An In-Depth Guide: How Many Watts Does a Refrigerator Use?
Ever wondered about your refrigerator's energy consumption? This essential appliance, running 24/7, significantly impacts your electricity bill. On average, refrigerators use between 350 to 780 watts of electricity. This translates to approximately 2.9 to 6.5 amps at 120 volts. However, actual usage varies based on factors like size, age, and efficiency. By knowing your refrigerator's wattage, you can make informed decisions about energy usage, potentially leading to substantial savings on your utility bills over time. Understanding how many watts a refrigerator uses is crucial for managing your household's energy efficiency.
How much electricity does a refrigerator use?
Understanding your refrigerator's power consumption is crucial for managing household energy usage and costs. A typical home refrigerator uses between 350 to 780 watts of electricity, which translates to approximately 2.9 to 6.5 amps at 120 volts. However, it's important to note that refrigerators don't constantly operate at their maximum wattage due to their cycling on and off throughout the day.
To estimate a refrigerator's actual energy usage, you can divide its stated wattage by 3. For instance, a 500-watt refrigerator would use about 167 running watts. The exact refrigerator power consumption varies depending on factors such as age, make, and model. Side-by-side fridge/freezer combos, for example, have different energy requirements for each compartment, with freezers typically using more energy to maintain colder temperatures.

How many watts does a refrigerator use per hour?
When considering how many watts a fridge uses per hour, we need to account for its cycling nature. On average, a refrigerator might consume between 100 to 250 watt-hours per hour. This variation is due to factors like the frequency of door openings, ambient temperature, and the refrigerator's settings. Energy-efficient models tend to be on the lower end of this range, while older or larger units may use more. Remember, refrigerator electricity usage isn't constant throughout the day.
How many watts does a refrigerator use per day?
To calculate daily refrigerator wattage consumption, we multiply the hourly usage by 24. This means a typical refrigerator might use between 2,400 to 6,000 watt-hours (or 2.4 to 6 kilowatt-hours) per day. In terms of energy costs, this could translate to about $0.30 to $0.80 per day, depending on your local electricity rates. Over a year, refrigerator power consumption could account for approximately $110 to $290 of your electricity bill, making it one of the more significant energy users in many households.
How many volts and amps does a refrigerator use?
The easiest way to know the energy consumption of your refrigerator is checking out the energy guide that comes with the refrigerator. Energy guide is a mandatory label in the US. On the label, you can easily find out the estimated yearly electricity use as well as the estimated yearly operating cost.

Here are the steps to calculate volts and amps according to data from the EnergyGuide label showing 564 kWh:
- Convert annual kWh to watt-hours (Wh): Multiply 564 kWh by 1,000 to get 564,000 Wh per year.
- Calculate average daily watt-hours: Divide 564,000 Wh by 365 days: 564,000 / 365 = 1,545.21 Wh per day.
- Determine average hourly wattage: Divide daily watt-hours by 24 hours: 1,545.21 / 24 = 64.38 W on average per hour.
- Calculate amperage (assuming 120V outlet): Divide average wattage by voltage: 64.38 W / 120 V = 0.54 amps.
How much does it cost to power a refrigerator?
Did you know that refrigerators typically account for about 7% of a household's total energy consumption? This makes them one of the most power-hungry appliances in your home. The average refrigerator wattage is about 167 watts, using approximately 1,463 kWh annually. To estimate your refrigerator's electricity usage and cost:
Find the yearly electricity use (kWh) on the Energy Guide label.
Multiply this by the average U.S. electricity rate of 16.88 cents per kilowatt-hour.
Using these figures:
Annual cost: 1,463 kWh × $0.1688/kWh = $246.95
Monthly cost: $246.95 ÷ 12 = $20.58
Actual costs may vary based on your specific model, local rates, usage patterns, and appliance condition.
Monthly and yearly costs to run a refrigerator by state
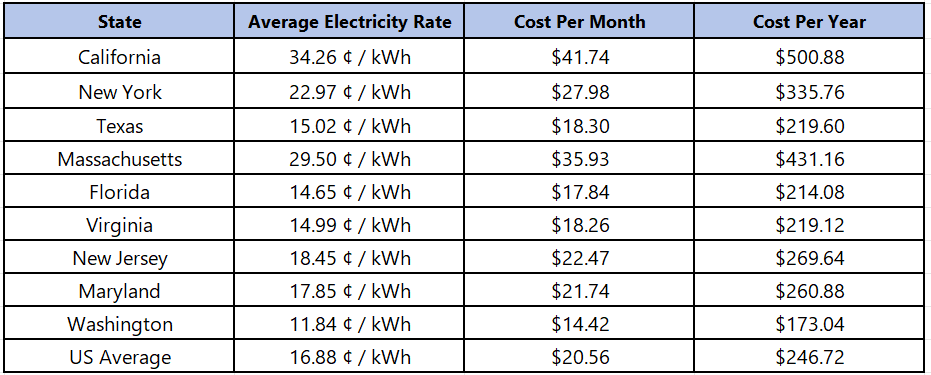
Average electricity rates are based on April 2024 data from the U.S Energy Information Administration (EIA).
