How Solar Panel Efficiency and Cost Changed Over Time
Solar panel technology has undergone a remarkable transformation, reshaping the renewable energy landscape. Over the past decades, two key factors have driven this revolution: the dramatic decrease in solar panel cost and the significant increase in solar panel efficiency. These trends have made solar energy increasingly accessible and attractive for both residential and commercial applications. As manufacturing techniques improved and demand grew, the cost per watt of solar panels plummeted, while advancements in materials and design boosted their ability to convert sunlight into electricity. Understanding these changes is crucial for anyone interested in renewable energy, from homeowners considering installation to policymakers shaping energy strategies. Let's explore how these developments are powering a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Solar Panel Efficiency over Time
The evolution of solar panel efficiency over time is a testament to human innovation and technological progress. Since their inception in the 1950s, photovoltaic efficiency over time has shown remarkable improvement, transforming solar energy from a niche technology to a mainstream power source.
In the early days, solar efficiency over time was relatively low, with panels converting only about 6% of sunlight into electricity. However, continuous research and development led to steady advancements. By the 1990s, commercial panels reached efficiencies of 14-15%, making solar energy more viable for widespread use.
The 21st century has seen exponential growth in solar panel efficiency. Current solar panel efficiency for commercially available models typically ranges from 15% to 22%. High-end panels can even reach efficiencies of 22-23%, a significant leap from earlier generations.
Several factors have contributed to this improvement in solar efficiency over time:
- Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques
- Multi-junction cells capturing more of the light spectrum
- Innovations like perovskite technology showing rapid efficiency gains
Is Solar Panel Efficiency Important
Solar panel efficiency is a critical factor in the effectiveness and adoption of solar energy technology. Higher efficiency in photovoltaic systems leads to increased energy output from the same amount of sunlight, which has significant implications. Improved efficiency allows for better space utilization, making solar viable in areas with limited installation space. It also enhances cost-effectiveness, as fewer panels are needed to meet energy requirements, reducing installation and maintenance costs. Environmentally, higher efficiency means less raw material use and a lower carbon footprint. More efficient panels contribute to grid stability by providing more consistent and reliable energy output. As solar panel efficiency over time continues to improve, these benefits become more pronounced, driving further adoption and technological advancement in the renewable energy sector.
