Bifacial Solar Panels: Everything You Need to Know
The concept of bifacial solar panels might seem cutting-edge, but its roots stretch back further than you might imagine. Born from a flash of inspiration in the 1960s, this innovative idea remained largely dormant for decades. It wasn't until the early 2000s that bifacial technology began to emerge from the shadows of solar innovation. Unlike traditional solar panels, these innovative devices capture sunlight from both sides, significantly increasing energy yield. By harnessing reflected light from surrounding surfaces, bifacial panels can boost energy production by up to 30% compared to their monofacial counterparts. As the world seeks sustainable energy solutions, bifacial solar panels emerge as a promising option, combining increased efficiency with reduced installation costs.
What Is a Bifacial Solar Panel
As the name implies, a bifacial solar panel is a module that has photovoltaic cells on both the front and back sides, designed to capture sunlight from both sides of the panel. Unlike traditional solar panels that only collect light from the front, bifacial panels harness energy from both their front and back surfaces.
These innovative panels typically feature a transparent backing, allowing them to absorb direct sunlight from the front and reflected light from the ground or nearby surfaces on the rear. This dual-sided approach significantly boosts their energy-generating potential.
Key features of bifacial solar panels include:
- Double-sided light absorption
- Increased energy yield (up to 30% more than traditional panels)
- Improved performance in low-light conditions
- Versatility in various installation settings
Bifacial panels are particularly effective in environments with highly reflective surfaces, such as snow, sand, or light-colored roofs. They can be installed vertically, horizontally, or at an angle, making them adaptable to diverse architectural designs and geographical locations.
As the solar industry continues to advance, bifacial panels represent a promising solution for maximizing energy production in both residential and commercial applications. Their ability to generate more power in the same footprint as traditional panels makes them an attractive option for those looking to optimize their solar energy systems.
How Do Bifacial Solar Panels Work
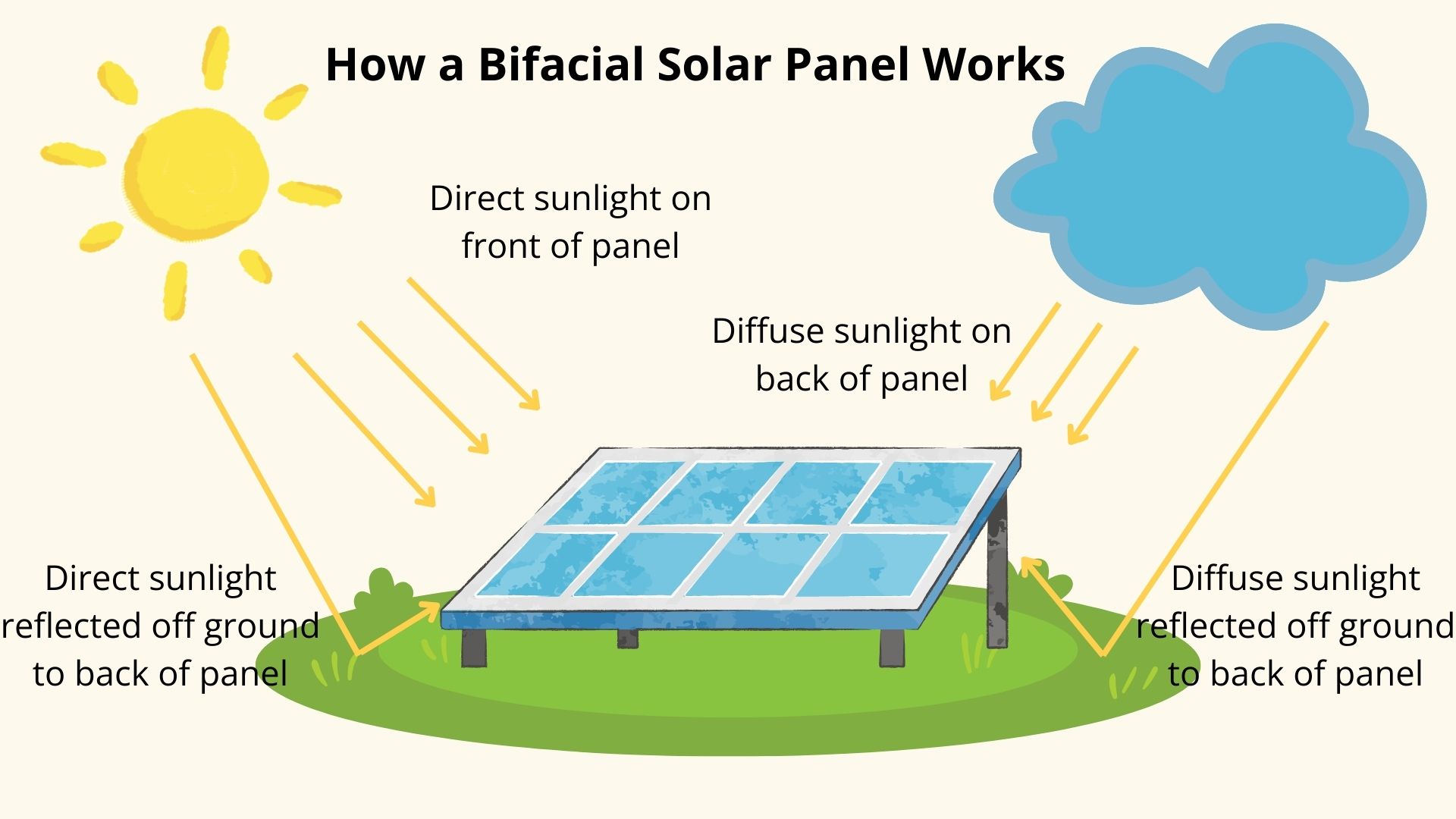
Bifacial solar panels work by harnessing sunlight from both their front and rear surfaces, maximizing energy capture. The front side operates like a traditional solar panel, converting direct sunlight into electricity. The innovation lies in the panel's rear side, which is designed to absorb reflected and diffused light from the surrounding environment. This is made possible by a transparent or translucent back sheet, allowing light to penetrate both sides of the panel. The specialized photovoltaic cells within are optimized to convert light from any direction into usable energy. The effectiveness of the rear side, known as the bifaciality factor, typically ranges from 65% to 90% of the front side's capacity. Mounting considerations play a crucial role, with elevated installations or reflective surfaces underneath enhancing rear-side production. This dual-sided approach allows bifacial panels to generate more electricity in various lighting conditions, making them particularly effective in environments with high albedo or diffused light.
