Floating Solar Panels: All You Need to Know
How did it come to this that we are now fixing photovoltaic cells on floating structures that are anchored on the water bodies of lakes, ponds, or reservoirs? In the present world where there is a shift towards the use of renewable energy sources, floating solar panels provides a perfect opportunity of utilizing the water surfaces to produce clean electricity in a most efficient manner. The advantages of floating solar panels over the ground-mounted systems include; higher power production, cheaper to install and lower evaporation rates.
What is a Floating Solar Panel?
The floating solar panel means a solar photovoltaic facility which is installed on a structure that is floated on water. It consists of several components:
- Hall cells that capture the sun’s rays and convert them into electricity.
- The peripheral components are the floating structures which are manufactured from HDPE and plastics that offer buoyancy to the system.
- Mooring systems such as anchors and chains to keep the floating system in place.
- Subsea cables to transmit the generated electricity to shore.
- Inverters, junction boxes and other electrical parts.
The floating structures are designed to withstand water currents, winds, and corrosive effects of water. The panels are mounted on these structures using suitable inclination to maximize solar capture throughout the day.
Compared to ground-mount and rooftop solar systems, floating solar panels offer the unique ability to generate electricity from unused water surfaces such as hydroelectric dams, lakes, ponds and reservoirs.
Floating Solar System: Components
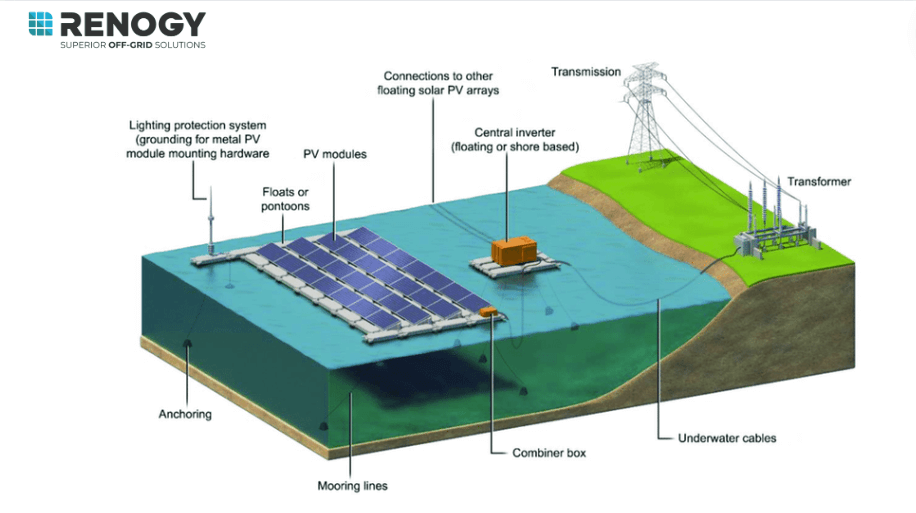
A complete floating solar system consists of the following key components.
Floating Platform
This provides the buoyant base on which solar panels are mounted. Common materials used are HDPE, polyethylene, polypropylene etc. Advanced floating structures come with tilt angle adjustment design for better orientation.
Mooring System
This secures the floating system to the water bed. Nylon ropes, steel chains, anchors and pickets are used for the mooring. Proper mooring ensures the floating solar array remains stable in all weather conditions.
Solar Panels
The main power generation element is photovoltaic panels that directly convert sunlight into DC electricity. Waterproof panels with anti-corrosive glass are preferred.
Mounting Structure
Aluminum and galvanized steel mounting structures securely hold the solar panels in place over the floating platform. They are designed for minimum wind and wave impact.
Inverters
Convert the DC power produced by solar panels into alternating AC current that can be fed into the grid. Floating solar requires marine grade inverters due to the humid environment.
Cables
Cables run along the underside of the floating structure to connect the solar panels and transmit electricity to shore via seabed transmission lines. Submersible cables with polyethylene insulation work best.
Monitoring Systems
Sensors, meters and other monitoring systems allow remote monitoring of the floating solar power plant's performance and output. They enable predictive maintenance.
Anchoring and Mooring Systems
Strong anchors, mooring cables, chains and pickets fixed to the waterbed keep the floating solar array in position. The system can swing freely based on water currents while remaining anchored. Proper design and setup of these components is crucial for a floating solar system to withstand the challenging marine environment and generate maximum clean energy.
How Floating Solar Panels Work?