How many solar panels does it take to run a refrigerator?
To determine how many solar panels are needed to run a refrigerator, consider its energy consumption. Most refrigerators use about 100-800 kWh annually. If we assume an average usage of 500 kWh, and a typical solar panel generates about 300 watts, you'll need approximately 2-4 panels. This calculation assumes 4-5 hours of sunlight per day. Always factor in your local sunlight conditions and panel efficiency for more accurate results. Investing in solar panels not only powers your fridge but also contributes to reducing your carbon footprint and lowering electricity bills.
Renogy 200 Watt 12 Volt Monocrystalline Solar Panel are a great choice for efficient solar energy. Known for durability and high efficiency, they suit both residential and off-grid applications. Easy to install and compatible with various systems, Renogy offers a range of wattages to fit your energy needs. With strong customer support and reliable warranties, investing in Renogy panels provides peace of mind.
- Portable at 15.9lbs: compact, foldable, and lightweight.
- Superior fiberglass material for decades of reliability.
- 1-minute setup with IP68 solar connectors and aluminum kickstands.
Tips for cutting fridge power consumption
Refrigerators are essential appliances in modern homes, running 24/7 to keep our food fresh and safe. But have you ever wondered about their impact on your energy bill? Let's dive into the world of refrigerator power consumption and explore ways to make your fridge more energy-efficient.
Factors Influencing Refrigerator Power Consumption
Several factors affect how much electricity your refrigerator uses:
- Size and capacity: Larger refrigerators generally consume more power than smaller ones.
- Temperature settings: Lower temperature settings increase power consumption.
- Usage patterns: Frequent door openings and storing warm foods can impact energy use.
- Ambient temperature: Fridges work harder in warmer environments, using more electricity.
- Maintenance: Well-maintained refrigerators operate more efficiently.
Tips for Reducing Refrigerator Electricity Usage
To cut down on your fridge's power consumption, consider these energy-saving tips:
- Optimize temperature settings: Set your fridge to 37-40°F (3-4°C) and freezer to 0-5°F (-18 to -15°C).
- Keep it full: A well-stocked fridge retains cold better, reducing energy use.
- Clean the coils: Regularly vacuum the condenser coils to improve efficiency.
- Check door seals: Ensure door gaskets are tight to prevent cold air leakage.
- Cool foods before storing: Let hot items cool to room temperature before refrigerating.
- Minimize door openings: Plan ahead to reduce the frequency of opening the fridge.
- Defrost regularly: For manual defrost models, remove ice buildup to improve efficiency.
- Consider upgrading: If your fridge is old, invest in an ENERGY STAR certified model.
By implementing these tips, you can significantly reduce your refrigerator's electricity consumption, lowering your energy bills and environmental impact.
Frequently asked questions about powering a refrigerator
1. What's the best time to run a refrigerator?
Refrigerators should run continuously to maintain food safety. However, you can optimize energy usage by minimizing door openings during peak hours (typically 4 PM to 9 PM). Perform maintenance tasks like defrosting or cleaning during off-peak hours. Some smart refrigerators can automatically adjust their cooling cycles to take advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak times, further reducing energy costs while ensuring consistent temperature control.
2. What size battery do you need to back up a refrigerator?
To back up a refrigerator, you'll need a battery with at least 100-200 amp-hours capacity and a 2000-watt inverter. The exact size depends on your fridge's power consumption and desired backup time. Modern energy-efficient refrigerators may require less. Consider factors like fridge size, age, and ambient temperature. For extended outages, a solar-powered system or generator might be more practical than relying solely on batteries.
3. What are ENERGY STAR appliances?
ENERGY STAR appliances are products certified by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Department of Energy for superior energy efficiency. These appliances, including refrigerators, washers, and HVAC systems, consume less energy than standard models, reducing utility bills and environmental impact. ENERGY STAR certification ensures the appliance meets strict energy performance standards without sacrificing features or functionality, making them a smart choice for eco-conscious consumers.
4. How many kWh does a house use per day?
The average household in the United States uses roughly 893 kWh per month, or about 30 kWh per day. However, these values might differ greatly based on a variety of circumstances. Energy use is determined by factors such as home size, location, climate, number of people, and equipment type. Learn more details about how many kwh does a house use per day.
Conclusion
When considering "how many watts does a refrigerator use," it's important to note that consumption varies widely. On average, modern refrigerators use between 100-400 watts while running. However, energy usage isn't constant due to cooling cycles. A typical fridge might consume 1-2 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy daily, or about 40-80 watts per hour. Factors influencing wattage include size, age, efficiency rating, and usage patterns. To determine your refrigerator's exact wattage, check its energy label or use a wattage meter. Remember, ENERGY STAR certified models generally use less power, helping reduce both energy bills and environmental impact.