Bifacial Solar Panels Advantages and Disadvantages
Due to their price and efficiency, bicluster solar panels are growing in popularity. Bifacial panels are becoming more popular than monofacial panels, therefore more residences and businesses are installing them to take advantage of the benefits. But do the benefits really exceed the drawbacks?

Pros of Bifacial Solar Panels
- Increased Energy Production: Bifacial panels yield 5-30% more power than traditional panels. This boost comes from their ability to capture light from both sides, significantly increasing energy output.
- Better Low-Light Performance: These panels excel in capturing diffused and reflected light. This feature extends their daily operational hours and improves performance in less sunny conditions.
- Durability: Most bifacial panels feature a double-glass construction, enhancing their resilience. This robust design typically results in longer warranties and an extended operational lifespan.
- Versatility: Bifacial panels are suitable for various installation types, including ground, rooftop, and carports. Their flexibility allows for creative deployment in diverse settings.
- Potential for Lower LCOE: Higher energy yield can lead to better long-term economics. Over time, the increased production often offsets the higher initial investment.
- Reduced PID: The glass-on-glass design of bifacial panels helps minimize potential induced degradation. This results in more stable performance over the panel's lifetime.
Cons of Bifacial Solar Panels
- Higher Initial Cost: Bifacial solar panels generally come with a higher price tag than conventional models. This increased upfront investment can be a deterrent for some buyers, particularly in residential applications.
- Complex Installation Requirements: Maximizing benefits requires careful planning and potentially more sophisticated mounting systems. Installers need to consider factors like optimal tilt angle, elevation, and surrounding reflective surfaces.
Bifacial Vs. Monofacial Solar Panels
Monofacial solar panels, the traditional choice, feature photovoltaic cells on one side only. They capture direct sunlight from the front surface, with an opaque backing. These panels are less expensive and simpler to install, making them popular for residential rooftop applications.
Bifacial solar panels, in contrast, absorb light from both sides. This dual-sided design captures direct sunlight from the front and reflected or diffused light from the rear. While more expensive, bifacial panels can produce up to 30% more energy under optimal conditions.
The choice between the two depends on the installation environment. Bifacial panels excel in areas with reflective surfaces or elevated installations, while monofacial panels suit standard rooftop setups. Bifacial panels offer higher energy yields per square foot, ideal for maximizing output in limited spaces, but at a higher initial cost.
Are Bifacial Solar Panels Worth It
Determining whether bifacial solar panels are worth the investment depends on several factors. These innovative panels offer the potential for increased energy production, but their value proposition varies based on specific installation conditions and project goals.