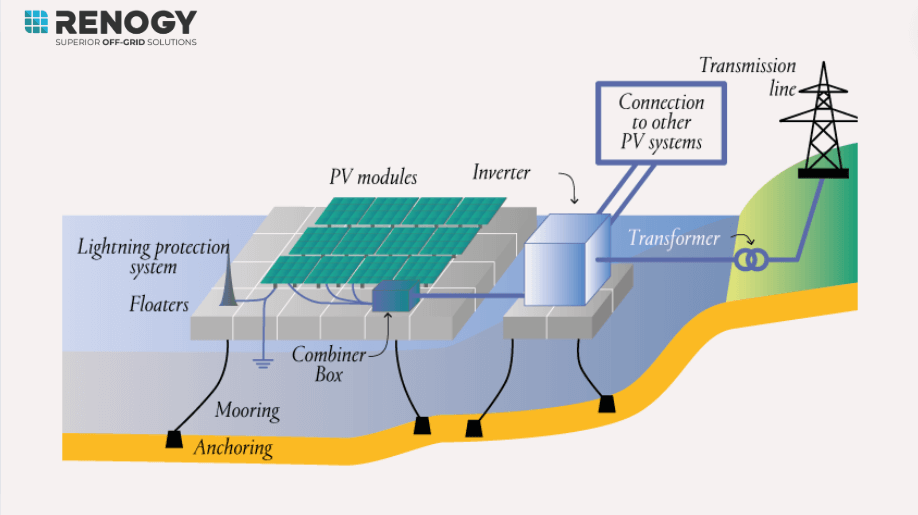
Actually, floating solar panels are similar to the usual solar panels in that they operate under the conversion of light into electricity. Here are the steps:
- Light from the sun illuminates the photovoltaic solar panels placed on the floating structures.
- Solar cells located within the panels absorb the light and then enable the freeing of electrons. This produce Direct Current (DC) electricity.
- The DC current is conveyed through cables to junction boxes and inverters.
- Inverters convert the DC into Alternating Current (AC) which is compatible with grid supply systems and home appliances.
- The AC power is transmitted via seabed cables to reach land.
- Finally, the electricity is fed into the grid or supplied for local use.
So in a nutshell, floating solar panels produce clean renewable electricity just like conventional panels but have the advantage of leveraging large unused water surfaces available for solar installations. This allows scaling up solar power generation, especially in space-constrained geographies.
How Much Do Floating Solar Panels Cost?
The installation of floating solar panels is slightly expensive as compared to the ground-mounted installations and it costs about 10-20% higher. However, because of the higher efficiency of the generation and lower operations and maintenance costs, floating solar can offer a very low levelized cost of electricity over the system’s lifetime. Here is a breakdown of the key costs involved:
Capital Cost
This covers the upfront investment for procurement and installation of the system. The capital cost ranges between $0.25 to $0.30 per watt for floating solar compared to $0.15 to $0.25 for fixed-tilt ground mount systems. Location, scale, type of water body and other factors impact the project cost.
Operations and Maintenance
Annual O&M costs for floating solar power plants are estimated to be 2-5% of capital costs. This is lower than ground mount systems as the water environment reduces soiling and allows natural cooling of panels. Costs involve periodic cleaning, component replacement, insurance etc.
Decommissioning
At the end of life, floating solar systems have to be removed from water. This decommissioning cost can be $20,000 to $50,000 for a 1MW floating solar power plant. Proper recycling helps recover some value from the dismantled components.
While the upfront investment is still higher for floating solar versus conventional ground or rooftop systems, the levelized cost becomes very competitive due to better solar yield, lower O&M costs and dual land-water use. The technology is expected to achieve parity with ground-mount systems in the near future as deployment scales up globally.
Pros and Cons of Floating Solar Panels
Pros
- Higher efficiency - Cooling effect of water increases solar panel efficiency by 5-10%. Annual energy yield per MW is up to 20% more than ground mount systems.
- Better use of space - Leverages unused water surface available for solar plants, especially in land-scarce regions. No deforestation required.
- Lower evaporation - Shading effect of panels reduces water evaporation from reservoirs and dams. This preserves water.
- Low maintenance - Natural cleaning from rain and water reduces operations and maintenance costs. Easy panel washing.
- Dual usage of infrastructure - Floating solar complements hydroelectric dams by using existing transmission infrastructure.
Cons
- Higher capital cost - Floating solar systems are still 10-20% more expensive than conventional ground mount setups.
- Special components needed - Requires specialized marine-grade panels, floaters, cables etc. which increase costs.
- Vulnerable to storms - Storms and high waves can cause structural damage. However, proper anchoring minimizes this risk.
- Aquatic ecosystem impact - Can negatively impact water quality and affect marine ecology if not managed properly. Strict environmental studies are required.
- Limited applications - Suitable only for calm water bodies like lakes, ponds, reservoirs. Not practical for oceans.
