On Grid Solar System: A Comprehensive Guide 101
In the face of climate change and rising energy costs, on-grid solar systems have emerged as a crucial component of the global transition to renewable energy. These systems play a vital role in reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, while offering significant economic benefits to users. The concept of solar power isn't new – photovoltaic cells were first developed in the 1950s. However, recent technological advancements and declining costs have propelled on-grid solar systems into the mainstream. Today, they represent a cornerstone of sustainable energy strategies for homes, businesses, and communities worldwide. As governments and individuals alike seek to address environmental concerns and energy security, on-grid solar systems offer a practical, efficient solution that balances modern energy needs with ecological responsibility.
What is On-Grid Solar System
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is a renewable energy setup that connects directly to the public electricity grid. This innovative system allows homes and businesses to generate their own clean electricity from solar panels while maintaining a link to the traditional power grid. On-grid systems typically consist of solar panels, an inverter, and a bi-directional meter, enabling users to power their properties with solar energy, feed excess electricity back to the grid, and draw from the grid when needed.
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Grid Connection
- Battery Storage
- Reliability and Power Supply
- Cost and Complexity
On-Grid: Connected to the public electricity network, allowing for two-way power flow.
Off-Grid: Completely independent of the grid, relying solely on solar energy and battery storage.
On-Grid: Generally doesn't require batteries, as the grid acts as a backup power source.
Off-Grid: Requires a battery bank to store excess energy for use during low sunlight periods.
On-Grid: Offers consistent power supply by drawing from the grid when solar production is insufficient.
Off-Grid: Depends entirely on solar production and battery capacity, which may limit power availability.
On-Grid: Usually more cost-effective and simpler to install due to fewer components.
Off-Grid: Higher initial costs and more complex setup due to the need for batteries and additional equipment.
Benefits of On Grid Solar
On-grid solar power systems offer numerous advantages for homeowners and businesses alike. Whether you're considering a grid tie solar kit or a full-scale on-grid solar installation, here are the key benefits that make this renewable energy solution increasingly popular:
1. Reduced Electricity Bills
One of the most immediate benefits of on-grid solar is the significant reduction in your electricity bills. By generating your own power, you'll draw less energy from the grid, leading to lower monthly costs. In many cases, the savings can offset the initial investment in your grid tie solar system over time.
2. Energy Independence
While still connected to the grid, on-grid solar power provides a degree of energy independence. You're less reliant on utility companies and less affected by rising energy prices. This control over your energy production can provide peace of mind and long-term financial stability.
3. Environmental Impact
By choosing on-grid solar, you're actively reducing your carbon footprint. Solar energy is clean, renewable, and produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. This makes it an excellent choice for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their ecological impact.
4. Low Maintenance
On-grid solar systems are known for their simplicity and reliability. Unlike off-grid systems, they don't require battery banks, which can be expensive and need regular maintenance. Most grid tie solar kits are designed for durability and can operate efficiently for decades with minimal upkeep.
5. Net Metering Benefits
Many areas offer net metering programs for on-grid solar power systems. This allows you to sell excess electricity back to the grid, potentially earning credits on your utility bill. It's an excellent way to maximize the value of your solar investment, especially during peak sunlight hours when you're likely producing more than you consume.
6. Increase in Property Value
Homes and businesses equipped with on-grid solar systems often see an increase in property value. As energy costs continue to rise, properties with their own power generation capabilities become increasingly attractive to potential buyers.
7. Scalability
On-grid solar systems are highly scalable. You can start with a small grid tie solar kit and expand your system over time as your energy needs grow or as you have the budget to invest in more panels. This flexibility makes solar accessible to a wide range of consumers and businesses.
8. Energy Security
While on-grid systems typically shut off during power outages for safety reasons, they still contribute to overall energy security. By reducing strain on the grid, especially during peak hours, on-grid solar helps to create a more stable and resilient energy infrastructure for everyone.
How Does On-Grid Solar System work
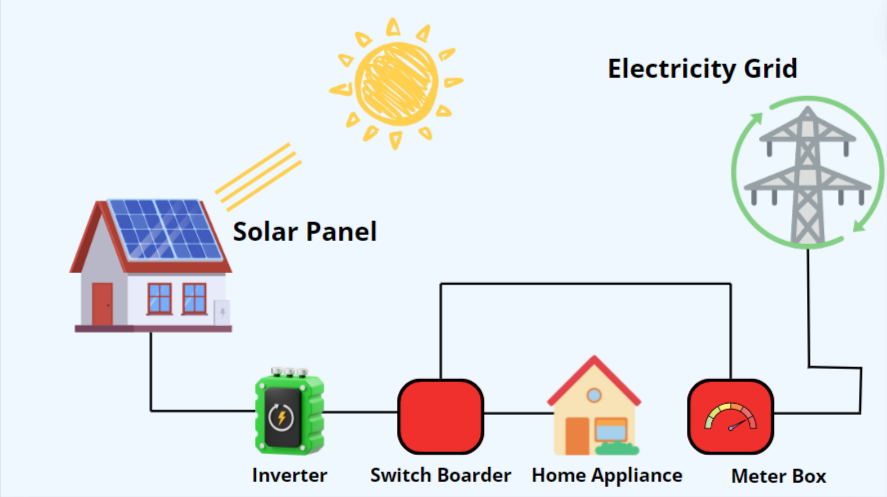
An on-grid solar system operates by integrating solar energy production with the public electricity grid. Solar panels on your property capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity flows to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity used in homes and businesses.
