How Efficient Are Solar Panels [2024 Guide]
As solar energy gains prominence in our pursuit of sustainable power sources, understanding solar panel efficiency becomes crucial. This article aims to uncover solar panel efficiency, exploring its significance and impact on solar energy adoption. Whether you're considering solar power for your home or simply curious about the technology, grasping these concepts will provide valuable insights into the world of solar energy.
Solar Panels Efficiency Explained
Solar panel efficiency is a crucial metric in the world of photovoltaic technology, measuring how effectively a solar panel converts sunlight into usable electricity. Typically expressed as a percentage, it represents the portion of solar energy that a panel can transform into electrical power under standard test conditions. Modern residential solar panels generally achieve efficiencies between 15% and 22%, with high-end models pushing towards 25%.
However, it's important to note that even panels with seemingly modest efficiency ratings can produce significant amounts of power over their operational lifetime, typically 25-30 years, making solar energy an increasingly viable and sustainable power source for a wide range of applications.
How Efficient Are Solar Panels
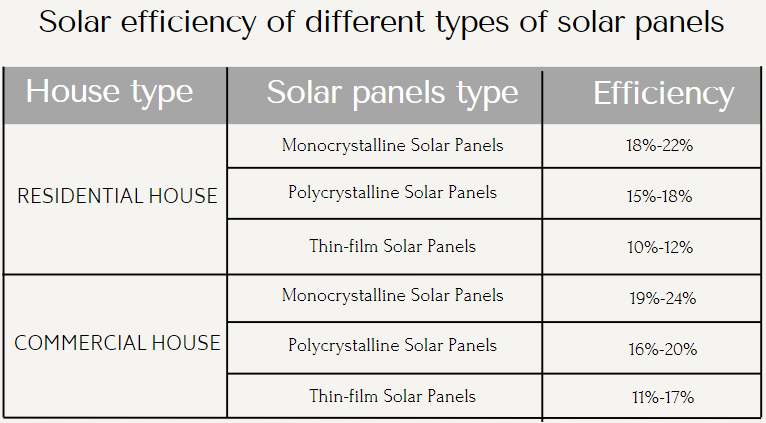
Solar panel efficiency, a key measure of solar power efficiency, has seen significant improvements over the years. Current commercial panels typically achieve solar energy efficiency rates ranging from 15% to 22%. High-end monocrystalline silicon panels can reach efficiencies of up to 22-23%. Polycrystalline panels usually fall between 15-17% efficiency, while thin-film technologies generally range from 10-13%. However, laboratory prototypes have demonstrated much higher solar energy efficiency, with multi-junction cells reaching over 45% under concentrated sunlight. It's important to note that these lab results don't translate directly to real-world solar power efficiency.
Factors Affecting Solar Power Efficiency
Numerous factors influence solar panel efficiency.These include irradiance, temperature, location, shading, tilt and others. All are important considerations when planning your solar project for on grid or off-grid solar .
Irradiance
Irradiance refers to the amount of solar energy that hits a square meter of a surface per second. Irradiance is measured using standard testing conditions and doesn’t consider any other factors that may affect efficiency.
Mohamed Amer Chaaban from Penn State University is an expert in the relationship between irradiance and power output in photovoltaic modules. The diagram below demonstrates shows how solar panels operating under irradiance of 1250W/m2 have a better power outcome than those under 750W/m2.

