AC vs. DC Power: What’s the Difference?
Power (or wattage) measures the amount of electricity a device or appliance can generate or consume. It is generally categorized into two types: AC power and DC power. Due to their unique characteristics, both types play an important part in our daily lives.
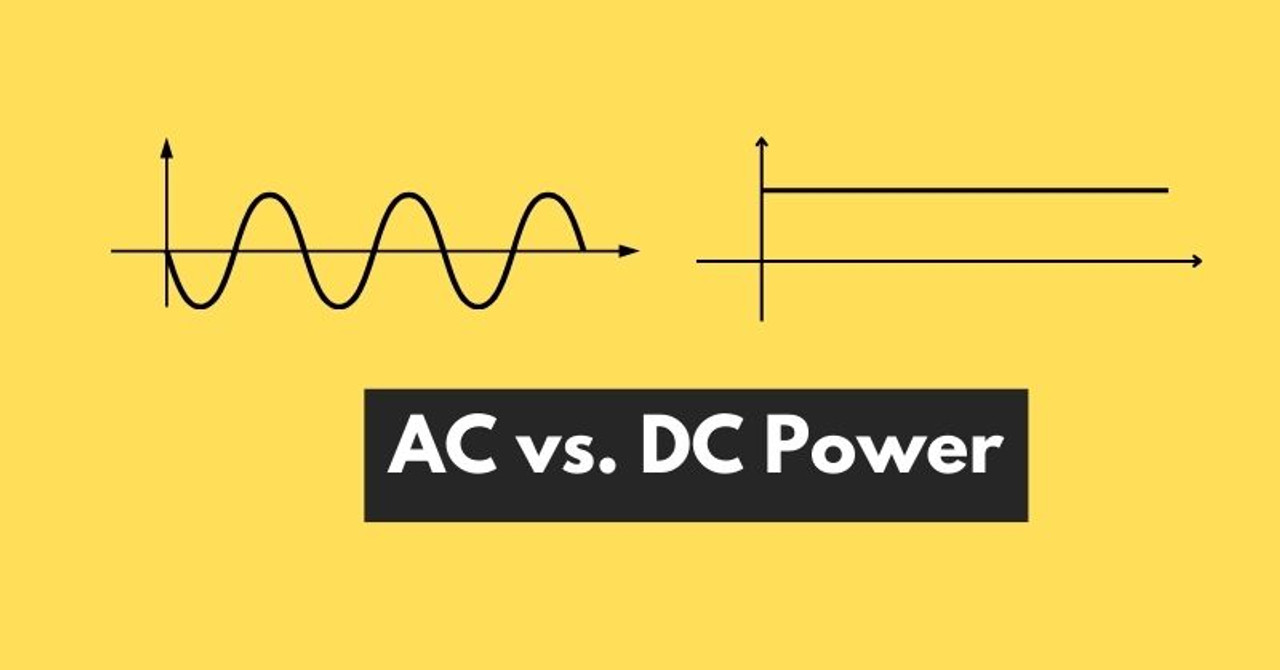
The major difference between AC and DC power is their direction of flow. AC power flows in two directions (back and forth) and is considered suitable for buildings and homes, whereas DC power follows a unidirectional path when flowing through the circuit and is perfect for electronics and batteries.
This article presents a comprehensive comparison between AC vs DC power and helps you understand how they are different from each other. It also discusses whether AC or DC power is better.
What is AC power?
As the name depicts, Alternating Current (AC) changes its direction when flowing through the circuit. It flows in both positive and negative directions to power up various home or commercial appliances. The switching between the positive and negative sides happens very quickly.
In the United States, 60HZ is the standard frequency for AC power. It means that the AC current flows from positive to negative and then from negative to positive 120 times in one second. Remember, AC power supply may vary from one country to another.
For example, the standard AC power provides 120V at 60Hz and 230V at 50Hz in the United States and United Kingdom, respectively. Therefore, if you plan to travel between different places, you should keep this difference in mind. Essentials like laptops and mobile phones can run perfectly from 110V to 240V. So, running these devices won't be an issue.
Not all devices can run on both 120V and 240V. For instance, if you plug a 120V appliance into a 240V socket, its fuse will be blown away. In worst cases, the device may be completely damaged.
How does AC power work?
Mechanical generators use electromagnetic induction to convert thermal or kinetic energy into electrical power. If we talk about solar-powered generators, they capture DC power from sunlight and use a solar inverter to convert it into AC power.
