. The primary purpose of wiring solar panels in parallel is to increase the overall current (amperage) output of the system while maintaining a constant voltage. This configuration is commonly used in both residential and commercial solar installations, particularly when higher current outputs are required or when dealing with partial shading issues.

How do Solar Panels in Parallel Work?
Understanding the difference between series and parallel connections is crucial when examining how parallel-wired solar panels function:
- Voltage: Unlike in series connections, the voltage remains constant in a parallel setup. It equals the voltage of a single panel. For example, if you have three panels each producing 30 volts, the total voltage output of the parallel connection would still be 30 volts. This consistent voltage is a key characteristic that distinguishes parallel from series configurations.
- Current (Amps): In parallel wiring, the currents from each panel add up. This additive property of current is one of the main benefits of parallel connections. If each panel in our example produces 10 amps, the entire parallel array would produce 30 amps (10A + 10A + 10A). This increased current output is particularly advantageous for systems requiring higher amperage or when using certain types of inverters.
Solar Panel in Series vs Parallel: Which is Better
When deciding between wiring your solar panels in series or parallel, it's crucial to consider several factors to determine which configuration is best for your specific needs. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, impacting system performance in different ways.
Series Wiring: Pros and Cons
Advantages:
- Higher System Voltage: Wiring solar panels in series increases the overall voltage of your system. This is beneficial for reducing power loss over long cable runs, as higher voltage systems experience lower losses compared to lower voltage ones.
- Efficiency with MPPT Charge Controllers: Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controllers perform better with higher voltage inputs. Series wiring can therefore enhance the efficiency of your solar power system.
- Simplified Installation: With fewer cables required, series wiring simplifies the installation process, making it cleaner and potentially reducing costs associated with cabling.
Disadvantages:
- Shade Sensitivity: If one panel in a series string is shaded, the performance of the entire string is reduced. This can significantly impact the overall energy output.
- Inflexibility: Series systems need to match the voltage requirements of your inverter or battery bank. This can limit flexibility in system design and expansion.
Parallel Wiring: Pros and Cons
Advantages:
- Shade Tolerance: In a parallel setup, shading on one panel has minimal impact on the performance of the others. This makes parallel wiring a better choice for locations with variable shading.
- Stable Voltage: Parallel wiring maintains a consistent voltage that matches the output of a single panel. This makes it easier to align with the voltage requirements of inverters and battery banks.
- System Redundancy: If one panel fails in a parallel system, the other panels continue to operate, ensuring continued energy production and increased system reliability.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Current: Parallel wiring increases the overall current in the system, which can necessitate the use of thicker cables and higher-rated components. This can increase installation costs.
- Voltage Drop: Over long distances, parallel systems can suffer from significant voltage drops, reducing efficiency. This is particularly relevant for large installations where cables need to run over long distances.
Series vs Parallel: Which is Right for You
To determine whether to wire your solar panels in series or parallel, consider the following factors:
1. System Voltage Requirements
For systems that need to operate at higher voltages, such as those using Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controllers, series wiring is typically more suitable. Higher voltage systems can be more efficient and easier to manage over long distances.
2. Shading Conditions
If your installation site is prone to shading, parallel wiring is often the better choice. Parallel systems ensure that shading on one panel does not drastically reduce the entire system's output, providing more reliable performance under variable conditions.
3. Component Compatibility
Ensure that your inverter, battery bank, and other components are compatible with the voltage and current levels of your chosen wiring method. Many grid-tied inverters require higher voltages, favoring series connections, while some off-grid systems might benefit from the redundancy and shade tolerance of parallel connections.
- Portable at 15.9lbs: compact, foldable, and lightweight.
- Superior fiberglass material for decades of reliability.
- 1-minute setup with IP68 solar connectors and aluminum kickstands.
Frequently Asked Questions about Series vs Parallel
1. Can I Mix Series and Parallel Solar Panels?
Yes, you can mix series and parallel solar panels, a method known as a "series-parallel" configuration. This setup combines the benefits of both wiring methods, increasing both voltage and current. Ensure all panels have similar electrical characteristics to avoid mismatches and optimize performance. Consulting with a solar energy professional can help design the best series-parallel configuration for your system.
2. Should 12V Solar Panels Be Wired in Series or Parallel?
12V solar panels can be wired in either series or parallel, depending on your system requirements. For higher voltage systems, wire them in series to increase the overall voltage. For increased current and better performance under shaded conditions, wire them in parallel. Assess your energy needs, inverter specifications, and shading conditions to determine the best configuration.
3. Can You Add More Solar Panels to an Existing System?
Yes, you can add more solar panels to an existing system. Ensure compatibility with your existing inverter and battery bank. If your current setup is in series, you may need to adjust the voltage and current to match the new panels. Consult with a solar energy professional to ensure seamless integration and to optimize your system's performance.
4. Do Solar Panels Charge Faster in Series or Parallel?
Solar panels do not necessarily charge faster in series or parallel; it depends on the system configuration and conditions. Series wiring increases voltage, which can be more efficient for long distances, while parallel wiring increases current, which can be better for shaded conditions. The charging speed is influenced by the overall system design and component compatibility.
Conclusion
In the debate of solar panel series vs parallel, the best choice depends on your specific needs and system conditions. Series wiring increases voltage, making it ideal for minimizing power loss over long distances and optimizing MPPT charge controller efficiency. Parallel wiring, on the other hand, enhances current, improves shade tolerance, and maintains voltage stability. By understanding the differences between these configurations, you can optimize your solar energy system's performance. For reliable and high-quality solar panels, consider Renogy.