What Does an Inverter Do, and How Does It Work
Inverters are crucial components in contemporary electrical systems, performing an important purpose in energy conversion. These devices effectively convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC), allowing a variety of appliances and equipment to operate. Inverters are critical components of renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power installations, since they transform produced DC electricity into useable AC power for residential and commercial uses. They are also used in UPS systems, electric cars, and industrial machines.This article explores the fundamental principles of inverters, their diverse applications, and their significance in advancing energy efficiency and sustainability.
What is an inverter?
An inverter is a crucial electronic device that transforms direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Think of it as a power converter that bridges the gap between different types of electrical currents. Inverters play a vital role in various applications, from renewable energy systems to household appliances. They enable us to use DC power sources, such as solar panels or batteries, to power AC devices like computers, refrigerators, and air conditioners. Inverters come in different sizes and capacities, ranging from small units for portable electronics to large industrial-scale systems for power plants. Their ability to efficiently convert and regulate electricity makes them indispensable in our modern, energy-dependent world.
What does an inverter do?
The main function of an inverter is to convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), but its capabilities extend far beyond this basic task. In renewable energy systems, such as solar installations, when solar panels collect sunlight and convert it into electricity, it is sent to inverters, which convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by the solar panels into AC power that can be used by homes and businesses. They also synchronize this electricity with the grid, ensuring seamless integration and allowing excess energy to be fed back into the system.
In uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), inverters provide a backup power source during outages, swiftly switching to battery power and converting it to AC to keep critical equipment running. For electric vehicles, inverters manage power flow between the battery and motor, controlling speed and efficiency.
Moreover, inverters often incorporate advanced features like power conditioning, voltage regulation, and harmonic filtering. These functions improve power quality, protect connected devices from electrical fluctuations, and enhance overall system efficiency. Some modern inverters even include smart capabilities, allowing remote monitoring and control through mobile apps or web interfaces.
By performing these diverse tasks, inverters play a crucial role in enabling the widespread adoption of renewable energy, improving power reliability, and facilitating the electrification of transportation.
How does an inverter work?
At its core, an inverter works by rapidly switching the polarity of a DC power source to create an AC output. This process involves sophisticated electronic circuitry and components such as transistors, capacitors, and transformers. The inverter first chops the DC input into pulses using high-frequency switches. These pulses are then shaped and smoothed to form a sine wave, which mimics the AC power from the electrical grid.
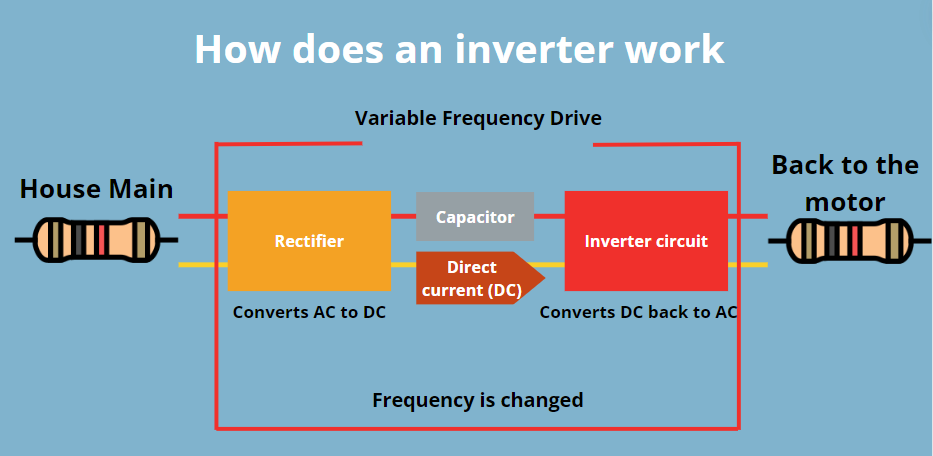
Modern inverters often employ advanced techniques like pulse-width modulation (PWM) to achieve greater efficiency and cleaner output. They may also use microprocessors to control the switching process, monitor performance, and adjust parameters in real-time. Some inverters include multiple stages of conversion and filtering to produce a highly stable and pure sine wave output.
The specific design and operation of an inverter can vary depending on its intended application, with factors like power capacity, efficiency, and output quality influencing the chosen technology and components.
Benefits of using inverter
Inverters offer numerous advantages across various applications, making them essential in our modern electrical landscape:
Enhanced Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Inverters play a crucial role in harnessing renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. By converting DC power from these sources into usable AC electricity, inverters contribute to reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable living. They enable users to tap into clean energy, potentially lowering electricity bills and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.
Flexibility in Power Supply
Inverters provide flexibility in electricity use and distribution. They allow AC appliances to run on DC power sources, expanding energy access in remote or off-grid locations. This capability is valuable for camping, RVing, and areas with unreliable grid electricity.
