How to Read Your Electric Bill Easily?
When you see your bill, it has many figures at first sight. Lots of values are provided, some are costs of units and others are taxes. It is hard to read the bill accurately. You can understand the calculations related to the bill when you understand all the given terms and units. How different parameters affect the cost of electricity is a huge issue that needs to be resolved. How can you manage your electricity bill as per your budget?
This article will help you understand the different parameters that are important to know and how these parameters affect your electricity prices. This article will help you learn how to read an electric bill easily.
Electricity Bills: Understanding the Basics
Understanding basic parameters is necessary for a precise and comprehensive interpretation of the bills. As mentioned earlier, these bills contain a significant amount of data in digital and graphic form. Let’s begin with an understanding of the electricity bill from its basics.
First, when you receive your electricity bill you must know the due date to pay. So, let’s figure out how it affects us.
When Is My Billing Period?
In most countries, citizens receive electricity bills every month. People use electricity for a month, and at the end of the month, they must pay their bills. The following figure shows the USA's electricity bill. On the bottom right side, the due date is “03/30/2021” given.
For instance, the reading date means when the data of used electricity was recorded, and the Due date means when you must pay. The reading date is important in the billing period. If the reading date is recorded during a high electricity consumption period, the bill will be high. This usually happens when you consume more electricity during peak hours, which can vary from place to place. At some locations, peak hours are related to different weather conditions.
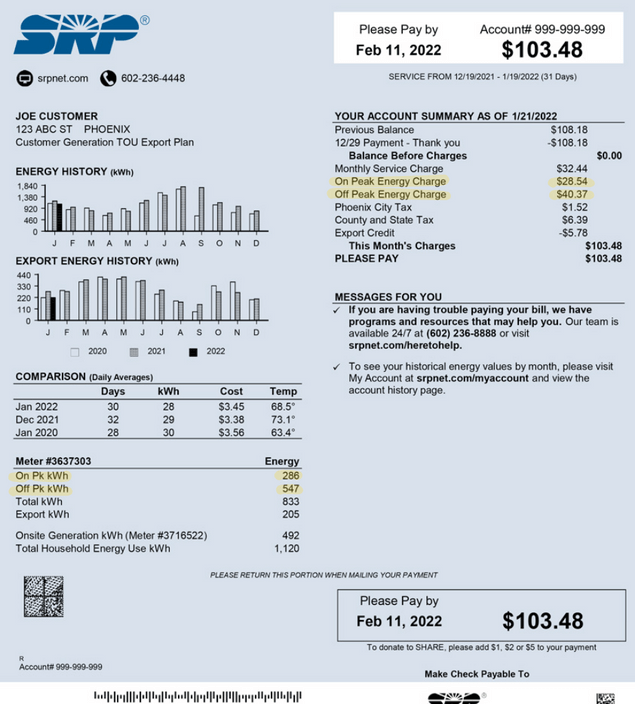
Where Can I find My Account Number?
Let’s discuss the significance of the account number. Your electricity provider company (PEPCO in the USA) provides you with an account number. That account number is your identity like your roll number in your class. Your account number is mentioned at the top of your bill as you can see in the following figure:
This account number is essential when you pay your electricity bill online.
Do Not Miss Your Payment Due Date
The due date means that you must pay your electricity bill on/before this date. If the due date has passed, and the bill is unpaid. Then you must pay a fine as a punishment with the due amount in most of the countries. That’s why it is said that “do not miss the payment due date”.
Know Your Rate Structures
Bills are not made through just numbers. These numbers take a lot of calculations. These rate structures mean there are different parameters which are used to generate the bills, for instance flat charges or tiered charges etc. These structures are briefly discussed below:
Fixed vs Variable Charges: What is the difference?
Fixed charges mean you have set some fixed costs that do not involve additional compensation. Fixed charges are supposed to be paid irrespective of consumed electricity. These charges include fees for the following variables.
- Maintenance of the grid
- Administrative costs
- Meter rent
- Transmission charges
- Connection charges
Variable charges are dependent on the consumed electricity. Variable charges keep varying according to the rates of units of electricity. Most of the electricity bill is composed of variable charges. These charges include.
