Lithium-Ion Battery Safety: Are Lithium Ion Batteries Safe?
Are lithium batteries safe? It's a question many of us have wondered about, especially after hearing stories of phones catching fire or laptops overheating. Let's face it - we rely on these little power packs every day, from our phones to our cars. But should we be worried?
The truth is, lithium batteries are generally safe, but like anything, they're not without risks. Most issues stem from manufacturing defects, damage, or extreme conditions. So while you don't need to panic, it's worth understanding how to treat these batteries right. After all, a little knowledge goes a long way in keeping your gadgets (and yourself) safe and sound.
What are lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries are rechargeable power sources that have revolutionized portable electronics and electric vehicles. These energy-dense devices use lithium ions to store and release electricity, offering longer life cycles and higher capacities than traditional battery types. Lithium batteries come in various forms, including lithium-ion and lithium-polymer, each with specific advantages. They power a wide range of products, from smartphones and laptops to electric cars and renewable energy storage systems. While known for their efficiency and lightweight design, lithium batteries require proper handling and disposal due to their potential fire risk and environmental impact.
Are lithium batteries safe?
There are different types of lithium batteries, each with its own level of stability and safety. However, all lithium batteries are safe to use as long as they are properly handled and maintained.
It's important to note that all battery types, by definition, store chemical energy. This means every battery, if mishandled or overcharged, has the potential to be a hazard by releasing hazardous materials or igniting a fire. Lithium-ion batteries, however, have been perceived as more volatile due to their much higher specific energy combined with a greater sensitivity to overcharging.
Lithium batteries can pose safety risks under certain conditions. The primary concern is thermal runaway, a situation where the battery overheats rapidly. Improperly managed, a lithium-ion battery will reach a "thermal runaway" state more easily than other types, such as lead-acid batteries. This is due to its lower cell resistance and higher energy storage capacity.
Other potential risks include the flammability of the electrolyte used in lithium batteries, sensitivity to extreme temperatures, and the potential for short circuits if the separators between positive and negative electrodes fail. These risks have led to high-profile incidents, such as smartphone fires and electric vehicle battery explosions. However, such events are relatively rare considering the billions of lithium batteries in use worldwide.
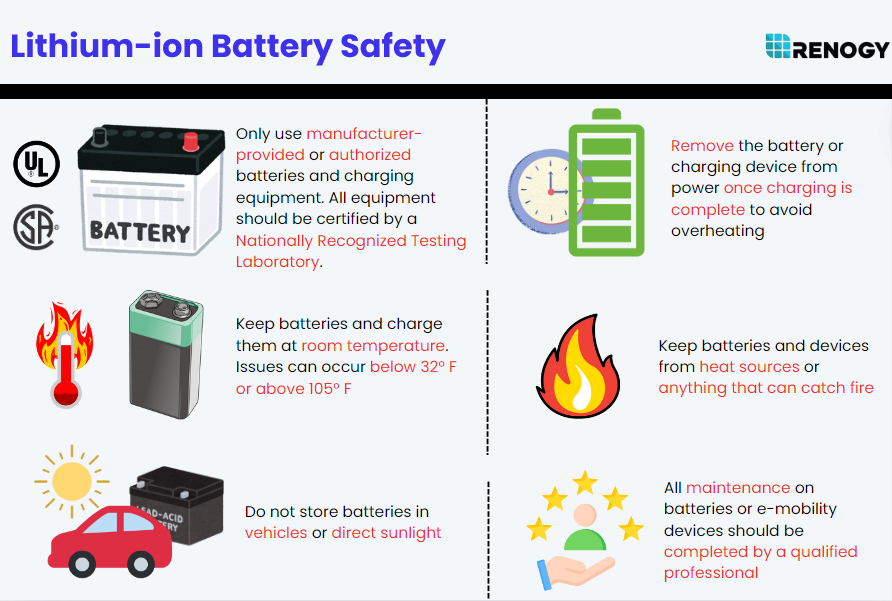
Benefits of lithium batteries
The safety of lithium batteries is obviously critical. However, numerous more advantages make lithium batteries the best option for campers.
High energy density
One of the most significant advantages of lithium batteries is their high energy density. This means they can store more energy in a smaller, lighter package compared to other battery types. For consumers, this translates to longer-lasting power in compact devices. In electric vehicles, high energy density allows for extended driving ranges without adding excessive weight to the vehicle.
Longer lifespan
Lithium batteries boast an impressive lifespan, capable of hundreds or even thousands of charge cycles before significant degradation occurs. This longevity not only provides better value for consumers but also reduces electronic waste, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Rapid charging capabilities
Many lithium battery technologies support fast charging, allowing devices to power up quickly. This feature is particularly valuable in smartphones and electric vehicles, where minimizing downtime is crucial for user convenience and practical usability.
