How Rechargeable Lithium Batteries Work: A Scientific Explanation
Welcome to the wonderful world of rechargeable lithium batteries. These powerhouses are energy-dense, compact, and have completely transformed our technological landscape. Without lithium batteries, laptops wouldn't be portable, smartphones wouldn't fit in your pocket, and electric vehicles would be far less advanced.
At Renogy, we specialize in innovative battery solutions, so keep reading to learn how these remarkable power sources work, their average life cycle, and how to maximize their potential. Let's dive in.
Are lithium-ion batteries rechargeable?
Not all lithium batteries are rechargeable. To understand this key distinction, let's explore the difference between lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Traditional lithium batteries are primary cell batteries that cannot be recharged. These energy-dense power sources are ideal for devices requiring constant, long-term power like watches, smoke detectors, and medical implants. Once depleted, they must be completely replaced.

Lithium-ion batteries, conversely, are fully rechargeable secondary cell batteries. Their unique design allows lithium ions to move bidirectionally—from anode to cathode during discharge and from cathode to anode during charging. This remarkable capability makes lithium-ion batteries incredibly versatile, powering everything from small electronics like wireless earbuds to large-scale applications such as home backup power systems and electric vehicles.

The ability to recharge makes lithium-ion batteries more cost-effective and environmentally friendly compared to their non-rechargeable counterparts. As technology advances, these batteries continue to improve in energy density, charging speed, and overall performance, driving innovation across multiple industries.
What takes place when a lithium battery is charged?
What precisely occurs when a lithium-ion battery is recharged, then? Let's examine the operation of a lithium battery and the internal processes that take place while charging.
How does a lithium battery work?
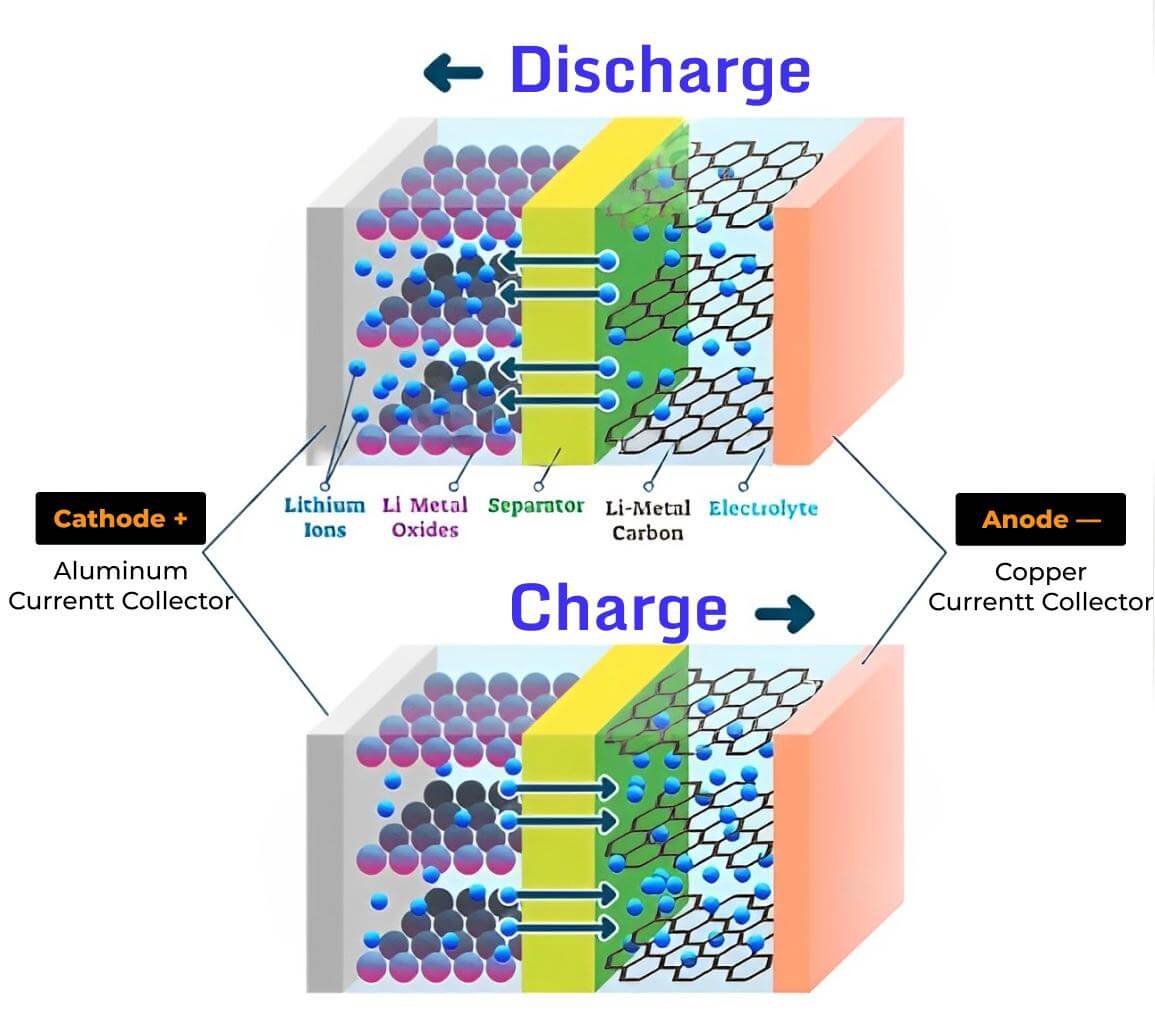
To understand the charging process of a lithium-ion battery, we must first explore its internal components. Each lithium-ion cell consists of four critical elements: an anode, typically made of graphite; a cathode, composed of materials like lithium iron phosphate or lithium cobalt oxide; a liquid electrolyte containing lithium salt; and a crucial separator.
The anode and cathode are the primary sites of energy storage and transfer. During different stages of battery use, lithium ions move between these components, enabling power generation and storage. The electrolyte serves as a medium for ion transportation, while the separator prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode, ensuring safe and controlled energy transfer.
What does the battery management system (BMS) do?
The Battery Management System (BMS) plays a critical role in the charging process. This electronic control unit constantly monitors battery temperature and ensures all cells charge and discharge uniformly. By maintaining balanced cell performance, the BMS helps maximize battery potential and extend its overall lifespan, making lithium-ion batteries both efficient and reliable for a wide range of applications.
How does recharging a lithium-ion battery work?
During charging, a fascinating reversal occurs within the battery's internal structure. Unlike the discharge process where lithium ions flow from the anode to the cathode, charging triggers the opposite movement. Lithium ions now migrate from the cathode back to the anode, storing electrical energy for future use. This bidirectional ion movement is what makes lithium-ion batteries uniquely rechargeable and versatile across numerous technological applications.
Do rechargeable lithium batteries require a special charger?
Yes, rechargeable lithium batteries do require a special charger designed specifically for their chemistry. Unlike other battery types, lithium batteries operate within a precise voltage range, and charging them improperly can cause significant damage or even safety hazards.
A battery charger works by increasing the system voltage above the battery's voltage to deliver the charge. For lithium-ion batteries, using a programmable charger that matches the battery's unique charging requirements is critical to ensure efficient and safe charging. Most lithium batteries include a Battery Management System (BMS) that monitors and protects the battery from overcharging, overheating, or other potential risks. However, relying solely on the BMS without the correct charger can still stress the battery and shorten its lifespan.
Using the wrong charger can be detrimental. For example, lead-acid battery chargers are designed to periodically pulse high voltages to prolong the life of lead-acid batteries. While this works for lead-acid chemistry, it can overcharge and damage lithium-ion batteries, which are sensitive to voltage fluctuations. Overcharging can lead to excessive heat generation, reduced capacity, and, in extreme cases, battery failure or fire hazards.