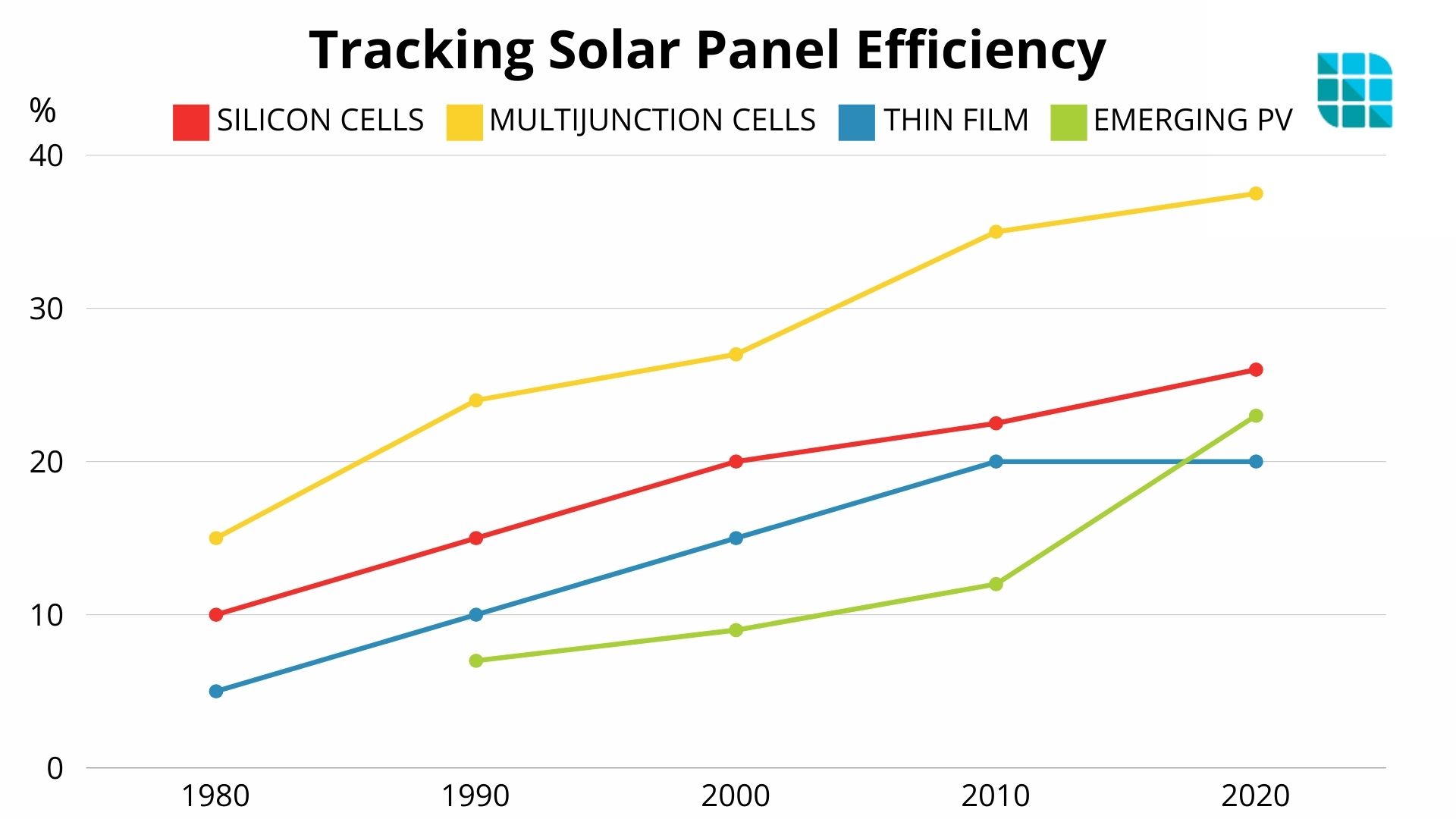
Tracking Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency has dramatically improved since the technology's inception, driving widespread adoption of photovoltaic systems. This timeline highlights key milestones in solar efficiency over time, showcasing the evolution from early innovations to current solar panel efficiency standards.
1954: First practical silicon solar cell invented, with about 6% efficiency
1960s: Space applications push efficiency to 14%
1970s: Terrestrial solar cells reach 13-15% efficiency
1985: Silicon cells achieve 20% efficiency in the laboratory
1990s: Commercial panels typically offer 14-15% efficiency
1999: Spectrolab achieves 32.3% efficiency with a multi-junction solar cell
2006: University of Delaware creates a 42.8% efficient multi-junction cell
2010: Commercial panels commonly reach 15-17% efficiency
2015: SunPower announces a 22.8% efficient commercial panel
2019: Scientists at NREL develop a six-junction solar cell with 47.1% efficiency
2021: Oxford PV achieves 29.52% efficiency with perovskite-silicon tandem cell
2024: Top commercial panels offer 22-23% efficiency, with some reaching 24%
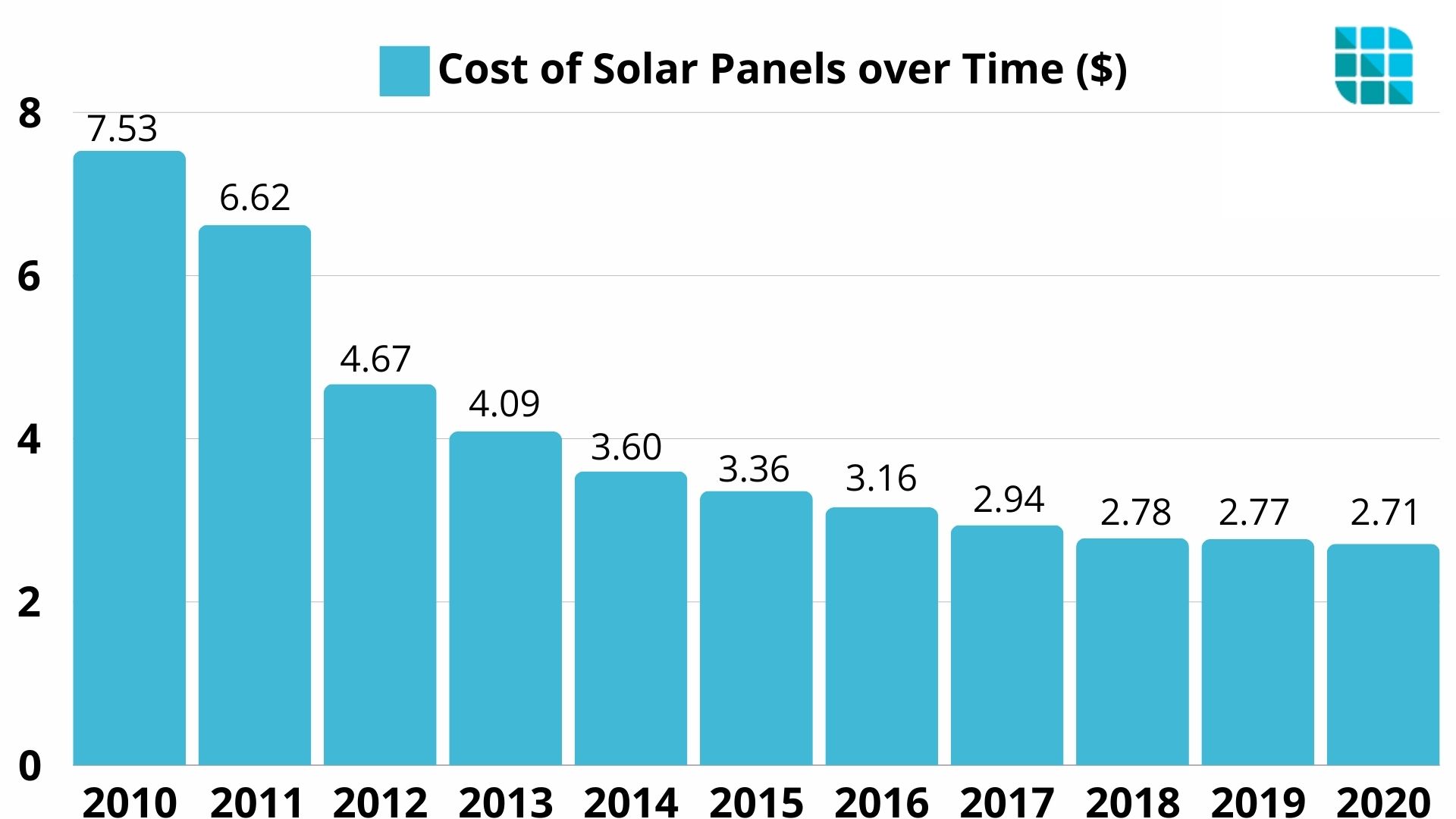
Cost of Solar Panels over Time
The cost of solar panels has dramatically decreased over the past few decades, making solar energy more accessible. In the early 1970s, solar panels cost around $100 per watt, restricting their use to specialized applications. By the 2000s, advancements in technology and manufacturing reduced prices to about $10 per watt.
A key principle in this decline is Swanson's Law, which states that the price of solar photovoltaic modules drops by approximately 20% for every doubling of cumulative shipped volume. This principle has consistently driven down costs over the years.
As of 2024, the average cost per watt for solar panels was between $2.41 and $3.66, making solar energy more affordable than ever. This decrease is attributed to innovations in solar technology, economies of scale, and growing global demand for renewable energy.
Looking ahead, the cost of solar panels is expected to continue falling. The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that by 2030, solar energy could become one of the cheapest sources of electricity worldwide. The ongoing reduction in solar panel costs underscores the transformative potential of solar energy, making it an increasingly viable option for homeowners and businesses.
Will the Cost of Solar Continue to Decline
Yes, the price of solar power will continue to drop. The cost of solar panels has significantly decreased over the past decade, making solar energy more accessible than ever. Advances in technology, increased manufacturing efficiency, and government incentives have all contributed to this decline. As solar panel technology continues to evolve, we can expect the cost of solar panels to keep dropping. Innovations like more efficient photovoltaic cells and streamlined production processes will