(Pic 5. The power output delivered by PV modules under different irradiance conditions. The higher the irradiance is, the more power a solar panel can generate. Data from e-education
Climate
Weather conditions play a significant role in performance and efficiency of solar panels. Lower temperatures tend to help your system deliver more voltage at high efficiency. However, if your system is in an area with lots of cloudy days you’ll produce less power, and snow accumulation on the panels will reduce power output as well.
It may seem counterintuitive, but high temperatures can also reduce solar efficiency. As temperatures climb, the voltage and the power output of solar panels decrease. When the temperature is above 77°F or 25°C, solar panels generate less power because of reduced efficiency. Solar panels are tested using standard temperature conditions of a constant 77°F or 25°C. Look for the “temperature coefficient”, on a panel’s spec sheet. It will tell you how much power a solar panel loses once the temperature goes over 77°F.
Shading
When planning your system, make sure your PV modules can operate free from shadows cast by trees or nearby buildings. Shade can prevent solar panels from absorbing enough light to complete power conversion even in peak daylight hours.
Hot spots, caused by partial shading, can greatly reduce the performance of PV modules. The hot spot effect is one of the most common reasons that solar panels fail. Partially shaded cells don’t produce energy, while other cells operate as usual to produce current. As a result, the current generated by non-shaded cells doesn’t pass through shaded cells and can lead to concentrated heat. Overheating can eventually develop into a hot spot and damage adjacent cells or even the whole module.
Bypass diode and half-cut cells deal with the effects of shading differently. The diagram below shows a full cell module (left) and half-cut cell module (both 6 strings). Each is shaded on half the module. For the module on the left, the bypass diode is at the top of the panel, and all 6 strings of cells stop working because the current is unable to pass through the shaded area.
However, the module on the right uses half-cut cell technology and can mitigate the effect of shading. The half-cut cell panel is split in half and consists of 6 groups of cell strings with the bypass diode in the middle. Half the solar panel is shaded and has stopped working. The other 3 cell strings still produce 50 percent more power than the traditional module on the left. The cells that are working are also distributing excessive heat to reduce the risk of hot spots.

(Pic 6. Bypass diodes are configured at different locations on solar panels: one at the top of the panel while the other is in the middle.)
Orientation & tilt of solar panels
The way solar panels are positioned on your rooftop can significantly impact their efficiency. This is referred to as orientation, meaning the compass direction your panels face most of the time. In the northern hemisphere, we advise you to orient your solar panels to the south or west to get the most sun exposure.
However, getting the right orientation for your solar panels is only one part of maximizing performance. Tilt plays an important role as well. If possible, always tilt panels at an angle toward the sun rather than lying flat. Solar panels should be mounted with a minimum 20 degree tilt toward the sun when possible. For example, the ground mounted solar panels are always positioned with tilt brackets.
How To Maximize Solar Panel Efficiency
There are several ways to maximize the efficiency of your solar panels. While some factors are hard to change, others can be controlled such as installation angle, shading and dust to maximize solar panel efficiency.
Optimize angle and orientation
In the Northern Hemisphere, panels should generally face true south and be tilted at an angle equal to your latitude. This maximizes sunlight exposure throughout the year. Consider adjustable mounts to optimize angle seasonally.
Avoid shading
Trim trees, relocate panels if possible, or use micro inverters or power optimizers to mitigate the effects of partial shading.
Cleaniness
Clean panels with water and a soft brush or sponge, or hire professional cleaning services for larger installations.
How Solar Panel Efficiency is Calculated
You may be wondering how efficiency is calculated and how solar companies use them as a selling point. Below is a step-by-step demonstration of how to calculate the efficiency of a solar panel.
Step 1: Determine the module’s maximum power output under optimal conditions
To get the maximum power output of a solar panel (Pmax), we use the maximum power output of a module before the encasing process. After encasing solar cells in glass, the extra layer reduces sunlight absorption, leading to a lower efficiency rating. This figure should be in Watts (W). In the case of our 100W monocrystalline solar panel (compact design), the maximum power output of the module before encasing is 108W after testing in the lab.
To get the maximum power output of a solar cell, divide maximum power output by the number of the solar cells in the module. In this case, the maximum power output a solar cell can deliver is:
108W/36 (pcs)=3W/cell
Step 2: Find the dimensions of the solar cell
You can find the dimensions of a module in its the specifications. The size information is either in millimeters (mm) or inches (in). You’ll need to convert these figures into meters (m) for other calculations.
The dimensions of this 100W solar panel are: 41.8 x 20.9 x 1.4 in / 1.06 x 0.53 x 0.035 m
The dimensions of its solar cells are: 6.5 x 3.3 in / 0.1651 x 0.08382 m
Step 3: Determine the module’s maximum absorbed power at standard testing conditions (STC)
First let’s look at the definition of standard testing conditions for the factors considered in panel efficiency.
- Irradiance 1000W/m2: This means 1000W of solar energy is absorbed by a square meter on a module at a given time.
- Temperature 25°C: Solar cells are tested at 25°C. Note that this does not refer to the ambient temperature.
- Air Mass 1.5: This metric is related to the angle the sunlight hits a given spot on the earth. The smaller the number, the smaller the distance sunlight needs to travel to reach the earth’s surface.
To get the maximum absorbed power at standard testing conditions, multiply the irradiance 1000W/m2 and the solar panel/solar cell area. In this case, the calculation is:
1000W/m2 x (1.06 x 0.53 m)=561.8W
1000W/m2 x (0.1651 x 0.08382 m)=13.8W
Step 4: Calculate cell efficiency
The final step is to divide the total power output by the absorbed energy of the panel/solar cell.
The module efficiency of this 100W solar panel:
100W/1000W/m2 x (1.06 x 0.53 m) ≈ 18%
The solar cell efficiency of this 100W solar panel:
3W/1000W/m2 x (0.1651 x 0.08382 m) ≈ 22%
If you are tired of these tedious calculations, you can use the renogy solar efficiency calculator to help.