How many cycles can a lithium battery be recharged?
The number of recharge cycles a lithium battery can handle depends on several factors, including the battery type, quality, and how it is used. Not all lithium batteries are the same, and differences in cell design significantly impact their overall lifespan. For instance, cylindrical cells tend to offer greater durability and longevity compared to prismatic or lithium polymer cells.
High-quality lithium batteries, like those using cylindrical cells, can deliver between 3,000 to 5,000 charge-discharge cycles before they degrade to 80% of their original capacity. This means even with heavy daily use, such batteries can last for years while maintaining reliable performance.
On the other hand, lithium batteries built with prismatic cells typically offer 1,000 to 2,000 cycles, while lithium polymer batteries may have an even shorter lifespan due to their design and sensitivity to stress. Renogy lithium batteries, known for their reliability, offer up to 4,000 cycles with proper usage, making them a durable option for long-term applications. Therefore, the choice of battery type plays a crucial role in determining its recharge cycle life.
When should your lithium-ion battery be recharged?
When is the best time to recharge your lithium-ion battery? Most lithium battery manufacturers recommend recharging once the battery has used about 80% of its capacity. This practice ensures the battery remains within its optimal range, helping extend its overall lifespan.
However, some advanced lithium batteries feature a 100% depth of discharge (DoD) rating. This means they can be fully discharged without causing damage, allowing you to maximize usage before recharging. While this flexibility is useful, frequent deep discharges may still slightly reduce long-term performance over time.
To keep your lithium-ion battery performing its best, monitor its charge levels and recharge when it's around 20% remaining. Avoid letting the battery sit at extremely low levels for extended periods, as this can stress the cells. By following these guidelines, you can optimize both the efficiency and longevity of your lithium-ion battery.
Lithium vs. lead-acid: Battery charging compared
Lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries differ significantly in their chemistry, content, and recharging capabilities. For instance, lithium-ion batteries boast a much higher energy density and are less affected by Peukert's law. This means that lead-acid batteries generally have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries. Depending on the type and usage of a lead-acid battery, you might only get between 100 to 300 full discharge cycles.
Moreover, our lithium batteries charge at twice the speed of lead-acid batteries. You can start and stop charging at any time without damaging the battery, making them ideal for solar power systems and other applications that require quick charging.
Note: Before making a purchase, find out the truth about lead-acid versus lithium batteries.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries have transformed energy storage with their high energy density, compact design, and impressive lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. While they may come with a higher price tag, their longevity and efficiency make them a superior investment for electronics, RVs, and renewable energy systems. With proper care and charging, they deliver outstanding performance over hundreds of cycles. For a reliable and long-lasting option, consider the Renogy LiFePO4 Battery, known for its durability and advanced technology. What's your experience with lithium-ion batteries? Are they worth the upgrade? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Frequently asked questions
Are rechargeable lithium batteries worth it?
Yes, rechargeable lithium batteries are worth the investment. They offer long lifespan, fast charging, and high energy density. Despite higher initial costs, their durability and efficiency make them cost-effective in the long term for electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems.
Do rechargeable lithium batteries exist?
Yes, rechargeable lithium batteries are widely used in modern electronics. These batteries are long-lasting, eco-friendly, and cost-effective over time. They power devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, offering a reliable and sustainable solution compared to disposable batteries.
How to revive a lithium battery that won't charge?
To revive a lithium battery that won't charge, clean the terminals, try a different charger, and perform a deep discharge by fully draining the battery. If it still doesn't work, the battery may need replacing or resetting its internal protection circuit. Always practice proper charging habits for longevity.