drive prices down further. Additionally, as demand for renewable energy sources rises, economies of scale will likely continue to reduce costs. The combination of these factors suggests that the cost of solar panels will continue to decline, making solar energy a more viable and attractive option for households and businesses. Investing in solar panels now can lead to long-term savings and environmental benefits, as the trend towards cheaper and more efficient solar energy solutions shows no signs of slowing down.
Frequently Asked Questions About Solar Panel Efficiency
1. How are solar panels used today?
Solar panels today primarily generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial use. They're installed on rooftops or in open areas to convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells. This energy powers homes, businesses, and can be fed back into the grid. Solar panels also support off-grid applications, providing electricity in remote areas or during emergencies.
2. How was solar energy used in the past?
Historically, solar energy heated water or air for industrial and residential needs. Ancient civilizations used magnifying glasses to start fires. In the 19th century, solar thermal systems heated water and air. Advances in the mid-20th century enabled direct conversion of sunlight into electricity, gradually shifting solar energy from heating to electricity generation.
3. How has solar energy changed over time?
Solar energy has evolved with technology, efficiency gains, and environmental awareness. In the mid-20th century, photovoltaic technology enabled direct electricity conversion. Advances since then have reduced costs, expanded installations globally, and driven innovation. Supportive policies and environmental concerns have accelerated adoption, making solar energy a mainstream electricity source today.
4. When did solar panels become popular?
Solar panels gained popularity in the late 20th century due to technological advancements and energy crises. The 1970s oil crises spurred interest in alternative energy sources like solar power. By the early 2000s, declining costs, environmental awareness, and government incentives led to widespread adoption. Today, solar panels are ubiquitous, with global installations growing steadily as a clean energy solution.
Conclusion
By 2024, solar panel costs have decreased significantly, with prices averaging around $3 per watt for residential installations. This decline reflects ongoing advancements in technology and economies of scale. Concurrently, solar panel efficiency rates have improved to approximately 20% to 22%, maximizing energy production per panel. Tools such as the Solar Calculator enable consumers to make informed decisions about installation costs and potential savings. Renogy, known for its reliability and innovation, remains a recommended choice for those seeking efficient and cost-effective solar solutions. Investing in solar panels now promises substantial long-term benefits in savings and sustainability.