- Energy charges which mean the amount of electricity used in a month. It is calculated in kilo watt hours (kWh).
- Fuel Adjustment charges indicate the price of the fuel in the generation of electricity.
- Peak-hour charges show the usage of electricity in restricted hours such as 5-7 pm in some countries.
Tiered Pricing
There is a certain threshold limit for the usage of electricity. It is different in different regions. Companies or utilities which provide electricity set different rates based on usage tiers. Rates are different for each tier. When you are in a lower tier say the first 200 units, you pay a lower rate per unit. When you exceed 200 units of consumption, you move into the next tier where the rate per unit is higher than the previous. In the USA, when you exceed tier 01 where the rate of electricity is 0.32$ per unit, the price per unit goes higher by 0.41$. By knowing the tiered pricing, you would be careful to cross that threshold limit.
In this way, you will control the utility of electricity and the bills.
Time-of-use Rates
Utilities have designed a pricing model where the electricity rate per unit changes at different times of the day. In this model, there are three time zones in a day: peak-off hours, peak hours and mid-peak hours. Peak hours mean the time in which demand for electricity per unit is high, for instance, 12 pm to 4 pm in summer. In these hours, rates of electricity are relatively higher than in other time zones of the day.
This model is designed to manage the load on electricity. You should avoid using high-voltage appliances like irons in peak hours to control the billing price.
Understanding Your Electric Bill Breakdown
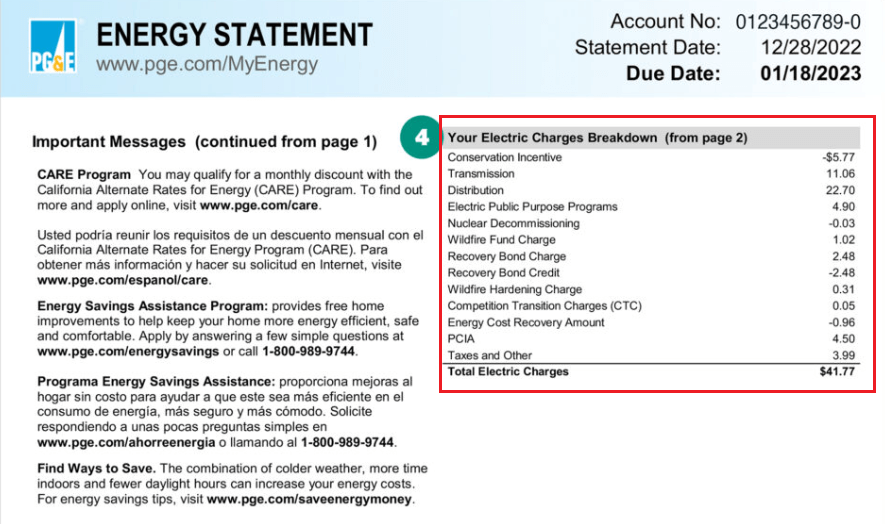
When you receive your electric bill, you might be surprised to see that it's not just a simple charge for the electricity you've used. In fact, your bill is made up of several components, each reflecting different aspects of the cost of providing you with reliable electrical service. Let's break down these charges to help you better understand what you're paying for:
1. Base Charge (or Customer Charge)
This is a fixed monthly fee that covers the basic costs of having an account, such as meter reading and billing. You'll see this as a flat rate, regardless of how much electricity you use.
2. Energy Charge
This is the core charge for the actual electricity you've consumed. It's typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and is often the largest part of your bill. Some utilities use tiered pricing, where the rate changes based on your usage level.
3. Distribution Charge
This fee covers the cost of delivering electricity to your home through local power lines. It's often calculated based on your energy usage.
4. Transmission Charge
This covers the cost of moving electricity from power plants to your local area. Like the distribution charge, it's usually based on your energy consumption.