The Efficiency of Solar Panels Under Extreme Weather
High temperature & low temperature
High temperature will increase the resistance in the panel circuit, and the efficiency of the solar panel will decrease. In a low temperature environment, thick snow is easy to accumulate on the solar panel. When the thickness of the snow on the solar panel exceeds 5cm, the solar cell will stop working. So the solar panel needs to be maintained regularly on snowy days to ensure that it works at normal efficiency.
Hail
Although solar panels are strong and durable, severe hail may still damage the solar panel, reduce its efficiency or even make it unusable.
Strong wind
Solar panels are easily affected by strong winds. As the wind speed increases, the efficiency of solar panels will decrease.
Ice
The surface of solar panels without silicon coating is prone to ice. The ice surface will reflect sunlight, and the efficiency of solar panels absorbing sunlight will be greatly reduced.

What Are the Most Efficient Solar Panels in 2024
Although not everyone needs to buy high-efficiency solar panels for their roofs, for financial reasons. But a solar panel that is efficient but not expensive is likely to be what everyone needs. Renogy provides most efficient solar panels, including monocrystalline solar panels and bifacial solar panels of various wattages. The solar power efficiency can be up to 30%, and buying Renogy solar panels can also obtain a 30% residential clean energy credit.
The Future of Solar Panel Efficiency
The first selenium solar cell developed in 1883 by American inventor Charles Fritts, had an efficiency of just 1 percent. Today you can find a wide variety of solar panels with efficiencies ranging between 15 and 22 percent. The efficiency of current solar panels has increased significantly in recent years with advances in materials and technology, and the efficiency percentage of the most efficient solar panels can achieve about 22.8 percent. how efficient will solar power be in the future? we have no exact number but one thing is sure: plenty of solar technology advancements are coming soon.
FAQ
Can solar panels be 100% efficient?
No, There is no solar panels reach 100% solar efficiecy far from now. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory tracks the highest efficiencies achieved in standardized lab conditions in 2022. The highest-ever solar cell efficiency was 47.6%.
Is solar panel efficiency important?
Yes. The efficiency of solar panels is important. Under the same conditions, choosing high-efficiency solar panels can reduce energy loss, generate more electricity in the same time, and improve your economic benefits. But if you are short of money or your house has a large roof area, the efficiency of solar panels is not your priority.
Are more efficient solar panels more expensive?
In general, yes. higher-performance panels are typically more expensive.

![How Efficient Are Solar Panels [2024 Guide] How Efficient Are Solar Panels [2024 Guide]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-fhnch/images/stencil/1280w/uploaded_images/cover-how-efficient-are-solar-panels.jpg?t=1662373565)