Power Quality Improvement
Advanced inverters enhance overall power quality by stabilizing voltage fluctuations, reducing harmonic distortions, and protecting sensitive equipment from power surges. This feature is particularly valuable in industrial settings where consistent, high-quality power is essential for maintaining productivity.
Smart Monitoring and Control
Modern inverters offer intelligent features for real-time energy monitoring and remote management. These capabilities enable users to optimize their energy consumption and participate in smart grid initiatives.
Economic Benefits
Inverters can lead to significant economic advantages through reduced electricity bills, potential income from selling excess power back to the grid, and increased property values for homes with solar systems.
What is a power inverter used for?
A power inverter converts direct current (DC) from a battery or solar panel into alternating current (AC), used by most household appliances. With the help of a power inverter, you may utilize all types of equipment that runs on AC power, including electric lights, kitchen appliances, microwaves, TVs, radios, laptops, etc. Here are some common uses for power inverters:
- Home Backup Power: Inverters are pivotal in home backup power systems. During power outages, they convert stored DC power from batteries into AC power, allowing essential devices like refrigerators, lights, and medical equipment to continue operating. This ensures comfort and safety during emergencies.
- Renewable Energy Systems: In solar power systems, inverters play a critical role by converting the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity. This AC power can be used to run household appliances or fed into the electrical grid, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Vehicle Power: In recreational vehicles (RVs), boats, and other vehicles, inverters allow the use of standard household appliances and electronics, such as microwaves, TVs, and laptops, by converting the vehicle’s DC power from its battery to AC power. This enhances convenience and comfort during travel and outdoor adventures.
- Portable Power: In remote or off-grid locations, portable power stations and generators equipped with inverters provide reliable AC power. This is particularly useful for outdoor activities, construction sites, and emergency situations where access to the grid is unavailable.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): In UPS systems, inverters are essential for providing backup power to critical devices like computers, servers, and communication equipment. During power interruptions, the inverter quickly switches to battery power, ensuring continuous operation and preventing data loss or damage to sensitive electronics.
How to use inverter?
- Safety First: Place your inverter in a well-ventilated area, away from heat sources and moisture.
- Connect to Power Source: For portable use, plug the inverter into a 12V socket or connect directly to a battery. For home systems, have a professional connect it to your solar panels or battery bank.
- Power On: Use the inverter's on/off switch or remote control to turn it on.
- Connect Devices: Plug your AC devices into the inverter's outlets. It's best to start with lower-power devices to ensure everything's working correctly.
- Monitor Usage: Keep an eye on the inverter's display (if available) to avoid overloading.
- Power Down: When finished, turn off and unplug your devices before switching off the inverter.
Conclusion
Solar inverters are essential components in photovoltaic systems, playing a crucial role in renewable energy adoption. These devices efficiently convert DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC power used in homes and businesses. As grid integration becomes increasingly important, solar inverters are evolving to support smart grid functionalities and energy storage solutions. For reliable and efficient solar power systems, Renogy offers a range of high-quality inverters designed to meet diverse energy needs and provides better quality warranty and excellent after-sales service.
Frequently asked questions
1. Why and When would you need an inverter?
You need an inverter when you want to use AC-powered devices with a DC power source. This is common in off-grid situations, RVs, boats, or during power outages. Inverters are essential for solar power systems, converting DC electricity from panels into usable AC power. They're also crucial for backup power systems, allowing you to run household appliances from batteries during blackouts.
2. What does an inverter do in a rv?
In an RV, an inverter converts 12V DC power from the vehicle's battery or solar panels into 120V AC power. This allows you to use standard household appliances and electronics while on the road or camping off-grid. The inverter enables you to run devices like laptops, TVs, microwaves, and phone chargers without needing to be connected to shore power or running a generator.
3. What size solar inverters do I need for my system?
The size of your solar inverter depends on your total power needs and solar array capacity. Generally, your inverter should be rated at 1.1 to 1.3 times your solar panel array's wattage. For example, a 5kW solar panel system would typically require a 6kW inverter. Consider future expansions and peak power demands when sizing. Consult with a solar professional for precise calculations.
4. What are the different types of solar inverters?
Solar inverters primarily come in two types based on their output waveform:
Pure Sine Wave Inverters: Produce a smooth, consistent electrical output identical to grid power. Ideal for sensitive electronics and appliances.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters: Generate a stepped waveform approximating a sine wave. More affordable but may not be suitable for all devices.
Find out the difference betweem modified vs pure sine wave inverters.
5. How long will a 12V battery last with a 2000 watt inverter?
The duration depends on the battery's capacity (Ah) and the actual power draw of your devices. Assuming a 100Ah battery and full 2000W usage, it would last about 30 minutes. However, typical usage is much lower. With a 500W average load, the same battery could last about 2 hours. For longer runtime, use larger batteries or reduce power consumption.