The polarity of AC current is reversed after a fixed interval measured in Hz. One Hz is equal to one complete cycle (one positive and one negative). The rapid switching helps AC current travel across long distances, making transmission easier. This is why AC power has become the global standard.
Pros
- Transmission lines of up to 1,000km feature less power loss.
- Modifying voltage with transformers is relatively less expensive.
- Thinner cables are needed for power transmission lines.
- No need to think of the positive and negative terminals when plugging in a device.
Cons
- Working with high voltages becomes more dangerous.
- For extremely long-distance transmission, AC power is less efficient.
What Uses AC Power
- Household Appliances: AC power is the standard electricity supply for most household appliances. From refrigerators and washing machines to air conditioners, ovens, and vacuum cleaners, nearly all household devices are designed to run on AC. This is because AC is more easily transmitted over long distances with less energy loss compared to DC, making it ideal for powering homes and commercial buildings.
- Industrial Machinery: AC power is widely used in industrial machinery and equipment. Motors, conveyor belts, pumps, and other heavy machinery commonly rely on AC because it can easily be transformed into the necessary voltage and current to power large motors efficiently. AC motors are more durable and cost-effective for continuous use, which is why they dominate in industrial applications.
- Electric Grids and Power Transmission: The global power grid is built around the transmission and distribution of AC power. AC allows electricity to be transmitted over long distances with less loss of energy compared to DC, making it the preferred method for large-scale electrical distribution. Electrical substations use transformers to step up or step down the AC voltage as needed, enabling efficient power delivery to homes, businesses, and industries.
What is DC power?
Unlike AC power, the polarity of DC current does not change throughout its flow. It means that DC current flows in one direction only. Most modern appliances and consumer electronics have transistors that can't operate on AC current. This is the reason why these appliances run with DC power.
Though you can plug these appliances directly into your AC socket, rectifiers (adapters) convert AC power into DC and run them. A DC power source always has a positive and a negative terminal. Electricity flows in a single direction between these two terminals.
How does DC power work?
As stated earlier, the polarity of DC power does not fluctuate. It only flows from a power source to a DC appliance. In the case of a solar electric system, power flows from PV cells to an off-grid system.
The constant flow of DC power allows it to charge various batteries. To meet the appliances' requirements, a DC-to-DC battery converter may be required to adjust the desired voltage levels. This is how DC power works to operate all DC appliances or devices.
Pros
- Unlike AC power, you can store DC energy in batteries.
- The design of DC generators is simpler than AC generators.
- DC power is a stable flow of electricity due to its unchanged polarity. This is why it is considered more safe for sensitive equipment.
- When transmitting electricity over extremely long distances, DC power is more efficient than AC power.
- You can use an inverter to convert DC power into AC and run any AC appliance you want.
Cons
- The long-distance transmission of DC power is costlier than transmitting AC power.
- A DC system costs more than an AC system due to higher insulation needs.
- You can't change the DC voltage level without losing a significant amount of energy.
What Uses DC Power
- Battery-Powered Devices: DC power is the type of current supplied by most batteries, such as lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries. As a result, any device that runs on batteries typically operates on DC power. Examples include smartphones, laptops, portable electronics, flashlights, and power tools. The batteries in these devices generate DC power, which directly drives their electronic systems, providing reliable and steady energy.
- Solar Power Systems: Solar panels generate DC power through the photovoltaic effect, converting sunlight into electricity. In solar energy systems, the DC electricity produced by the solar panels is either stored in batteries (in off-grid systems) or converted into AC power using an inverter for household or industrial use. Since solar panels themselves generate DC, this type of power is central to solar energy applications.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Electric vehicles primarily use DC power, as the batteries in EVs store and provide direct current. During charging, the onboard charger converts AC power (from the grid) into DC to store it in the vehicle’s battery. The stored DC is then used to power the electric motor and other vehicle systems. DC is essential for EVs, providing smooth power delivery and enabling efficient energy storage and use.
- LED Lighting: Most LED lights use DC power for operation. Although the standard current in household power grids is AC, many LED lights include built-in drivers that convert AC into DC to ensure stable and efficient operation. LEDs themselves are semiconductor devices that work best with direct current, offering better performance and longevity when powered by DC rather than AC.
What's the difference between AC and DC power?
As we have discussed above, the major difference between AC and DC power is that AC current constantly changes its polarity (from positive to negative and negative to positive). In contrast, DC current flows in a single direction only. The difference in polarity makes AC and DC power suitable for different appliances and devices.
AC power can be easily adjusted compared to DC power when it comes to stepping up or down the voltage levels to meet the appliances' requirements. This property makes AC power more suitable for transmitting electricity through the utility grid or power lines.