While the higher initial investment is a drawback, the advantages of greater efficiency, lower maintenance, and water conservation make floating solar an economical renewable energy solution in the long term. Proper impact assessments and ecological studies can help mitigate the risks.
How Efficient are Floating Solar Panels?
Floating solar panels have higher efficiency than conventional ground-mounted panels due to two key factors.
1. Cooling effect of water
The water body underneath the floating panels acts as a natural heat sink maintaining a cool temperature. This lowers the rate of efficiency loss caused by solar cell heating. Studies show that a 5°C reduction in temperature can increase solar cell efficiency by 3-4%.
2. Cleaner panels
Rain and the occasional wash by waves keep the panel surface clean. This maintains their ability to absorb sunlight without any soiling losses. Annual generation per watt is 5-10% more compared to fixed-tilt ground solar systems.
According to various field studies, the annual solar power generation per MW of installed capacity for floating solar arrays is up to 20% more than equivalent ground-based systems. For example, a 2016 study by the National University of Singapore found a 10.6% higher yield for floating solar compared to a rooftop system. The cool ambient temperature enabled 8.3% more yield while rain-washing offered a further 2.3% boost.
With a capacity utilization factor of around 20%, 1 MW of installed floating solar capacity can deliver 1,700 - 1,900 MWh of clean electricity annually. This performance advantage makes floating solar an attractive option for meeting renewable energy targets.
Where Are Floating Solar Panels Used Today?
While floating solar is still an emerging technology, rapid adoption is underway in Asia, Europe and America. Here are some major projects and deployments:
- China - Has over 50% of the world's floating solar capacity. The 150 MW Floating Solar Power Plant in Anhui province is currently the largest operational floating PV plant globally.
- India - Has installed over 600 MW of floating solar, including a 100 MW plant at Ramagundam Dam.
- South Korea - Major projects include a 1.2 MW floating solar farm on a reservoir in Gimhae and a 45 MW installation on Saemangeum tidal flats.
- Singapore - Home to one of the early floating solar test-beds within Tengeh Reservoir since 2016. Currently has over 60 MW installed.
- Thailand - Hosts Southeast Asia's largest floating solar farm spanning 45 hectares in Sirindhorn Dam. The 45 MW capacity powers over 15,000 households.
- UK - Europe's largest floating solar system on Queen Elizabeth II Reservoir has a capacity of 6.3 MW and powers over 1,800 homes.
- USA - States like California, Colorado and Florida have pilot floating solar projects ranging from hundreds of kW to over 1 MW capacity.
Floating Solar Panels vs Traditional Solar Panels
Here is a comparison between floating solar panels and conventional ground-mounted systems.
| Parameter | Floating Solar Panels | Ground-mount Solar Panels |
| Solar yield per MW | Up to 20% more | Comparatively lower |
| Land usage | Do not occupy any land | Require large land areas |
| Location options | Lakes, reservoirs, dams | Need open flat terrain |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher due to dust/soiling |
| Installation | More complex | Simpler process |
| Cost | 10-20% higher capital cost, Lower O&M | Lower initial investment |
| Aesthetics | More visually appealing | Can be an eyesore on landscape |
| Water conservation | Reduce evaporation from water body | No impact on water |
| Environmental impact | Minimal as no deforestation. Need aquatic studies | Risk of habitat destruction |
In summary, floating solar panels deliver higher efficiency and solar generation from the same installed capacity. By leveraging water surfaces unused for any economic activity, they allow expanding solar power capacity even in densely populated regions with land constraints. The tradeoff is the higher capital cost, which is expected to even out over time. Proper impact assessments can mitigate adverse aquatic effects.
Conclusion
Floating solar PV systems are a novel way of dealing with land limitations and increasing solar energy production through utilizing the vast untapped water resources which otherwise would have been used for renewable generation.
Considering their exceptional attributes such as better efficiency, reduced maintenance costs and water conservation, floating solar farms are likely to experience a steep growth curve in countries that have scarcity of land resources. In the event that ecological consequences are closely monitored and assessed, floating solar may be able to support further development of renewable energy for a brighter future.
FAQ
Are floating solar panels better than regular solar panels?
Floating solar panels have some advantages compared to regular ground-mounted solar panels, but also some limitations. Main advantage of floating panels is they don't take up valuable land space. However, durability may be lower than ground-based systems.
Can floating solar panels withstand storms and waves?
Floating solar systems are designed and secured to withstand effects of winds and water currents. Proper mooring mechanisms keep the arrays anchored securely even during storms. Regular maintenance ensures their stability.
Are there any environmental risks with floating solar panels?
There can be some ecological impacts if not implemented properly, such as effects on water temperature and quality. Proper environmental studies must be conducted and aquatic life preserved through good system design and monitoring.