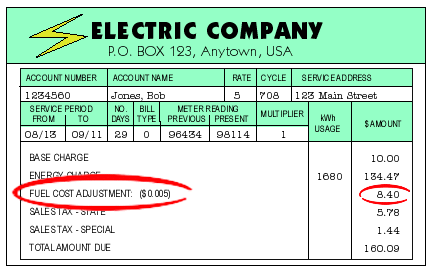
5. Fuel Cost Adjustment
This charge (or credit) reflects fluctuations in the cost of fuel used to generate electricity. It can vary month to month based on market prices.
6. Environmental Surcharge
Not present on all bills, this charge helps cover costs associated with meeting environmental regulations. It may be a fixed fee or based on your usage.
7. Taxes
Various state and local taxes are often applied to your electricity bill. These can vary significantly depending on where you live.
8. Public Benefit Programs
Many utilities include charges to fund energy efficiency programs, low-income assistance, or renewable energy development. These are usually small charges based on your energy usage.
9. Franchise Fee
This is a fee that utilities pay to local governments for the right to use public property for their equipment. It's often a percentage of your total bill.
10. Nuclear Decommissioning (if applicable)
In areas served by nuclear power, this small charge helps fund the eventual shutdown and dismantling of nuclear facilities.
Remember, not all of these charges will appear on every bill. The specific breakdown depends on your location, utility company, and local regulations. Some bills may also include special charges such as storm recovery fees or renewable energy surcharges.
Here are a few things you can do to get a better understanding of your electric bill:
- Review your own bill and compare it to this list. Which charges do you see?
- Look for any charges you don't understand and consider contacting your utility for clarification.
- Pay attention to how each charge is calculated (fixed fee, per kWh, or percentage of bill) to better understand what drives your total cost.
- Consider how your energy usage affects not just the energy charge, but other usage-based fees as well
Understand Your Monthly Electricity Consumption
One of the most important sections of an electrical bill is to understand electricity consumption. Electricity consumption means the amount of electricity you use during a billing period. Electricity consumption is expressed in kWh on the bill. It is often listed on the top of the bill like 3.5 kWh means you consumed 3500 watts during the billing period. A history of electricity consumption is also given on the bill in kWh. This history gives you insights about in which billing period, most electricity is used.
Other sections include peak-off hours and peak hours. To fully understand electricity consumption, you need to know how much electricity is used in peak-off and peak hours. Electricity consumption during these hours is also expressed in kWh on the bill.
A section of the electricity bill shows the rate you have been charged per unit to help you calculate the price of electricity consumption.
What Exactly KiloWatt Hour is?
When reading an electricity bill, many people get confused about the concept of kilowatt-hours (kWh). A common misconception is that kWh represents the power used at any given moment, but this isn't correct. Let's clarify what a kilowatt-hour really means:
What is a Kilowatt-Hour (kWh)?
A kilowatt-hour is a measure of energy consumption over time, not instantaneous power usage. It represents the amount of energy used when 1 kilowatt (1000 watts) of power is consumed for 1 hour. The hours in kilowatt-hour is crucial – it indicates that we're measuring energy use over time. Don't confuse it with power (measured in watts or kilowatts) is the rate of energy use at a specific moment. Your bill shows total energy consumption, not peak power usage.
Here are some examples:
- A 100-watt light bulb running for 10 hours uses 1 kWh (100W × 10 hours = 1000 watt-hours = 1 kWh).
- A 2000-watt appliance running for 30 minutes also uses 1 kWh (2000W × 0.5 hours = 1000 watt-hours = 1 kWh).
How to Convert kWh to watts?
While your electricity bill uses kilowatt-hours (kWh), you might sometimes need to convert this to watts, especially when considering the power rating of appliances. Here's how to do it:
1 kilowatt (kW) = 1000 watts (W), So, 1 kWh = 1000 watt-hours (Wh)
If you know the time period over which the kWh were consumed, you can calculate the average wattage. The formula is:
Average Watts = (kWh × 1000) / Hours of use
Let's say you used 30 kWh over a 24-hour period.
Average Watts = (30 kWh × 1000) / 24 hours = 1250 watts
This means, on average, you were using 1250 watts of power continuously over that 24-hour period.