With unmatched technological advancements, DC power has gained popularity in the past few years. One of the key components of electronic devices - a transistor - runs on a DC power supply. Though DC appliances like smartphones and laptops are plugged into AC sockets, their charging adapters convert AC power into DC power to ensure a seamless operation.
Another significant difference between the two power types is that DC power is easier to control than its AC alternative. You can easily store DC power in batteries and then convert it into AC power to run various appliances as and when needed.
For example, portable power sources like the Renogy LYCAN 5000 Power Box use highly efficient LiFePO4 batteries to provide a consistent power supply for energy-hungry devices. Similarly, the Renogy Elite Portable Solar Generator uses reliable lithium-ion batteries to deliver enough power to charge a wide range of smartphones and other small devices during power outages.
Both AC and DC power are important in our daily electricity usage. With the increasing demand for hybrid and electric vehicles, DC power has now started playing a crucial role by providing an environmentally friendly, renewable power supply.
Simply put, an AC power supply is suitable for home appliances where adjusting different voltage levels is required for various needs. In comparison, DC power plays its part where a unidirectional current flow is required, such as in solar panels and batteries.
How AC and DC power are used together today?
As listed and discussed below, AC and DC power are used together in four different ways.
- AC-DC power supply: AC power is converted into DC for appliances that have an AC power input but operate on a DC power supply, such as a laptop charger.
- AC/DC power supply: The voltage levels are adjusted with AC/DC power supplies to match the output of specific devices.
- AC DC combination: Both AC and DC power are required to operate many appliances like washing machines. It needs DC power to run the circuit board and AC power to spin the cleaning tub using a motor. This is the concept of hybrid systems, where two or more power types are required for complete operation.
- DC-DC power supply: DC power is converted into AC using a transformer to change the voltage level. Then, a rectifier is used to convert AC power back into DC power.

Converters and inverters play a crucial role in converting power from one form to another. An inverter converts DC power into AC power. Inverters are frequently used in electrical grids and home appliances. For example, you can use an inverter to utilize DC energy stored in batteries by converting it into AC power.
In comparison, converters have the ability to convert AC power into DC and vice versa. They are commonly used in solar energy systems, industrial setups, and consumer electronics. For example, you can use a converter to run appliances like AC televisions and air conditioners.
Which is better: AC or DC power?
Both AC and DC power offer unique value. No power source is better than the other. Both perform well in different conditions.
Whether AC or DC power will perform well largely depends on your energy consumption needs. In the case of large power generation and distribution, AC power will be a suitable source of energy. This is why electric sockets in homes and commercial buildings offer an AC power supply.
In contrast, DC power has fewer applications. It becomes an ideal power source for low-current and low-voltage appliances. For example, you need a DC power supply to run electronic devices, such as charging digital cameras, mobile phones, laptops, etc.
When we look at overall performance, AC power performs well in a range of scenarios like flexibility, reach, and system cost. At the same time, AC power does not support consistent voltage and a smooth flow of current.
In a DC power supply, the current flows smoothly, and voltage remains consistent, making it a top choice for running devices with sensitive circuitry. Nowadays, the demand for DC appliances is on the rise, and it is increasing every other day.
Looking at this trend, it is safe to say that DC power will replace AC power somewhere in the near future, but it still needs a lot of research and technological advancements.
Frequently asked questions
Why is AC power used in homes instead of DC?
There are several reasons behind this fact. AC power is cheaper and safer to work with. Most home appliances need AC power because they are inductive. Moreover, less energy losses occur when transmitting AC power.
Can I use DC power for household appliances?
Yes, you can use DC power to run home appliances. The reasons why it is not common are as follows.
- More energy losses occur when transmitting DC power.
- Changing levels of DC voltage is more complex.
- Unlike AC power, the same voltage level of DC power is more dangerous.
Is DC power safer than AC?
As our body is more resistant to DC; therefore, DC power is considered safe. However, both DC and AC power can be lethal in different conditions.
Conclusion
AC power vs DC power? Which one is better? Is this what you are concerned about? Well, both play important roles in different scenarios. It means no one is better than the other, but both are useful in different conditions. AC current changes its polarity after a specific period (measured in Hertz), whereas the polarity remains unchanged in the case of DC power.
If you plan to generate high power and distribute it cost-effectively, AC power will be a suitable option. In contrast, if you want to power low-voltage or low-current devices that use transistors, a DC power supply will be required for a seamless operation.