For large-scale solar farms or commercial installations with ample space and reflective surfaces, bifacial panels often prove their worth. The additional energy yield, which can range from 5% to 30% more than traditional panels, can significantly offset the higher initial costs over time. This increased efficiency is particularly valuable in areas with high electricity rates or limited installation space.
Residential applications present a more nuanced scenario. While the energy boost is appealing, the higher upfront costs and potential installation complexities may extend the payback period. Homeowners should carefully consider their roof orientation, local climate, and surrounding reflective surfaces to assess the potential benefits.
How to Install Bifacial Solar Panels
Installing bifacial solar panels is a smart way to boost your energy efficiency. Here's a concise five-step guide to help you get started:
1. Site Assessment and Planning
Begin by evaluating your site to identify the optimal location for your bifacial solar panels. Choose areas with high reflectivity, such as snow-covered or sandy regions, to maximize the panels' efficiency. Ensure there are no obstructions like trees or buildings that might cast shadows on the panels. Additionally, check local regulations and obtain any necessary permits to comply with legal requirements.
2. Choose and Prepare the Mounting System
Select a mounting system that supports bifacial panels, such as ground mounts, rooftop mounts, or tracking systems. Prepare your installation site by clearing debris and leveling the ground if you’re using a ground mount. For rooftop installations, ensure the roof is structurally sound and can support the panels' weight. Assemble and install the mounting system according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring it is securely anchored.
3. Install the Bifacial Solar Panels
Carefully mount the bifacial solar panels onto the prepared system. Secure the panels using the provided clamps or brackets, ensuring there’s adequate space between the panels and the surface below to allow reflected light to reach the underside. Proper installation is crucial for both stability and efficiency.
4. Connect Electrical Components
Connect the solar panels to the inverter and integrate them into your home’s electrical system. Ensure all electrical connections are properly insulated and waterproofed to prevent any hazards. It’s highly recommended to hire a certified electrician for this step to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
5. Optimize and Monitor
Adjust the angle and orientation of the panels to maximize exposure to both direct and reflected sunlight. Tracking systems can be particularly beneficial for this purpose. After installation, test the system to ensure it’s functioning correctly and monitor its performance regularly. Clean the panels periodically to remove any dirt or debris and schedule maintenance checks to ensure long-term efficiency and durability.
Tips for Installing a Bifacial Solar System
- Don't Block the Back Sides of the Panels. Bifacial solar panels capture sunlight from both sides, boosting energy generation. Ensure that inverters or racking do not block the back of the panels. If racks are necessary, leave space to allow sunlight to reach the cells.
- Allow Space Between Panel Rows. Leave 3-5 inches between panel rows to let snow fall through in winter, preventing pile-up and aiding in melting, which produces heat for the panels.
- Maintain 42.5 Inches Between the Ground and the Panels. The IEEE recommends a 42.5-inch height from the ground to allow snow to accumulate without shading the panels and to ensure optimal performance.
- Use Reflective, Light-Colored Materials Under the Panels. For maximum power output, avoid dark and non-reflective surfaces under the panels. Use reflective, light-colored materials or white EPDM for rooftop installations.
Conclusion
Bifacial solar panels offer significant advantages in energy generation by capturing sunlight from both sides, making them a smart choice for maximizing efficiency. When installing these panels, ensure that the back side remains unobstructed, allow sufficient spacing between panel rows, and maintain an optimal height from the ground. Additionally, use reflective, light-colored materials underneath the panels to further enhance their performance.
For those seeking high-quality bifacial solar panels, the Renogy Bifacial 220 Watt 12 Volt Monocrystalline Solar Panel is an excellent option. With its advanced bifacial design, this panel can generate up to 285 Watts, significantly outperforming traditional mono-facial panels. Its ten bus bars ensure excellent performance even when partially shaded, and the PERC monocrystalline cells help reduce heat and increase voltage, optimizing overall efficiency.

Choose Renogy for reliable and high-performance bifacial solar panels that meet your energy needs while maximizing power output and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bifacial Solar Panels
1. How efficient are bifacial solar panels?
Bifacial solar panels can be up to 30% more efficient than traditional monofacial panels due to their ability to capture sunlight from both the front and back surfaces. This dual-sided light absorption significantly boosts their overall energy output.
2. Can you use bifacial solar panels on a roof?
Yes, bifacial solar panels can be installed on a roof. For optimal performance, use reflective, light-colored roofing materials to enhance the sunlight reaching the back side of the panels, maximizing their efficiency.
3. What is the average cost of bifacial solar panels?
The average cost of bifacial solar panels ranges from $0.50 to $0.70 per watt, translating to approximately $500 to $700 for a 1-kilowatt system. Prices vary based on brand, quality, and installation factors.











