Are batteries AC or DC?Beginners' Guide
You might have heard of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) before. But do you know the difference between the two? Or perhaps you've wondered, "Are batteries AC or DC?" The answer is straightforward—batteries provide direct current. Whether it’s the lithium battery in your phone or the alkaline battery in your remote, they deliver a steady flow of DC to power your devices.
But here’s the interesting part: why does your phone charger plug into an AC outlet yet charge a DC battery? The secret lies in the charger itself, which converts AC to DC, making it compatible with your battery. From flashlights to electric cars, batteries play a crucial role in keeping our gadgets running smoothly, thanks to their consistent DC output. In this article, we’ll unravel the relationship between AC and DC, and clarify why batteries rely on direct current.
Let’s get into a bit more detail!
Understanding AC & DC
When tackling the question, “Are batteries AC or DC?”, it’s essential to first understand the two primary forms of electricity: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). These currents shape how electricity is generated, transmitted, and used—and knowing their differences is key to understanding why batteries rely on DC.
Alternating Current (AC)
Alternating current is a current whose direction and magnitude change periodically with time. Figuratively speaking, like ocean waves, alternating current constantly oscillates back and forth between the positive and negative poles. This alternating flow allows for efficient transmission over long distances.
Alternating Current Application
In our homes, nearly every electrical device, from refrigerators and televisions to air conditioners and washing machines, operates on alternating current (AC). This is also true for industrial machinery, office buildings, and public infrastructure. AC's dominance is due to its efficiency in transmitting electricity over long distances. By stepping up the voltage for transmission and then stepping it down for use, AC minimizes energy losses and makes it practical to deliver power to homes and businesses far from power plants.
Direct Current (AC)
Differ from alternating current (AC) changes direction periodically, direct current (DC) is a type of electrical current that flows in a constant direction, from the positive pole to the negative pole of a circuit.
Direct Current Application

From the smartphones we carry to the laptops we use and the cars that drive us, and even the solar panels powering our homes, direct current (DC) is the underlying power source. The reason is simple: DC provides a constant flow of electricity, making it ideal for powering sensitive electronic components. Think of it like this: if your computer ran on AC, it'd be like trying to balance on a rocking boat. The constant change in direction would make it super hard for all those little computer chips to do their job. But with DC, it's smooth sailing, so you can binge-watch your favorite shows or play games without any hiccups.
|
Characteristics |
Alternating current (AC) |
Direct current (DC) |
|
Direction of current |
Periodic variation |
No change |
|
Generation method |
Generator |
Batteries, solar cells, etc. |
| Advantages | High transmission efficiency, suitable for long-distance transmission | Good stability, suitable for electronic equipment |
| Disadvantages | Electromagnetic interference | Higher generation and transmission costs |
Are batteries AC or DC
For those of you wondering are batteries AC or DC? batteries are DC (direct current) devices. This means they provide a steady flow of electricity in a single direction, from the battery’s negative terminal to its positive terminal. Whether it’s the AA batteries in your TV remote or the lithium-ion battery in your smartphone, they all supply DC power to keep your devices running smoothly.
Why Are Batteries DC?
The reason lies in how batteries work. Inside a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that generates electricity. This process naturally produces a direct flow of electrons, making DC the most practical and efficient type of current for batteries.
What Happens When Batteries Power AC Devices?
You might wonder, "If batteries are DC, how do they power devices that run on AC?" The answer is in the devices themselves. For example:
- Laptops: When you plug your laptop into an external battery pack, the battery provides DC power. Inside your laptop charger, there’s a built-in inverter that converts DC to AC for the laptop’s internal components. This conversion ensures your laptop gets the type of power it needs while charging safely.
- Solar-Powered Homes: In off-grid solar systems, solar panels generate DC electricity, which is stored in batteries. However, most household appliances run on AC. To bridge this gap, an inverter converts the DC power from the battery into AC electricity, allowing you to use devices like refrigerators, washing machines, or microwaves seamlessly.
These converters are essential for bridging the gap between DC batteries and AC-powered appliances.
Applications of DC Batteries
Batteries have countless uses in our everyday lives:
- Small Electronics: From flashlights to remote controls, DC batteries provide the steady power these devices need.
- Rechargeable Devices: Phones, laptops, and cameras rely on rechargeable DC batteries to store energy efficiently.
- Electric Vehicles: EVs use powerful DC batteries to drive motors and operate onboard systems.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Solar panels generate DC electricity, which is stored in batteries for later use in homes or off-grid setups.
Renogy DC Battery Explained
When it comes to powering your devices with DC electricity, especially in off-grid or renewable energy setups, Renogy's Core Mini Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries offer a reliable and efficient solution. Whether you're outfitting a solar-powered cabin, camping, or running a tiny home, these batteries provide the power you need.
Core Mini - 12.8V 300Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery
If you need significant power storage for your off-grid lifestyle, the Core Mini - 12.8V 300Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery is an excellent option. Compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, Core Mini offers higher energy density, providing three times the capacity of a traditional 300Ah battery. Moreover, the built-in BMS system intelligently monitors the battery's status, providing overcharge, over-discharge, overcurrent, and other protections, ensuring your peace of mind. Whether powering your RV or setting up an outdoor movie theater, this DC battery can handle it.
Core Mini - 12.8V 100Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery

This kind of 12.8V 100Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate DC battery is more suitable for powering smaller devices. It's 13% smaller and lighter than similar products, making it a great choice for kayaks and small RVs. Even in cold environments, the built-in low-temperature cutoff BMS ensures battery safety.
2000W 12V Pure Sine Wave Inverter
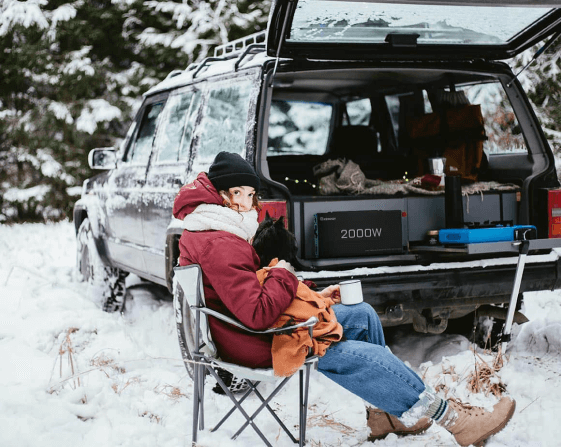

Renogy’s 2000W 12V Pure Sine Wave Inverter converts the DC power from your battery into AC power for various electronic devices. Whether you're running appliances like a microwave, refrigerator, or air conditioner, this inverter’s 2000W capacity ensures that your devices work efficiently without the risk of overheating or damage. Plus, with a peak surge capacity of 4000W, it can power multiple devices simultaneously, giving you the flexibility to run more than one device at a time without worry. The inverter operates quietly, and its cooling fan keeps it running smoothly, making it perfect for use in quiet, off-grid environments.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the question of " are batteries AC or DC" has a clear answer: all batteries use direct current. For reliable DC power solutions, consider the Renogy DC batteries and the battery inverters. These products ensure seamless energy storage and conversion, making them perfect for your off-grid adventures or home energy needs.
Are Batteries AC or DC FAQs
Are All Batteries AC or DC?
All batteries are DC. Batteries naturally produce direct current (DC) because the chemical reactions inside them generate a one-way flow of electrons. This unidirectional flow defines DC power. If you need AC power for devices, the DC power from the battery must be converted using an inverter. Some systems might market themselves as "AC batteries," but they are simply DC batteries with integrated inverters that convert the output to AC.
Is a 12V Battery AC or DC?
A 12V battery is DC. All batteries, including 12V ones commonly used in cars, RVs, and solar systems, produce direct current.
What happens if you try to run an AC device directly on DC power?
Running an AC device on DC power can damage the device, as AC devices are designed to operate with alternating current. Without an inverter, the circuit and internal components might overheat or fail.
Are there batteries that provide AC power?
Not directly. While some systems are marketed as “AC batteries,” these usually have built-in inverters that convert the DC power into AC before it’s output, but the battery itself remains DC.