Calculate Your Monthly Electricity Cost
If you want to calculate your monthly electricity cost, you can. It's easy to calculate. By calculating your monthly electricity cost, you can see that you are not giving extra money. So, let’s see how calculation is done:
First, you sould know the total number of kilowatts used in a month. The number of kWh used in a month is shown in a section labeled "total kWh used".
Second, you must know the rate per kWh set by the government or the company.
Lastly, multiply the rate per kWh by the total number of kWh used in the billing period.
Suppose you have used 350 kWh in a month and the rate is 0.75$ per kWh. Then your cost will be 350 × 0.75$ = 262.5$.
This shows just the cost of used electricity, do not forget the included taxes and fees in your bills.
Simple Ways to Lower Your Next Bill
Are you worried about your coming bill? How much will you have to pay? So, let’s find out some ways to lower your next bill:
Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances
Energy-efficient appliances are those devices which work efficiently consuming less electricity than traditional devices. It is one of the best ways to invest in upgrading home appliances to lower electricity bills. The following figure presents a difference between the old bulb (compact fluorescent) and the new energy-efficient LED bulb. LED bulbs take 9W while CFL takes 12W. The same is the case with refrigerators. Energy Star-rated refrigerators consume 15% less electricity than non-certified refrigerators.
Simple Ways to Reduce Electricity Bill
- Don’t use high-voltage appliances in peak hours.
- In the winter season, seal windows to keep the rooms warm so you do not need to turn on the heaters.
- In the summer season, use natural ventilation to avoid air conditioners.
- Install a smart or programmable thermostat, because they can adjust room temperature when you are not home.
- Use LEDs instead of TVs.
Practice Energy-Saving Habits
These habits are quite simple to follow but in our daily routine, we do not practice. These habits are turning the fan off when you leave the room, turning off the light, or plugging off the mobile charger. These small changes have a great effect on controlling the electrical bills.
Free Energy Audits: Are You Eligible?
After understanding your electric bill, you might be wondering how to reduce your energy consumption and costs. One valuable resource that many consumers overlook is the free energy audit. Let's explore what this is and how you might benefit from it.
An energy audit is a comprehensive assessment of your home's energy use. It identifies areas where you're losing energy and suggests improvements to increase energy efficiency.
Energy audits include:
- Inspection of your home's insulation
- Examination of heating and cooling systems
- Assessment of appliances and lighting
- Check for air leaks around windows and doors
- Review of past utility bills
Who Offers Free Energy Audits? Are You Eligible?
1. Utility Companies: Many utility providers offer free or low-cost energy audits to their customers. Often available to all customers, but some may have restrictions based on the type of residence or your energy usage history. Check your utility company's website or give them a call to inquire.
2. State Energy Offices: Some states have programs that provide free energy audits to eligible residents. Eligibility criteria vary by state but may include income limits or be targeted to certain groups (e.g., seniors, families with children).
3. Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP): This federal program provides free energy audits and improvements to low-income households, with priority given to elderly, persons with disabilities, families with children and households with high energy burdens.
How to Apply?
1. Contact your utility company directly to inquire about their energy audit services.
2. Check your state's energy office website for information on state-specific programs.
3. For WAP, contact your state WAP agency or visit the U.S. Department of Energy's WAP website.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electricity Bills
1. How do I dispute a possible error in billing?
If you find or suspect any error or mistake, contact the company, immediately. You should have snapshots of meter readings and other related numerical values etc.
2. Why is my bill higher than usual?
If you observe an unusual increase in your bills, then you must investigate why and how this rise occurred. There are several ways to check out the reason behind the increment in your bills:
- If rates of electricity per unit change i.e. increased, then it would cause a higher bill than usual.
- Compare your bill with the previous one. If you have purchased a new appliance this month might cause an increase in the bill than usual.
- Maybe special items like late fees or some additional charges are added to your bill which causes a higher bill than usual.
These are the possible reasons behind the higher bill than usual.
3. What is the average cost of electricity?
The average cost of electricity depends on the location and time of usage. Often, the average cost of electricity is presented on the official website every year.