Low self-discharge rate
When not in use, lithium batteries retain their charge much better than many other battery types. This low self-discharge rate means devices can sit unused for extended periods without losing significant power, making them ideal for emergency backup systems and infrequently used gadgets.
Lightweight design
The lightweight nature of lithium batteries is a crucial benefit, especially in portable electronics and electric vehicles. Reduced weight contributes to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles and greater portability in handheld devices.
The safest lithium battery: the LiFePO4
When it comes to lithium battery safety, LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries stand out as the gold standard. But are LiFePO4 batteries safe enough? Let's explore why these powerhouses are considered the safest option in the lithium battery family.
LiFePO4 batteries owe their superior safety profile to their unique chemistry. Unlike other lithium-ion batteries, LiFePO4 uses iron phosphate as the cathode material, which provides inherent stability. This stability translates to several key safety advantages:
- Thermal Resilience: LiFePO4 batteries are highly resistant to thermal runaway, a major safety concern with lithium batteries. They remain stable at high temperatures, significantly reducing the risk of fires or explosions.
- Chemical Stability: The iron phosphate cathode is more chemically stable than other lithium-ion chemistries. This stability means LiFePO4 batteries are less likely to release oxygen, a crucial factor in preventing battery fires.
- Longer Cycle Life: LiFePO4 batteries can withstand more charge cycles without degrading, which enhances their long-term safety. As batteries age, they can become more prone to safety issues, but LiFePO4's longevity mitigates this risk.
- Improved Abuse Tolerance: These batteries can better handle overcharging, short circuits, and physical impacts without compromising safety.
Ternary lithium vs. Lithium phosphate iron battery, which is safer?
When comparing battery safety, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are generally safer than Ternary Lithium (NMC) batteries.
Ternary lithium battery
Ternary lithium powerpack is geared with an anode composed of oxides, nickel, cobalt, and manganese. When temperature surpasses 180 °C, the anode decomposes and produces oxygen in quantity. Once the oxygen meets solvents, there will be a large number of gases, heat, and smoke coming into being and then getting trapped inside the battery case, which will lead to the battery bulging, bursting, and spilling out combustible electrolytes. The process is called thermal runaway.
It is very easy to catch fire when the combustible electrolytes meet oxygen, and the fire is hard to put out. From thermal runaway to a blast, the process could take only seconds. Even though it can be quenched temporarily, as long as the battery is still experiencing chemical reactions, the fire will come back continuously. The only solution is to wait till the chemical reactions completely consume the electricity stocked in the battery. However, waiting can be the cost of your property burned to a cinder.
Phosphate iron lithium battery
With an olivine phosphate anode, the phosphate iron lithium battery has better thermal stability, which means that when put in a high temperature or overcharged, their internal structure will not collapse easily or horribly like their ternary counterparts. Their temperature resistance point can go up to 700 to 800 Celsius degree. Even when the anodes start to submit to the high temperature, they won’t generate many gases. That being said, phosphate iron lithium batteries are much safer than ternary batteries.
Conclusion
When asking, "Are lithium batteries safe?" the answer largely depends on the type of lithium battery and its application. Overall, with proper management systems and handling, lithium batteries are generally safe and reliable. Take Renogy into consideration when selecting a safe lithium battery for solar systems. Renogy provides state-of-the-art battery management solutions, such as the intelligent BMS, DC home app, and REGO system, with sophisticated R&D and several patents. These systems guarantee accurate monitoring and automated protection for the highest level of safety.

Frequently asked question about lithium battery safety
1. Which lithium batteries are dangerous
Lithium batteries with higher energy densities, like Ternary Lithium (NMC) batteries, are more prone to overheating and thermal runaway, making them potentially dangerous. They can catch fire or explode if damaged or improperly handled. Batteries lacking robust safety features or those not meeting safety standards also pose risks.
2. How to put out a burning lithium battery?
To put out a burning lithium battery, use a Class D fire extinguisher, specifically designed for metal fires, as it can safely handle the intense heat and chemical reactions. Avoid using water, which can cause the fire to spread or react violently. If a Class D extinguisher is not available, move to a safe distance, and call emergency services immediately. Ensure the area is well-ventilated and follow all safety protocols to prevent injury and further damage.
3. What is the biggest problem with lithium batteries?
The biggest problem with lithium batteries is thermal runaway. This dangerous phenomenon occurs when a battery overheats, causing an uncontrollable chain reaction that generates even more heat and intensifies the chemical reactions inside the battery. This creates a vicious cycle that can lead to fires or explosions. To mitigate this risk, use batteries with advanced safety features, handle them carefully, and follow proper storage and charging guidelines.