The solar-generated AC electricity powers your property, reducing reliance on grid electricity. When your system produces excess electricity, it flows back into the public grid. A bi-directional meter records this outflow, often earning you credits through net metering.
During low solar production periods, like nighttime or cloudy days, your property automatically draws electricity from the grid. This seamless transition ensures a constant power supply without the need for battery storage.
For safety, on-grid solar systems shut down during power outages to prevent feeding electricity into the grid. Many systems include monitoring tools, allowing you to track energy production and consumption, helping optimize usage.
In essence, an on-grid solar system works by harnessing solar energy, converting it for home use, sharing excess with the grid, and switching to grid power when needed. This integration offers a reliable, efficient, and eco-friendly energy solution.
On-Grid Solar System Installation

The components of an on-grid solar system, or grid-tied solar system, are essential for its efficient operation and integration with the electrical grid. This type of system allows for the seamless flow of electricity between the solar panels, your home or business, and the utility grid. Each component plays a crucial role, from generating electricity to managing power distribution and ensuring safety. Understanding these components is key for anyone considering an on-grid solar system. For reliable and efficient solutions, Renogy Solar Kits are highly recommended.
Components of an On-Grid Solar System
- Solar Panels: Photovoltaic modules that convert sunlight into electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC power from the solar panels into AC power for home use and grid export.
- Mounting Structure: Secures the solar panels to your roof or ground-mounted frame.
- Electrical Wiring: Connects the system components and your home to the grid.
- Bi-directional Meter: Measures electricity flowing to and from the grid.
- Monitoring System: Tracks the performance and output of your solar system.
On-Grid Solar System Installation Step-by-Step Guide
- Site Assessment and System Design: Evaluate your property's solar potential and design a system that meets your energy needs. This includes determining panel placement, system size, and equipment selection.
- Permitting and Approvals: Obtain necessary permits from local authorities and approval from your utility company for grid connection. Your installer typically handles this process.
- Equipment Installation: Mount the solar panels, install the inverter, and set up the electrical components. This step usually takes 1-3 days, depending on system size and complexity.
- Electrical Wiring and Grid Connection: Connect the solar panels to the inverter and your home's electrical panel. Install the bi-directional meter and establish the connection to the power grid.
- Inspection and System Activation: Have the system inspected by relevant authorities. Once approved, activate your on-grid solar system and set up the monitoring software to track its performance.
Conclusion
An on-grid solar system offers an efficient and cost-effective solution for harnessing solar energy. By integrating seamlessly with the existing power grid, it allows users to reduce electricity bills and contribute to environmental sustainability. With the ability to sell excess power back to the grid, homeowners and businesses can achieve financial benefits alongside energy independence. Moreover, the on-grid solar system requires lower initial investment compared to off-grid systems, making it an attractive option for many. As technology advances and government incentives increase, adopting an on-grid solar system becomes a practical and forward-thinking choice for those looking to embrace renewable energy solutions.
FAQs about On-Grid Solar System
1. Which is better, on-grid or off-grid solar?
The choice between on-grid and off-grid solar depends on your needs. On-grid systems are ideal for reducing electricity bills and selling excess power back to the grid. Off-grid systems are better for remote areas without grid access, providing complete energy independence. On-grid systems are generally more cost-effective and easier to maintain, while off-grid systems require batteries and more substantial investment.
2. What are the disadvantages of grid-tied solar systems?
Grid-tied solar systems depend on the power grid, so they don't provide electricity during outages unless paired with a battery backup. Additionally, their performance is affected by grid reliability and regulations. Initial setup costs can be high, and there might be lower returns in areas with less favorable net metering policies. They also lack the complete independence of off-grid systems.
3. What is the difference between grid-tied and hybrid systems?
Grid-tied systems are connected to the power grid and rely on it for consistent power, allowing users to sell excess energy back to the grid. Hybrid systems combine features of both on-grid and off-grid systems, using batteries to store energy for use during outages or peak times. This provides greater energy independence and reliability, albeit with higher initial costs due to the battery storage component.











